Are you curious about the number of immigrants in Mexico, especially if you’re part of the LGBTQ+ community planning a visit or seeking a new home? At gaymexico.net, we provide the insights you need. Discover the real numbers, understand the trends, and learn about the diverse immigrant communities that enrich Mexico. Explore reliable data and resources to ensure a safe and informed experience.
1. What Is The Estimated Number Of Immigrants Living In Mexico?
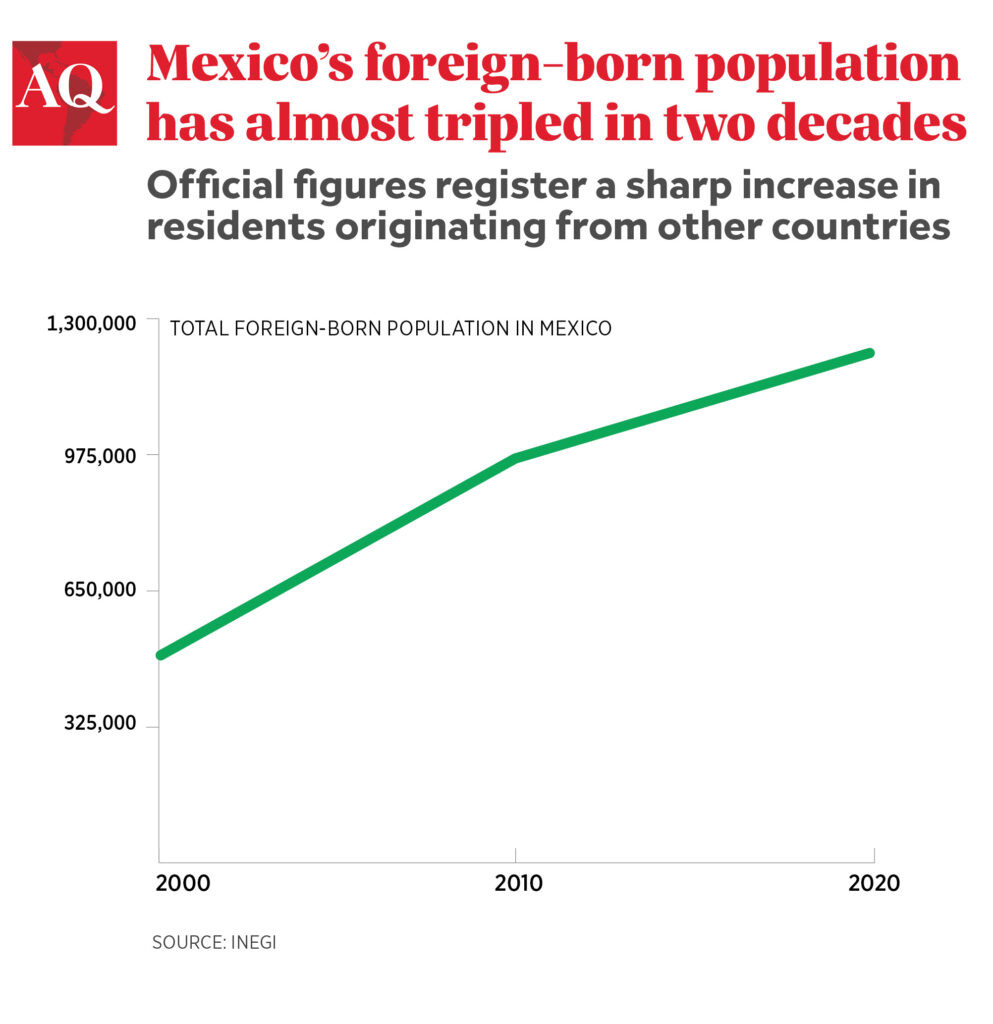
Officially, around 1.5 million immigrants reside in Mexico, a country with a population of approximately 130 million. However, this figure might underestimate the actual number due to various factors, including undocumented immigrants and those who enter as tourists but stay longer. This number is drawn from official sources but it is generally accepted that the actual amount is significantly higher.
Mexico’s unique position as a bridge between Latin America and the United States contributes to its complex migration patterns. Many people pass through Mexico on their way to the U.S., while others choose to stay, adding to the country’s diverse cultural landscape. The LGBTQ+ community will find that this diversity contributes to a more welcoming and accepting environment in many parts of Mexico.
2. Why Might The Official Figures Underestimate The Number Of Immigrants In Mexico?
Official immigration figures in Mexico may be lower than the actual number for several reasons:
- Undocumented Immigrants: Many individuals enter Mexico without proper documentation, seeking economic opportunities or refuge. These individuals are not typically included in official counts.
- Tourist Visas: Some immigrants enter Mexico on tourist visas and overstay their allowed time, effectively becoming undocumented. Mexico’s relatively lax tourism regulations, combined with strict residency laws, can incentivize this practice.
- Data Collection Issues: Differences in data collection methods between Mexican and international organizations can lead to discrepancies. For example, the U.S. State Department may report a higher number of U.S. citizens living in Mexico than Mexican authorities do.
- Refugee Status: Refugees seeking asylum in Mexico may not be immediately classified as immigrants, further affecting the official statistics.
- Reluctance to Self-Identify: Some immigrants may be hesitant to register with authorities due to fear of deportation or other legal repercussions.
These factors contribute to the challenges in accurately counting the immigrant population in Mexico. For LGBTQ+ individuals, understanding these nuances is crucial for navigating legal and social landscapes.
3. What Are The Main Countries Of Origin For Immigrants In Mexico?
The main countries of origin for immigrants in Mexico include:
- United States: Many U.S. citizens choose to live in Mexico, drawn by factors such as lower cost of living, cultural affinity, and retirement opportunities.
- Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador: These Central American countries experience significant outward migration due to factors like poverty, violence, and political instability. Many individuals from these countries transit through Mexico, with some choosing to stay.
- Venezuela: Economic and political crises in Venezuela have led to a significant increase in Venezuelan migrants seeking opportunities in Mexico.
- Argentina: A number of Argentinians, particularly those in upscale bars, are known to dominate upselling industries.
These diverse immigrant communities contribute to Mexico’s rich cultural tapestry and offer unique perspectives and experiences. For LGBTQ+ travelers and residents, this diversity can foster a sense of community and acceptance.
4. Where Do Most Central American Migrants Reside Within Mexico?
Most Central American migrants, particularly those from Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador, reside in the southern border state of Chiapas. This region is one of Mexico’s poorest and serves as a significant migratory sink due to its proximity to Central America.
- Guatemalans: 58.4% of Guatemalan migrants in Mexico live in Chiapas.
- Hondurans: 28% of Honduran migrants in Mexico live in Chiapas.
- Salvadorans: 25.5% of Salvadoran migrants in Mexico live in Chiapas.
The concentration of migrants in Chiapas presents both opportunities and challenges for the region, including increased demand for social services and potential strain on local resources. Understanding these dynamics is essential for anyone interested in the social and economic landscape of Mexico.
5. How Does Mexico’s Location Affect Its Immigration Patterns?
Mexico’s geographic location between countries with significant push factors, such as crime, poverty, and civil war legacies, and the world’s largest economy (the United States) makes it a crossroads for migration. This unique position results in several key effects:
- Transit Country: Millions of migrants pass through Mexico each year en route to the United States.
- Migratory Sink: Mexico inevitably becomes a destination for some migrants, especially those unable to cross the U.S. border or who choose to stay for other reasons.
- Diverse Migrant Flows: Mexico experiences a mix of economic migrants, asylum seekers, and refugees from various countries, creating a complex and dynamic immigration landscape.
- Political Implications: The Mexican government faces pressure to manage migration flows, often employing measures to dissuade migration, which can create tension with human rights advocates.
For LGBTQ+ individuals, understanding these geopolitical factors can provide context for the social and political climate they may encounter in Mexico.
6. What Impact Do Tourists and Refugees Have On Immigration Numbers?
Tourists and refugees significantly impact immigration numbers in Mexico, although their effects are often indirect:
- Tourists as Potential Immigrants: Some tourists may overstay their visas and become undocumented immigrants, blurring the line between temporary visitors and permanent residents. Mexico’s lax tourism regulations can facilitate this.
- Refugees Seeking Asylum: Refugees seeking asylum may initially be classified separately from immigrants. However, many refugees eventually integrate into Mexican society and become permanent residents.
- Increased Visibility of Migration: The growing number of tourists, migrants, and refugees in Mexico has made the effects of migration more visible than ever, influencing public perception and policy debates.
- Demand for Services: Both tourists and refugees increase demand for services such as healthcare, housing, and education, impacting local communities and economies.
These dynamics highlight the complex interplay between tourism, asylum, and immigration in Mexico.
7. What Is “Immigration In Disguise,” And Why Does It Occur?
“Immigration in disguise” refers to the practice of individuals entering and exiting Mexico perennially on tourist visas to avoid the complexities of obtaining residency. This phenomenon is driven by:
- Strict Residency Laws: Mexico has notoriously tough residency laws, making it difficult for foreigners to obtain legal status.
- Lax Tourism Regulations: Mexico’s relatively lenient tourism regulations allow visitors to stay for extended periods without strict oversight.
- Digital Nomadism: The rise of remote work has enabled many professionals to work from anywhere, incentivizing them to live in Mexico without formally immigrating.
- Cost Savings: Some individuals may find it more cost-effective to maintain tourist status than to navigate the bureaucratic hurdles and expenses of obtaining residency.
This practice is especially common among digital nomads and white-collar workers who can perform their jobs remotely.
8. How Has Digital Nomadism Affected Immigration In Mexico?
Digital nomadism has significantly altered immigration patterns in Mexico by:
- Increasing the Number of Long-Term Visitors: More individuals are choosing to live in Mexico for extended periods while working remotely, blurring the line between tourism and immigration.
- Driving Demand for Short-Term Rentals: The influx of digital nomads has increased demand for short-term rentals and co-working spaces, boosting local economies in popular destinations.
- Creating New Communities: Digital nomads often form communities and networks, sharing resources and experiences, which can enhance social integration and cultural exchange.
- Challenging Traditional Immigration Categories: The traditional categories of tourist and immigrant are becoming less distinct as more people embrace location-independent lifestyles.
For the LGBTQ+ community, digital nomadism can provide opportunities to live and work in Mexico while maintaining connections to global networks and resources.
9. What Factors Contribute To Migration From Central America To Mexico?
Several factors drive migration from Central American countries like Guatemala, Honduras, and El Salvador to Mexico:
- Poverty: High poverty rates in Central America push individuals to seek better economic opportunities in Mexico and the United States.
- Violence: Gang violence, drug trafficking, and political instability create unsafe conditions that force people to flee their homes.
- Political Instability: Corruption, weak governance, and lack of rule of law contribute to a sense of hopelessness and drive migration.
- Legacy of Civil War: The lingering effects of civil wars in the region continue to displace communities and disrupt livelihoods.
- Environmental Factors: Natural disasters, climate change, and environmental degradation exacerbate existing challenges and contribute to displacement.
These factors create a complex web of interconnected issues that drive migration from Central America.
10. How Does Mexican Xenophobia Affect Immigrant Communities?
Mexican xenophobia and malinchismo (a preference for all things foreign) can create challenges for immigrant communities in Mexico:
- Discrimination: Immigrants may face discrimination in employment, housing, and access to services due to xenophobic attitudes.
- Scapegoating: Migrants are sometimes blamed for the country’s economic and social problems, leading to resentment and hostility.
- Cultural Bias: Malinchismo can create a bias towards foreign cultures and products, devaluing local traditions and contributions.
- Limited Integration: Xenophobia can hinder the integration of immigrants into Mexican society, leading to social isolation and marginalization.
Despite these challenges, many immigrants find ways to build successful lives and contribute to Mexico’s cultural and economic landscape. The LGBTQ+ community can play a role in promoting tolerance and understanding by sharing their stories and experiences.
11. What Role Do Startups Play In Mexican Immigration?
Startups play a significant role in Mexican immigration by:
- Attracting Foreign Talent: Mexico’s growing startup ecosystem attracts entrepreneurs and skilled workers from around the world, contributing to economic innovation and job creation.
- Providing Opportunities for Immigrants: Many startups are founded by immigrants who see opportunities in the Mexican market that may not exist in their home countries.
- Driving Economic Growth: Successful startups like Kavak and Luuna generate revenue, create jobs, and contribute to Mexico’s overall economic growth.
- Fostering Innovation: Immigrant entrepreneurs often bring new ideas, perspectives, and business models to Mexico, fostering innovation and competitiveness.
Mexico’s strategic advantages, such as its proximity to the U.S. market and its relatively low cost of living, make it an attractive destination for startups.
12. What Policies Does The Mexican Government Implement Regarding Migration?
The Mexican government’s migration policies are complex and sometimes contradictory:
- Dissuading Migration: The government has deployed the army to deal with migrants and extended cash transfer schemes to Central America to discourage migration, reflecting a desire to control migration flows.
- Border Control: Mexico cooperates with the United States to control its southern border, often detaining and deporting migrants attempting to reach the U.S.
- Humanitarian Efforts: The government also provides humanitarian assistance to migrants, including shelter, healthcare, and legal aid, reflecting a commitment to human rights.
- Economic Development Initiatives: Mexico has launched economic development initiatives in Central America to address the root causes of migration, such as poverty and violence.
These policies reflect a balancing act between managing migration flows, protecting its own interests, and upholding humanitarian principles.
13. How Do Middle-Class Immigrants Capitalize On Opportunities In Mexico?
Middle-class immigrants capitalize on strategic advantages in Mexico that might not be available in their home countries:
- Lower Cost of Living: Mexico offers a lower cost of living compared to many developed countries, allowing immigrants to stretch their incomes further.
- Proximity to the U.S. Market: Mexico’s proximity to the U.S. market provides access to business opportunities and potential customers.
- Cultural Affinity: Many middle-class immigrants, particularly those from Latin America, feel a cultural connection to Mexico, making it easier to adapt and integrate.
- Startup Opportunities: Mexico’s growing startup ecosystem offers opportunities for entrepreneurs to launch and grow their businesses.
- Remote Work Options: The rise of remote work allows middle-class professionals to live in Mexico while working for companies based in other countries.
These factors make Mexico an attractive destination for middle-class immigrants seeking new opportunities and a better quality of life.
14. What Are Some Examples Of Successful Immigrant Communities In Mexico?
Several successful immigrant communities have formed in Mexico, including:
- Lebanese-Mexican Community: This community has thrived for over a century, blending Lebanese traditions with Mexican culture and contributing to the country’s culinary and political landscape.
- Korean Community: The Korean community, particularly in cities like Monterrey, has established businesses, restaurants, and cultural centers, catering to both Korean and Mexican customers.
- Haitian Community: The Haitian community in Tijuana has introduced new foods and cultural practices, while also advocating for their rights and fighting against discrimination.
- Venezuelan Community: Educated Venezuelans have found employment in various sectors, including tourism and customer service, contributing to the Mexican economy.
These communities demonstrate the resilience, adaptability, and contributions of immigrants to Mexican society.
15. How Can LGBTQ+ Individuals Find Support Within Immigrant Communities In Mexico?
LGBTQ+ individuals can find support within immigrant communities in Mexico through:
- LGBTQ+ Organizations: Several organizations in Mexico provide support and resources for LGBTQ+ individuals, including legal aid, healthcare, and social services.
- Community Centers: LGBTQ+ community centers offer safe spaces for socializing, networking, and accessing information.
- Online Forums: Online forums and social media groups connect LGBTQ+ immigrants with each other, providing a sense of community and support.
- Cultural Events: LGBTQ+ cultural events and festivals celebrate diversity and provide opportunities for individuals to connect with their peers.
- Religious Organizations: Some religious organizations are welcoming and affirming of LGBTQ+ individuals, providing spiritual guidance and community support.
It is essential for LGBTQ+ immigrants to research and connect with these resources to ensure their well-being and integration into Mexican society.
16. What Are The Challenges Faced By Haitian Immigrants In Mexico?
Haitian immigrants in Mexico face several challenges, including:
- Racism and Discrimination: Haitian immigrants often experience racism and discrimination in employment, housing, and healthcare.
- Language Barriers: The language barrier can make it difficult for Haitian immigrants to access services and integrate into Mexican society.
- Legal Status: Many Haitian immigrants lack legal status, making them vulnerable to exploitation and deportation.
- Healthcare Access: Some Haitian immigrants have been denied healthcare at local hospitals, highlighting the need for improved access to medical services.
- Economic Hardship: Haitian immigrants often struggle to find stable employment and adequate housing, leading to economic hardship.
These challenges underscore the need for greater support and advocacy for Haitian immigrants in Mexico.
17. How Can The Gaymexico.Net Website Help LGBTQ+ Immigrants In Mexico?
Gaymexico.net is an invaluable resource for LGBTQ+ immigrants in Mexico, offering:
- Comprehensive Information: The website provides up-to-date information on LGBTQ+-friendly destinations, events, and resources in Mexico.
- Community Connections: Gaymexico.net connects LGBTQ+ immigrants with local communities and organizations, fostering a sense of belonging and support.
- Safety Tips: The website offers tips and advice for staying safe and comfortable while traveling or living in Mexico as an LGBTQ+ individual.
- Legal and Social Updates: Gaymexico.net provides updates on legal and social issues affecting the LGBTQ+ community in Mexico, helping individuals stay informed and empowered.
- Cultural Insights: The website shares insights into LGBTQ+ culture and history in Mexico, promoting understanding and appreciation.
Gaymexico.net aims to be a comprehensive and reliable resource for LGBTQ+ individuals seeking information, support, and community in Mexico.
18. What Are The Benefits Of Living In Mexico As An Immigrant?
Living in Mexico as an immigrant offers numerous benefits:
- Rich Culture: Mexico boasts a vibrant and diverse culture, with a rich history, delicious cuisine, and lively traditions.
- Lower Cost of Living: The cost of living in Mexico is generally lower than in many developed countries, making it an attractive destination for retirees and budget-conscious individuals.
- Friendly People: Mexicans are known for their warmth and hospitality, making it easy for immigrants to feel welcome and integrate into local communities.
- Beautiful Scenery: Mexico offers a stunning variety of landscapes, from pristine beaches to lush jungles and majestic mountains.
- Healthcare Access: Mexico has a well-developed healthcare system, with both public and private options available to immigrants.
- Growing Economy: Mexico’s growing economy offers opportunities for employment and entrepreneurship.
These benefits make Mexico an attractive destination for immigrants seeking a better quality of life.
19. What Legal Protections Are Available To Immigrants In Mexico?
Immigrants in Mexico are afforded certain legal protections under Mexican law and international agreements:
- Constitutional Rights: The Mexican Constitution guarantees fundamental rights to all individuals within its territory, regardless of immigration status.
- Non-Discrimination Laws: Mexican law prohibits discrimination based on race, ethnicity, religion, gender, sexual orientation, and other protected characteristics.
- Refugee Protection: Mexico is a signatory to international agreements protecting the rights of refugees and asylum seekers.
- Access to Justice: Immigrants have the right to access the Mexican legal system and seek redress for grievances.
- Labor Rights: Immigrant workers are entitled to the same labor rights and protections as Mexican citizens, including minimum wage, safe working conditions, and the right to organize.
It is important for immigrants to be aware of their legal rights and seek legal assistance if they experience discrimination or abuse.
20. How Can Immigrants Contribute To Mexican Society?
Immigrants contribute to Mexican society in numerous ways:
- Economic Growth: Immigrants fill labor shortages, start businesses, and pay taxes, contributing to economic growth and prosperity.
- Cultural Enrichment: Immigrants bring new perspectives, traditions, and artistic expressions to Mexico, enriching the country’s cultural landscape.
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Immigrant entrepreneurs often create innovative products and services that benefit Mexican consumers.
- Social Cohesion: Immigrants can foster social cohesion by building bridges between different cultures and communities.
- Skilled Labor: Immigrants with specialized skills and knowledge can fill critical gaps in the Mexican workforce.
By embracing diversity and promoting inclusion, Mexico can harness the full potential of its immigrant communities.
21. Where Can I Find More Information About LGBTQ+ Life In Mexico?
For more information about LGBTQ+ life in Mexico, be sure to visit gaymexico.net. It’s your go-to resource for all things LGBTQ+ in Mexico.
- Comprehensive Guides: Find detailed guides about LGBTQ+-friendly cities and towns.
- Event Listings: Discover the latest LGBTQ+ events, from pride parades to local meetups.
- Community Stories: Read inspiring stories from LGBTQ+ individuals living in Mexico.
- Travel Tips: Get essential travel tips to ensure a safe and enjoyable trip.
- Resource Directory: Access a directory of LGBTQ+ organizations and services.
22. What Are Some LSI Keywords Related To Immigration In Mexico?
Here are some Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords related to immigration in Mexico:
- Migrant communities in Mexico
- Mexican immigration policy
- Immigration statistics Mexico
- Refugee crisis Mexico
- Economic impact of immigration in Mexico
- Immigrant rights in Mexico
- Central American migrants in Mexico
- Living in Mexico as a foreigner
- Immigration to Mexico from USA
- Immigrant integration Mexico
23. What Are Some Key Considerations For LGBTQ+ Individuals Considering Immigration To Mexico?
Key considerations for LGBTQ+ individuals considering immigration to Mexico include:
- Legal Protections: Understand the legal rights and protections available to LGBTQ+ individuals in Mexico.
- Social Acceptance: Research the level of social acceptance and tolerance in different parts of Mexico.
- Community Resources: Identify LGBTQ+ organizations and community centers that can provide support and resources.
- Healthcare Access: Ensure access to LGBTQ+-friendly healthcare providers and services.
- Safety and Security: Take precautions to protect your safety and security, especially in areas where LGBTQ+ individuals may face discrimination or violence.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Be aware of cultural norms and customs and show respect for local traditions.
By carefully considering these factors, LGBTQ+ individuals can make informed decisions about immigrating to Mexico and ensure a safe and fulfilling experience.
24. How Can I Contact Gaymexico.Net For Further Assistance?
For further assistance and more information, you can contact gaymexico.net:
- Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States
- Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177
- Website: gaymexico.net
Gaymexico.net is committed to providing comprehensive and reliable information to the LGBTQ+ community in Mexico.
Navigating immigration can be complex, but with the right information and resources, you can make informed decisions and build a fulfilling life in Mexico. Explore gaymexico.net today for comprehensive guides, community connections, and essential tips tailored for the LGBTQ+ community! Discover your new home in Mexico with confidence and support.
 Map of Mexico highlighting major cities and tourist destinations
Map of Mexico highlighting major cities and tourist destinations
FAQ About Immigration in Mexico
1. How many immigrants are living in Mexico as of 2024?
Around 1.5 million immigrants are officially recorded in Mexico, but the actual number could be higher due to undocumented individuals and tourists who overstay their visas.
2. What makes the official immigration numbers potentially inaccurate?
Undocumented immigrants, tourists overstaying visas, and varying data collection methods can lead to underestimates in official figures.
3. Which countries do most immigrants in Mexico come from?
The United States, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, and Venezuela are the primary countries of origin for immigrants in Mexico.
4. Why do many Central American migrants choose to live in Chiapas, Mexico?
Chiapas’s proximity to Central America, combined with its status as one of Mexico’s poorest states, makes it a migratory sink for those seeking refuge or economic opportunities.
5. How does Mexico’s geographical location influence its immigration patterns?
Mexico’s position between countries with significant push factors (poverty, violence) and the U.S. makes it both a transit country and a destination for migrants.
6. What role do tourists and refugees play in Mexico’s immigration statistics?
Tourists may become undocumented immigrants by overstaying visas, and refugees seeking asylum contribute to the overall number of people requiring services and support.
7. What is “immigration in disguise,” and why does it occur in Mexico?
“Immigration in disguise” involves individuals using tourist visas to avoid strict residency laws, often enabled by remote work opportunities.
8. How has digital nomadism affected immigration patterns in Mexico?
Digital nomadism has led to an increase in long-term visitors, driving demand for short-term rentals and challenging traditional immigration categories.
9. What are the primary factors driving migration from Central America to Mexico?
Poverty, violence, political instability, the legacy of civil war, and environmental factors contribute to migration from Central America.
10. Where can LGBTQ+ individuals find support within immigrant communities in Mexico?
LGBTQ+ organizations, community centers, online forums, and cultural events offer support and resources for LGBTQ+ immigrants in Mexico.
