The Gulf of Mexico, a fascinating and vital body of water, is actually part of the Atlantic Ocean. This means the LGBTQ+ community and allies planning a trip to Mexico can enjoy beaches connected to the vast Atlantic. Explore gaymexico.net for more insights into LGBTQ+-friendly destinations and travel tips. Delve deeper to uncover Mexican LGBTQ+ culture and Gulf Coast travel destinations for valuable insights and safe travel advice.
1. What Ocean is the Gulf of Mexico Part Of?
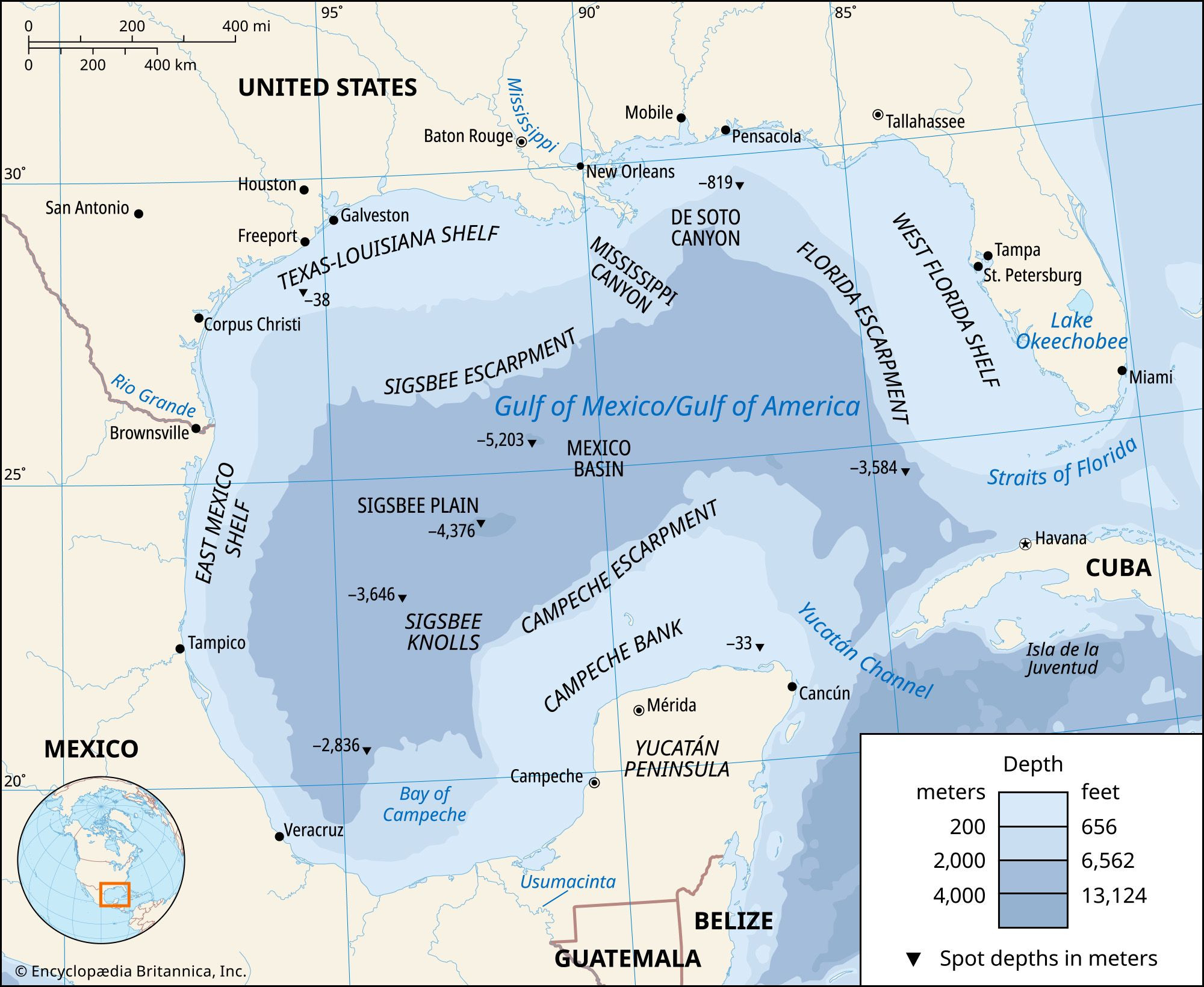
The Gulf of Mexico is not a separate ocean; it’s an arm of the Atlantic Ocean. More specifically, it is a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, partially enclosed by the North American continent. The Gulf is connected to the Atlantic Ocean through the Straits of Florida between Florida and Cuba, and to the Caribbean Sea via the Yucatan Channel between Mexico’s Yucatan Peninsula and Cuba. This connection to the Atlantic makes it influenced by the broader oceanic systems, including currents, climate patterns, and marine life.
2. What are the Key Geographic Features of the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is a significant body of water bordered by the United States, Mexico, and Cuba. Its geography includes diverse elements such as:
- Continental Shelf: An expansive submerged land area surrounding the gulf.
- Coastal Wetlands: Numerous marshes and mangrove forests along the coast.
- Abyssal Plain: A vast, flat area forming the gulf’s floor.
- Sigsbee Deep: The deepest point in the Gulf, reaching depths of over 12,000 feet.
 Gulf of Mexico / Gulf of America
Gulf of Mexico / Gulf of America
3. How Does the Gulf of Mexico Connect to Other Bodies of Water?
The Gulf of Mexico has two primary connections to other significant bodies of water:
- Straits of Florida: This channel connects the Gulf of Mexico to the Atlantic Ocean, allowing for the exchange of water and marine life between the two.
- Yucatan Channel: This passage links the Gulf of Mexico to the Caribbean Sea, facilitating the flow of water and marine species.
These connections are crucial for maintaining the ecological balance and oceanographic characteristics of the Gulf.
4. What Are the Main Currents in the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico’s circulation is dominated by the Loop Current, which brings warm Caribbean water into the Gulf through the Yucatan Channel. This current loops northward and then exits through the Straits of Florida, eventually becoming the Gulf Stream in the Atlantic Ocean. The Loop Current and its eddies influence the Gulf’s water temperature, salinity, and marine ecosystems. This Loop Current is a significant factor in the Gulf’s weather patterns and hurricane development, as it provides warm water which can fuel these storms.
5. How Deep is the Gulf of Mexico?
The average depth of the Gulf of Mexico is approximately 5,200 feet (1,585 meters). However, the deepest point, known as the Sigsbee Deep, reaches a depth of about 17,070 feet (5,203 meters). The depth varies significantly across the Gulf, with shallower waters along the continental shelf and deeper waters in the central basin.
6. What Countries Border the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is bordered by three countries:
- United States: The northern coastline of the Gulf is part of the U.S., including states like Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Texas.
- Mexico: The western and southern coastlines are part of Mexico, including states like Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, and Yucatan.
- Cuba: The southeastern edge of the Gulf is bordered by Cuba, an island nation in the Caribbean.
7. What is the Climate Like in the Gulf of Mexico Region?
The climate around the Gulf of Mexico ranges from tropical to subtropical. It is characterized by warm temperatures year-round and high humidity. Summers are hot and humid, with frequent thunderstorms. Winters are mild, although cold fronts can bring occasional temperature drops. The region is also prone to hurricanes, particularly from June to November.
8. What is the Significance of the Gulf of Mexico for Marine Life?
The Gulf of Mexico is a highly productive marine environment, supporting a diverse range of species. It serves as a crucial habitat for:
- Fish: Numerous species, including commercially important ones like red snapper, tuna, and grouper.
- Marine Mammals: Dolphins, whales, and manatees.
- Sea Turtles: Several species, including loggerhead, green, and Kemp’s ridley turtles.
- Seabirds: Pelicans, terns, and other coastal birds.
- Invertebrates: Shrimp, crabs, oysters, and various coral species.
The Gulf’s warm waters and nutrient-rich environment make it a vital feeding and breeding ground for many marine organisms.
9. What are the Economic Activities in the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is a hub of economic activity, supporting various industries, including:
- Fishing: Commercial and recreational fishing are significant, providing seafood and tourism revenue.
- Oil and Gas: Offshore oil and gas production is a major industry, with numerous platforms and pipelines.
- Shipping: Major ports along the Gulf coast handle a large volume of international trade.
- Tourism: Coastal tourism is a vital industry, with beaches, resorts, and recreational activities attracting visitors.
These activities contribute significantly to the economies of the bordering countries but also pose environmental challenges.
10. How Does the Gulf of Mexico Impact Weather Patterns?
The Gulf of Mexico plays a significant role in regional and even global weather patterns:
- Hurricanes: The warm waters of the Gulf provide energy for hurricanes, which can impact coastal areas with strong winds, heavy rain, and storm surges.
- Moisture Source: The Gulf is a major source of moisture for rainfall in the southeastern United States, influencing precipitation patterns.
- Temperature Regulation: The Gulf’s water temperatures influence regional climate, moderating temperatures along the coast.
11. What Environmental Concerns Exist in the Gulf of Mexico?
Several environmental issues threaten the health of the Gulf of Mexico:
- Oil Spills: Accidental oil spills can cause significant damage to marine ecosystems, as seen in the Deepwater Horizon disaster.
- Pollution: Runoff from agriculture, industry, and urban areas introduces pollutants into the Gulf, affecting water quality and marine life.
- Habitat Loss: Coastal development and erosion lead to the loss of important habitats like wetlands and mangroves.
- Climate Change: Rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification pose threats to coral reefs and other marine ecosystems.
Addressing these issues requires concerted efforts from governments, industries, and individuals.
12. What Role Does the Gulf of Mexico Play in LGBTQ+ Tourism?
The Gulf of Mexico, particularly along its coastal cities in the United States and Mexico, is increasingly becoming a destination for LGBTQ+ tourists. Cities like Puerto Vallarta in Mexico and various cities in Florida and Texas in the U.S. offer LGBTQ+-friendly beaches, resorts, and nightlife. The warm climate, beautiful scenery, and welcoming atmosphere make it an attractive destination for LGBTQ+ travelers looking for leisure and recreation. Platforms like gaymexico.net can offer more specific insights and tips for LGBTQ+ travel in the region.
13. How Can I Find LGBTQ+ Friendly Destinations Near the Gulf of Mexico?
To find LGBTQ+-friendly destinations near the Gulf of Mexico, you can use several online resources and travel platforms that provide information on gay-friendly cities, accommodations, and activities. Websites like gaymexico.net, specialized LGBTQ+ travel blogs, and mainstream travel sites often have sections dedicated to LGBTQ+ travel. You can also look for certifications or affiliations with LGBTQ+ travel organizations that indicate a commitment to inclusivity and safety.
14. Are There Specific Events for the LGBTQ+ Community in the Gulf of Mexico Region?
Yes, there are several LGBTQ+ events held in the Gulf of Mexico region, including pride festivals, circuit parties, and other cultural events. Cities like New Orleans, Houston, and Puerto Vallarta host annual pride celebrations that attract thousands of attendees. Additionally, there are smaller, localized events and gatherings throughout the year that cater to the LGBTQ+ community. Event calendars and LGBTQ+ community centers can provide details on upcoming events in specific locations.
15. What Legal Considerations Should LGBTQ+ Travelers Keep in Mind When Visiting the Gulf of Mexico?
When visiting the Gulf of Mexico, LGBTQ+ travelers should be aware of the varying legal protections and societal attitudes towards LGBTQ+ individuals in different regions. While some areas may have comprehensive anti-discrimination laws and same-sex marriage equality, others may have more conservative laws and attitudes. Researching the specific laws and cultural norms of the destination can help LGBTQ+ travelers prepare for their trip and ensure their safety and comfort. It’s always a good idea to stay informed about local laws and customs, especially regarding public displays of affection or gender expression.
16. How Has the Naming of the Gulf of Mexico Evolved Over Time?
Historically, the Gulf of Mexico has been known by various names. Before European contact, indigenous populations had their own names for the body of water. After European exploration, it was referred to as the “Gulf of New Spain” and the “Florida Sea” on various maps and publications. The name “Gulf of Mexico” gained prominence by the late 16th century, as seen in the writings of English geographer Richard Hakluyt. In recent years, there have been occasional discussions about renaming the Gulf, but “Gulf of Mexico” remains the most widely recognized and accepted name.
17. What Natural Resources are Extracted from the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is rich in natural resources, which are extracted for economic benefit. Major resources include:
- Petroleum and Natural Gas: The Gulf contains significant deposits of oil and gas, which are extracted through offshore drilling.
- Sulfur: Sulfur is extracted from wells drilled on the continental shelf off the coast of Louisiana.
- Oyster Shells: Obtained from shallow waters, oyster shells are used in the chemical industry as a source of calcium carbonate and for road construction.
- Fish and Seafood: Commercial fishing yields substantial catches of shrimp, flounder, red snapper, mullet, oysters, and crabs.
18. How Does Climate Change Affect the Gulf of Mexico?
Climate change poses significant threats to the Gulf of Mexico, including:
- Sea Level Rise: Rising sea levels threaten coastal communities and habitats, increasing the risk of flooding and erosion.
- Increased Sea Temperatures: Warmer waters can lead to coral bleaching, harm marine life, and intensify hurricanes.
- Ocean Acidification: The absorption of excess carbon dioxide by the ocean leads to acidification, which can harm shellfish and other marine organisms.
- Changes in Storm Patterns: Climate change may lead to more intense and frequent hurricanes, increasing the risk of damage to coastal areas.
19. What are the Major Environmental Protection Efforts in the Gulf of Mexico?
Several initiatives aim to protect the Gulf of Mexico’s environment, including:
- Coastal Restoration Projects: Efforts to restore and protect coastal wetlands, barrier islands, and other habitats.
- Water Quality Monitoring Programs: Programs to monitor and improve water quality by reducing pollution from various sources.
- Fisheries Management: Regulations to manage fish stocks and prevent overfishing.
- Marine Protected Areas: Designation of areas where certain activities are restricted to protect sensitive marine ecosystems.
- Oil Spill Prevention and Response: Measures to prevent oil spills and improve response capabilities in case of accidents.
20. How Can Tourists Help Protect the Gulf of Mexico?
Tourists can contribute to protecting the Gulf of Mexico by:
- Reducing Waste: Minimizing single-use plastics and properly disposing of trash.
- Conserving Water: Using water wisely and avoiding activities that pollute waterways.
- Supporting Sustainable Tourism: Choosing eco-friendly accommodations and activities that minimize environmental impact.
- Respecting Marine Life: Avoiding disturbance of marine animals and their habitats.
- Educating Themselves: Learning about the Gulf’s ecology and the challenges it faces, and sharing that knowledge with others.
21. What are the Major Rivers that Flow into the Gulf of Mexico?
Several major rivers drain into the Gulf of Mexico, carrying freshwater and sediments from vast inland areas. The most significant rivers include:
- Mississippi River: The largest river in North America, draining a vast area from the Rocky Mountains to the Appalachian Mountains.
- Rio Grande: Forming part of the border between the United States and Mexico.
- Apalachicola River: Draining parts of Florida, Georgia, and Alabama.
- Brazos River: Located entirely within the state of Texas.
These rivers play a crucial role in the Gulf’s ecosystem by providing nutrients and freshwater, but they also carry pollutants from agricultural and industrial activities.
22. How Do the Salt Domes Affect the Geology of the Gulf of Mexico?
Salt domes are geological structures formed by the upward movement of salt deposits beneath the Earth’s surface. In the Gulf of Mexico, these salt domes significantly impact the geology by:
- Creating Traps for Oil and Gas: Salt domes can create subsurface structures that trap oil and natural gas, leading to the formation of economically important hydrocarbon reservoirs.
- Deforming Sedimentary Layers: The upward movement of salt can deform and uplift overlying sedimentary layers, creating complex geological structures.
- Forming Surface Features: In some cases, salt domes can reach the surface, creating topographic features such as mounds or hills.
23. What Role Did the Gulf of Mexico Play in European Exploration?
The Gulf of Mexico played a significant role in the European exploration of the Americas:
- Entry Point: It served as a primary entry point for Spanish explorers in the 16th century, including figures like Christopher Columbus, who made initial contact with the region.
- Establishment of Colonies: Spanish explorers used the Gulf to establish towns, missions, and silver mines along the coast.
- Trade Route: The Gulf became an important trade route for Europeans, facilitating the exchange of goods and resources between the Americas and Europe.
24. How Can gaymexico.net Enhance My Travel Experience to the Gulf of Mexico?
Gaymexico.net provides a wealth of information for LGBTQ+ travelers planning a visit to the Gulf of Mexico, offering:
- Up-to-Date Information: Stay informed about the latest laws, events, and social attitudes relevant to LGBTQ+ individuals in the region.
- Community Connection: Connect with other LGBTQ+ travelers and locals to share experiences and recommendations.
- Safe and Welcoming Options: Find accommodations, venues, and activities that prioritize inclusivity and safety for LGBTQ+ visitors.
- Travel Tips: Access practical advice on how to navigate different destinations, ensuring a comfortable and enjoyable trip.
25. What are Some Popular Beaches for LGBTQ+ Travelers Near the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico boasts several beaches that are popular among LGBTQ+ travelers, including:
- Puerto Vallarta, Mexico: Known for its vibrant gay scene and beautiful beaches.
- South Beach, Miami, Florida: Offers a mix of lively nightlife and beachfront relaxation.
- Galveston, Texas: Features a welcoming atmosphere and various LGBTQ+-friendly establishments.
- Clearwater Beach, Florida: Provides a family-friendly environment with clear waters and sandy shores.
- New Orleans, Louisiana: Combines cultural richness with a progressive and inclusive community.
These beaches offer a range of experiences, from bustling social scenes to tranquil getaways, catering to diverse preferences within the LGBTQ+ community.
26. What are the Best Times to Visit the Gulf of Mexico for LGBTQ+ Travelers?
The best times to visit the Gulf of Mexico for LGBTQ+ travelers depend on personal preferences and priorities:
- Spring (March-May): Offers pleasant temperatures, fewer crowds, and various cultural events.
- Fall (September-November): Provides similar conditions to spring, with warm weather and fewer tourists.
- Summer (June-August): Attracts visitors seeking beach activities and lively nightlife, but can be hot and humid with potential hurricane risks.
- Winter (December-February): Offers mild temperatures and a quieter atmosphere, but some outdoor activities may be limited.
Consider local events, weather patterns, and personal comfort levels when planning your trip.
27. What Safety Tips Should LGBTQ+ Travelers Keep in Mind When Visiting the Gulf of Mexico?
While many areas around the Gulf of Mexico are welcoming to LGBTQ+ travelers, it’s essential to keep some safety tips in mind:
- Research Local Laws and Customs: Stay informed about local laws and customs related to LGBTQ+ rights and behavior.
- Be Aware of Public Displays of Affection: Exercise caution when displaying affection in public, particularly in more conservative areas.
- Stick to Known LGBTQ+-Friendly Areas: Focus your activities in areas known to be welcoming and inclusive.
- Use Reputable Transportation Services: Choose reliable transportation options, especially when traveling at night.
- Trust Your Instincts: If a situation feels unsafe or uncomfortable, remove yourself from the situation.
28. What Cultural Experiences are Available for LGBTQ+ Travelers in the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico offers a rich tapestry of cultural experiences for LGBTQ+ travelers, including:
- Pride Festivals: Attend annual pride festivals in cities like New Orleans, Houston, and Puerto Vallarta.
- Local LGBTQ+ Events: Participate in smaller, community-based events and gatherings.
- Historical Sites: Explore historical landmarks and museums that showcase LGBTQ+ history and contributions.
- Art and Music Scenes: Immerse yourself in the vibrant art and music scenes that often celebrate LGBTQ+ expression.
- Culinary Delights: Indulge in the diverse culinary traditions of the region, from Mexican cuisine to Creole and Southern dishes.
29. How Can I Stay Updated on LGBTQ+ Events and News in the Gulf of Mexico Region?
To stay updated on LGBTQ+ events and news in the Gulf of Mexico region:
- Follow Local LGBTQ+ Organizations: Subscribe to newsletters and social media accounts of local LGBTQ+ organizations and community centers.
- Check Event Listings: Regularly check event listings on websites and community calendars.
- Read LGBTQ+ Publications: Follow LGBTQ+ publications and blogs that cover news and events in the region.
- Join Social Media Groups: Join social media groups and forums focused on LGBTQ+ travel and community in the Gulf of Mexico.
30. How Does gaymexico.net Help Promote LGBTQ+ Tourism in the Gulf of Mexico?
gaymexico.net plays a vital role in promoting LGBTQ+ tourism in the Gulf of Mexico by:
- Providing a Centralized Resource: Offering a comprehensive platform for LGBTQ+ travelers to find information on destinations, accommodations, and events.
- Highlighting LGBTQ+-Friendly Businesses: Showcasing businesses and organizations that actively support the LGBTQ+ community.
- Sharing Travel Tips and Advice: Providing practical tips and advice to ensure safe and enjoyable travel experiences.
- Promoting Inclusivity and Diversity: Encouraging destinations to embrace inclusivity and celebrate diversity within the LGBTQ+ community.
- Connecting Travelers and Locals: Facilitating connections between LGBTQ+ travelers and local residents to foster cultural exchange and understanding.
By providing valuable resources and promoting inclusivity, gaymexico.net helps to create a more welcoming and accessible environment for LGBTQ+ travelers in the Gulf of Mexico region.
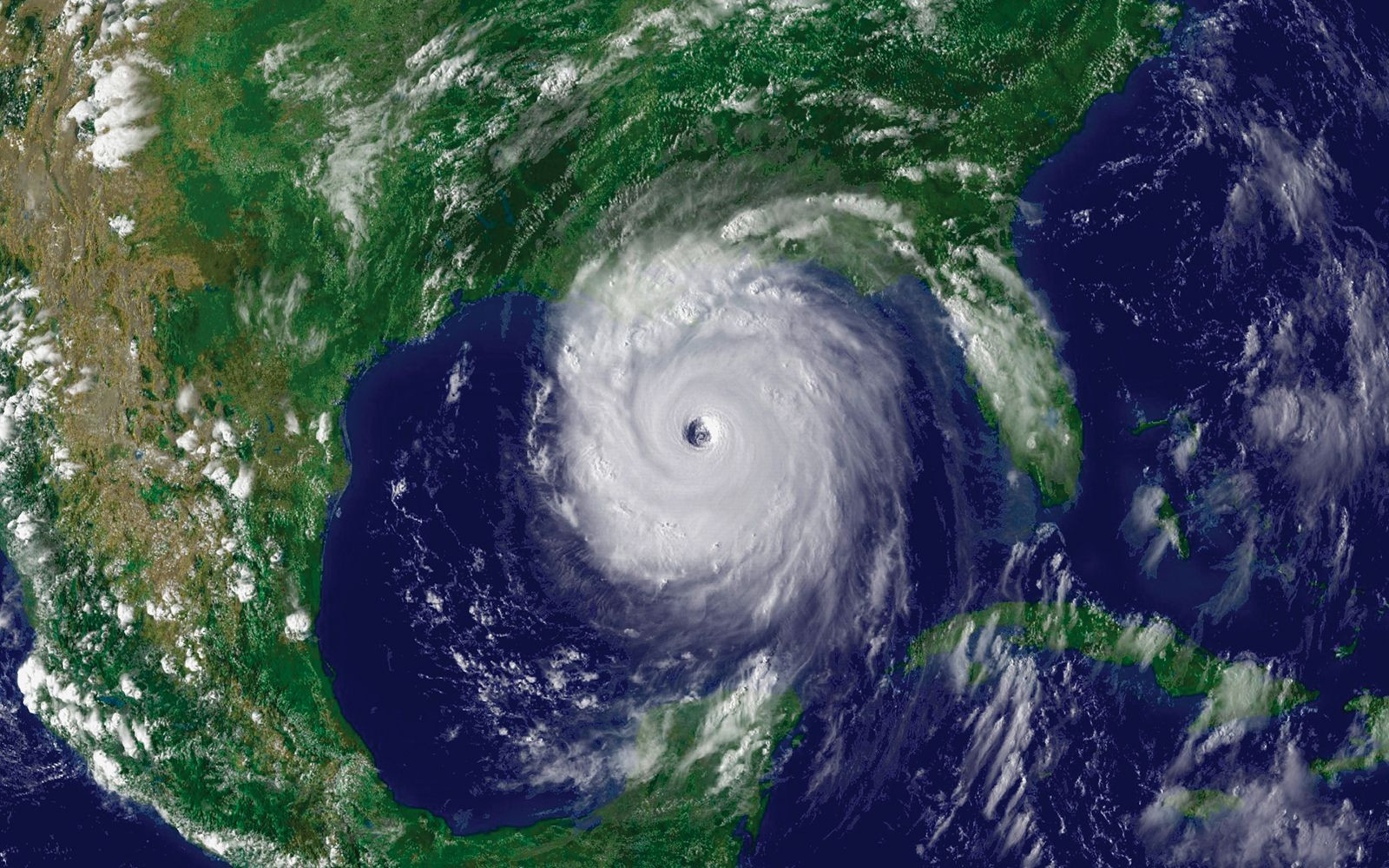 Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina
31. What is the Role of the Gulf of Mexico in Hurricane Formation?
The Gulf of Mexico is notorious for its role in hurricane formation due to several factors:
- Warm Waters: The warm waters of the Gulf provide the necessary energy for hurricanes to develop and intensify. Hurricanes are essentially heat engines, and the warmer the water, the more energy they can draw from it.
- Low Wind Shear: Hurricanes require an environment with low vertical wind shear (changes in wind speed and direction with altitude). The Gulf often experiences periods of low wind shear, allowing storms to organize and strengthen.
- Atmospheric Conditions: The Gulf’s location makes it susceptible to favorable atmospheric conditions, such as upper-level divergence, which helps to lift air and sustain storm development.
32. How Does the Gulf of Mexico Compare to Other Large Bodies of Water?
The Gulf of Mexico has several unique characteristics compared to other large bodies of water:
- Size: It is smaller than major oceans but larger than many seas. Its area is approximately 600,000 square miles (1.55 million square kilometers).
- Depth: The average depth is relatively shallow compared to oceans, but it contains the Sigsbee Deep, which is a significant depression.
- Enclosed Nature: It is partially enclosed by land, making it more susceptible to influences from the surrounding continents, such as river runoff and pollution.
- Warm Waters: Its warm waters contribute to its role in hurricane formation and support diverse marine life.
- Economic Importance: It is a major hub for oil and gas production, fishing, shipping, and tourism, contributing significantly to the economies of the bordering countries.
33. What is the Sigsbee Deep, and Why is it Important?
The Sigsbee Deep is the deepest point in the Gulf of Mexico, located in the Mexico Basin. It reaches a depth of about 17,070 feet (5,203 meters) below sea level. The Sigsbee Deep is important for several reasons:
- Geological Significance: It provides insights into the geological history and formation of the Gulf of Mexico.
- Unique Ecosystems: It may support unique deep-sea ecosystems adapted to extreme pressure and darkness.
- Scientific Research: It is a site of interest for scientific research, including studies of deep-sea currents, sedimentation, and marine life.
34. What are the Primary Types of Marine Life Found in the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is home to a diverse range of marine life, including:
- Fish: Red snapper, grouper, tuna, mackerel, and many other species.
- Marine Mammals: Dolphins, whales, and manatees.
- Sea Turtles: Loggerhead, green, Kemp’s ridley, and other sea turtle species.
- Invertebrates: Shrimp, crabs, oysters, coral, and various other invertebrates.
- Seabirds: Pelicans, terns, gulls, and other coastal birds.
The Gulf’s warm waters and nutrient-rich environment support a complex food web and provide habitat for numerous marine organisms.
35. How Have Oil Spills Impacted the Gulf of Mexico?
Oil spills have had devastating impacts on the Gulf of Mexico, including:
- Environmental Damage: Oil spills can contaminate water and sediments, harming marine life and ecosystems.
- Economic Losses: Oil spills can disrupt fishing, tourism, and other economic activities.
- Health Impacts: Exposure to oil and dispersants can have adverse health effects on humans.
- Long-Term Effects: Oil spills can have long-term ecological and economic consequences, affecting the Gulf’s resources for years to come.
The Deepwater Horizon oil spill in 2010 was one of the largest environmental disasters in history, causing widespread damage to the Gulf’s ecosystems and economy.
36. What are the Main Shipping Routes in the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is a major hub for shipping, with several important routes:
- Mississippi River: The Mississippi River is a major transportation artery, connecting the Gulf to inland areas and facilitating the movement of goods and commodities.
- Gulf Intracoastal Waterway: The Gulf Intracoastal Waterway is a system of canals and waterways that runs along the Gulf coast, providing a protected route for barge traffic.
- International Shipping Lanes: Major shipping lanes connect the Gulf to ports around the world, facilitating international trade.
37. How Does River Runoff Affect the Salinity of the Gulf of Mexico?
River runoff significantly affects the salinity of the Gulf of Mexico, particularly in coastal areas:
- Freshwater Input: Rivers carry freshwater into the Gulf, diluting the seawater and reducing salinity levels.
- Seasonal Variations: River runoff is often seasonal, with higher flows during periods of heavy rainfall or snowmelt. This can lead to significant variations in salinity levels throughout the year.
- Impacts on Marine Life: Changes in salinity can affect marine life, as some species are more tolerant of freshwater than others.
- Nutrient Input: River runoff also carries nutrients into the Gulf, which can stimulate algal growth and affect water quality.
38. How Can We Improve the Health of the Gulf of Mexico?
Improving the health of the Gulf of Mexico requires a multifaceted approach:
- Reduce Pollution: Implement stricter regulations to reduce pollution from agriculture, industry, and urban areas.
- Restore Habitats: Invest in coastal restoration projects to protect and restore wetlands, mangroves, and other habitats.
- Manage Fisheries: Implement sustainable fisheries management practices to prevent overfishing and protect marine ecosystems.
- Address Climate Change: Take action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change on the Gulf.
- Promote Education and Awareness: Educate the public about the importance of protecting the Gulf and encourage responsible behavior.
39. What are the Most Popular Tourist Attractions Near the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico region offers a wide array of tourist attractions, including:
- Beaches: Pristine beaches along the coasts of Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, Texas, and Mexico.
- National Parks: Everglades National Park, Padre Island National Seashore, and other natural areas.
- Historic Sites: Historic cities like New Orleans, Galveston, and St. Augustine.
- Theme Parks: Major theme parks in Orlando and other areas.
- Cultural Attractions: Museums, art galleries, and cultural centers in cities throughout the region.
40. What are Some Fun Facts About the Gulf of Mexico?
Here are some fun facts about the Gulf of Mexico:
- Deepest Point: The Sigsbee Deep is deeper than the height of ten Empire State Buildings stacked on top of each other.
- Hurricane Alley: The Gulf is one of the most active hurricane-prone areas in the world.
- Loop Current: The Loop Current is a powerful current that can significantly affect the Gulf’s water temperatures and weather patterns.
- Diverse Marine Life: The Gulf is home to a wide variety of marine species, including some that are found nowhere else in the world.
- Economic Importance: The Gulf supports a diverse range of industries, including fishing, oil and gas, shipping, and tourism.
Visiting gaymexico.net can give you all the information you need to plan your unforgettable trip. Remember, Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States. Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177. Website: gaymexico.net.
