How many Mexican undocumented immigrants reside in the United States? Gaymexico.net provides insights into this demographic, which significantly impacts the US labor force and economy, even within the LGBTQ+ community. Understanding this population helps us address issues of immigration, labor, and social inclusion, fostering a more welcoming environment for all. This article explores the numbers, demographics, and contributions of Mexican undocumented immigrants in the US, highlighting key statistics and ongoing debates around immigration reform using data-driven insights.
1. What is the Approximate Number of Mexican Undocumented Immigrants Living in the US?
Approximately 7.41 million undocumented immigrants of Hispanic origin resided in the United States in 2019, with Mexicans constituting the largest share at 63.6%, according to the Center for Migration Studies of New York (CMS). This means roughly 4.7 million undocumented immigrants in the US are Mexican. This substantial figure underscores the significant presence and influence of this demographic group within the broader undocumented immigrant population, highlighting their critical role in various sectors of the U.S. economy and society.
1.1 How Does This Number Compare to the Total Undocumented Immigrant Population?
Mexicans make up a significant portion of the total undocumented immigrant population in the US. While the exact figures fluctuate, Mexicans have consistently comprised the largest single nationality among undocumented immigrants. Understanding this proportion is vital for shaping immigration policies and resource allocation. The share of the Hispanic undocumented population has remained relatively stable, ranging between 72-76 percent.
1.2 What Factors Contribute to These Numbers?
Several factors contribute to the high number of Mexican undocumented immigrants in the US, including economic opportunities, proximity, and historical migration patterns. The demand for labor in certain sectors of the US economy, combined with economic challenges in Mexico, drives migration. Additionally, established social networks and communities in the US facilitate further migration.
2. Where Do Most Mexican Undocumented Immigrants Live in the US?
The majority of Mexican undocumented immigrants reside in a few key states, including California, Texas, Illinois, Florida and New York. These states offer a combination of job opportunities, established Hispanic communities, and varying levels of immigration enforcement. Understanding the geographic distribution helps tailor resources and services to meet the specific needs of these communities.
2.1 What are the Key States with Large Mexican Undocumented Populations?
California and Texas have the largest populations of Mexican undocumented immigrants, followed by Illinois, Florida, and New York. These states have historically been magnets for immigrants due to their economic opportunities and established communities.
2.2 Why are These States Popular Destinations?
These states are popular destinations due to their robust economies, particularly in sectors like agriculture, construction, and services, which often employ undocumented workers. Additionally, these states have large Hispanic communities that provide social support and cultural familiarity, making the transition easier for new arrivals.
3. What are the Demographic Characteristics of Mexican Undocumented Immigrants?
Mexican undocumented immigrants are predominantly of working age, with a relatively balanced gender distribution. Many have lived in the US for several years and contribute significantly to the labor force, often in essential but low-paying jobs. Understanding these demographic characteristics is essential for crafting effective and humane immigration policies.
3.1 What is the Age and Gender Distribution?
The majority of Mexican undocumented immigrants are of working age (16-64), with a significant portion in the prime working age range (25-54). The gender distribution is relatively balanced, with slightly more men than women. The vast majority of Hispanic undocumented immigrants are of working age (16-64) (91 percent), and most are of prime working age (25-54) (72 percent). Forty-six percent of Hispanic undocumented immigrants are female, and 54 percent are male.
3.2 How Long Have They Been Living in the US?
A significant portion of Mexican undocumented immigrants have lived in the US for many years, with many having resided in the country for over a decade. This long-term residency underscores their integration into American society and their contributions to the economy and communities. Slightly more than half (52 percent) have been living in the United States for 15 years or more.
3.3 What is Their Level of English Proficiency?
English proficiency varies among Mexican undocumented immigrants, with some being fluent and others having limited English skills. Language proficiency is often linked to education level and length of stay in the US. Half of the undocumented Hispanic population speaks English well, very well, or only English. Newly arrived immigrants may still be building their English-language skills in the United States.
4. What is the Education and Employment Status of Mexican Undocumented Immigrants?
Mexican undocumented immigrants often have lower levels of formal education but high rates of labor force participation. They are frequently employed in essential sectors such as construction, agriculture, and services. Addressing educational barriers and labor rights is crucial for improving their socio-economic conditions.
4.1 What are Their Education Levels?
The Hispanic undocumented immigrant population overall has relatively low levels of education. Legal status can be a barrier to higher educational attainment in the United States. Half of the Hispanic undocumented population, ages 18 and over, have less than a high school education. Twenty-nine percent have completed high school, 13 percent have some college education, and 7 percent have a college degree or higher education
4.2 In Which Sectors are They Primarily Employed?
They are concentrated in certain sectors such as service occupations or natural resources, construction, and maintenance occupations. Hispanic undocumented immigrants are more likely to be in the labor force (78 percent) than the US-born Hispanic population (68 percent), or the overall US-born population (63 percent). Nearly two-thirds of the overall Hispanic undocumented population is employed in either Service occupations or Natural resources, construction, and maintenance occupations.
4.3 What Role Do They Play in Essential Occupations?
Hispanic undocumented immigrants, and Hispanic immigrants overall, represent a larger share of the workforce in many of the top key low-skilled occupations, relative to their share of the overall US population. Hispanic undocumented immigrants are overrepresented in the following occupations:
- Construction laborers
- Maids and housekeeping cleaners
- Grounds and maintenance workers
- Chefs and cooks
- Janitors and building cleaners
- Laborers and freight, stock, and hand material movers
- Waiters and waitresses
- Drivers/sales workers and truck drivers
- Cashiers
5. What is the Labor Force Participation Rate Among Mexican Undocumented Immigrants?
Mexican undocumented immigrants have a high labor force participation rate, often exceeding that of the US-born population. This underscores their significant economic contributions, despite the challenges they face due to their legal status. Ensuring fair labor practices and pathways to legal status can benefit both immigrants and the broader economy.
5.1 How Does Their Participation Rate Compare to US-Born Workers?
Hispanic undocumented immigrants are more likely to be in the labor force (78 percent) than the US-born Hispanic population (68 percent), or the overall US-born population (63 percent). This highlights their strong work ethic and their importance in filling labor demands in various sectors.
5.2 What Types of Jobs Do They Typically Hold?
They typically hold jobs in sectors like construction, agriculture, and services, often performing physically demanding or low-paying tasks. Many of these jobs are considered essential, yet they often lack benefits and job security.
5.3 Are They Overrepresented in Certain Industries?
Hispanic undocumented workers represent a larger share of the essential workforce than their share of the population in the top five US states that host the largest share of this population. In all five states, Hispanic undocumented immigrants are overrepresented among essential workers.
6. What are the Economic Contributions of Mexican Undocumented Immigrants?
Mexican undocumented immigrants contribute significantly to the US economy through their labor and consumption. They fill essential jobs, pay taxes, and support local economies. Recognizing their economic contributions is vital for fostering a balanced and informed discussion about immigration reform.
6.1 How Do They Contribute to the US Economy?
They contribute through their participation in the workforce, filling jobs that might otherwise go unfilled, particularly in sectors like agriculture, construction, and services. Their labor helps keep these industries running and supports economic growth.
6.2 Do They Pay Taxes?
Many Mexican undocumented immigrants pay taxes through payroll deductions, sales taxes, and property taxes (either directly or indirectly through rent). These tax contributions help fund public services and infrastructure.
6.3 What is Their Impact on Local Economies?
Their presence supports local businesses, creates jobs, and contributes to the overall economic vitality of communities. Their spending on goods and services helps stimulate local economies.
7. What are the Challenges Faced by Mexican Undocumented Immigrants?
Mexican undocumented immigrants face numerous challenges, including wage disparities, limited access to social safety nets, and the constant threat of deportation. Understanding these challenges is crucial for developing policies that promote fairness, equity, and integration.
7.1 What are the Wage Disparities They Experience?
Legal status can be a barrier to higher earnings and financial stability, as shown by the wage gap between documented and undocumented Hispanic immigrants. The mean and median annual wages of Hispanic undocumented immigrants who are employed (ages 16 and above) are $28,252 and $25,000, respectively, whereas the mean and median wages for Hispanic documented immigrants are $40,032 and $30,000, respectively.
7.2 Do They Have Access to Social Safety Nets?
They often lack access to social safety nets such as unemployment benefits, food assistance, and healthcare, making them particularly vulnerable during economic downturns or personal crises.
7.3 What is the Risk of Deportation?
The constant risk of deportation creates stress and uncertainty for Mexican undocumented immigrants and their families. This fear can impact their willingness to report crimes, seek medical care, or participate in community activities.
8. What are the Potential Pathways to Legalization for Mexican Undocumented Immigrants?
Several legislative proposals aim to provide pathways to legalization for Mexican undocumented immigrants, including the Dream Act, the Farm Workforce Modernization Act, and comprehensive immigration reform. Understanding these proposals is essential for advocating for policies that address the needs of this population.
8.1 What is the Dream Act?
The Dream Act of 2021 provides conditional permanent residence and removal of conditions on permanent residence for undocumented immigrants who were younger than 18 years of age on age on the initial date of US entry, have been continuously physically present in the United States for four years preceding the bill’s enactment, and have fulfilled specified educational and other requirements specified in the bill.
8.2 What is the Farm Workforce Modernization Act?
The Farm Workforce Modernization Act of 2021 would provide undocumented farmworkers and their family members with a path to legal immigration status and citizenship.
8.3 What are Comprehensive Immigration Reform Proposals?
Comprehensive immigration reform proposals aim to address various aspects of immigration, including border security, enforcement, and pathways to legal status for undocumented immigrants. These proposals often include provisions for earned legalization, allowing undocumented immigrants to gain legal status by meeting certain requirements such as paying taxes, learning English, and passing a background check.
9. How Would Legalization Affect Mexican Undocumented Immigrants?
Legalization would provide Mexican undocumented immigrants with greater economic opportunities, access to social safety nets, and protection from deportation. It would also allow them to fully integrate into American society and contribute more effectively to the economy.
9.1 What are the Potential Economic Benefits of Legalization?
Legalization would lead to increased earnings, higher tax revenues, and greater economic productivity. Legalized immigrants would be able to pursue better jobs, start businesses, and invest in their communities.
9.2 How Would Legalization Impact Their Access to Social Services?
Legalization would allow them to access social services such as healthcare, education, and unemployment benefits, improving their overall well-being and reducing poverty.
9.3 What are the Societal Benefits of Legalization?
Legalization would reduce the fear and uncertainty experienced by Mexican undocumented immigrants and their families, allowing them to fully participate in civic life and contribute to their communities.
10. What Resources are Available to Support Mexican Undocumented Immigrants?
Various organizations and resources are available to support Mexican undocumented immigrants, including legal aid services, community organizations, and advocacy groups. These resources provide assistance with immigration issues, education, healthcare, and other essential needs.
10.1 What Legal Aid Services are Available?
Legal aid services provide free or low-cost legal assistance to Mexican undocumented immigrants, helping them navigate the complex immigration system and protect their rights.
10.2 Which Community Organizations Offer Support?
Community organizations offer a range of services, including English classes, job training, healthcare referrals, and social support. These organizations play a vital role in helping Mexican undocumented immigrants integrate into their communities.
10.3 How Can Advocacy Groups Help?
Advocacy groups work to promote policies that support Mexican undocumented immigrants, such as comprehensive immigration reform and protection from deportation. These groups raise awareness, lobby elected officials, and mobilize communities to support immigrant rights.
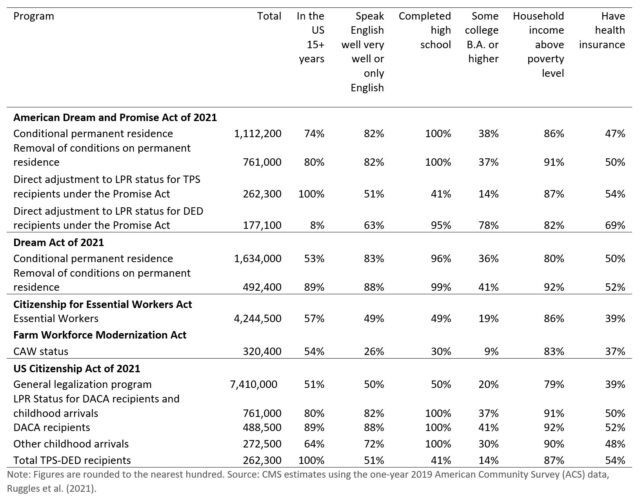 Table summarizing the estimated number and characteristics of the Hispanic undocumented population affected by various legislative programs.
Table summarizing the estimated number and characteristics of the Hispanic undocumented population affected by various legislative programs.
Understanding the number of Mexican undocumented immigrants in the US and their experiences is vital for fostering informed discussions and developing effective policies. At gaymexico.net, we strive to provide comprehensive resources and support for the LGBTQ+ community in Mexico, including information on immigration, legal rights, and cultural integration.
FAQ: Mexican Undocumented Immigrants in the US
- What percentage of the US undocumented population is Mexican? Mexicans constitute the largest share of the Hispanic undocumented immigrant population at 63.6%, according to the Center for Migration Studies of New York (CMS).
- Which US states have the highest number of Mexican undocumented immigrants? California and Texas have the highest number of Mexican undocumented immigrants.
- What types of jobs do Mexican undocumented immigrants typically hold? They typically hold jobs in sectors like construction, agriculture, and services.
- What is the labor force participation rate among Mexican undocumented immigrants? Hispanic undocumented immigrants are more likely to be in the labor force (78 percent) than the US-born Hispanic population (68 percent), or the overall US-born population (63 percent).
- Do Mexican undocumented immigrants pay taxes? Yes, many pay taxes through payroll deductions, sales taxes, and property taxes (either directly or indirectly through rent).
- What are some of the challenges faced by Mexican undocumented immigrants? Wage disparities, limited access to social safety nets, and the constant threat of deportation.
- What is the Dream Act and how would it affect Mexican undocumented immigrants? The Dream Act of 2021 provides conditional permanent residence and removal of conditions on permanent residence for undocumented immigrants who were younger than 18 years of age.
- What is the Farm Workforce Modernization Act? The Farm Workforce Modernization Act of 2021 would provide undocumented farmworkers and their family members with a path to legal immigration status and citizenship.
- How would legalization affect the US economy? Legalization would lead to increased earnings, higher tax revenues, and greater economic productivity.
- Where can Mexican undocumented immigrants find support and resources? Legal aid services, community organizations, and advocacy groups offer support.
Call to Action
Explore gaymexico.net for detailed travel guides, LGBTQ+ events, and community connections in Mexico. Contact us at Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States. Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177, or visit our website gaymexico.net to discover how you can explore Mexico safely and enjoyably.