The question of Why Did The Aztecs Settle In The Valley Of Mexico is intriguing, especially for our community at gaymexico.net. The Aztecs settled in the Valley of Mexico due to a combination of religious prophecy, strategic advantages, and economic opportunities. This decision shaped their destiny and ultimately led to the rise of their powerful empire, impacting cultural and historical landscapes that resonate even today. Let’s explore the factors that influenced this pivotal choice, revealing insights relevant to cultural enthusiasts and LGBTQ+ travelers alike seeking to connect with Mexico’s rich heritage. Discover LGBTQ+ history, cultural insights, and travel tips.
1. The Prophecy of Huitzilopochtli
The Aztec migration story begins with a powerful prophecy. According to their legends, the Aztec god Huitzilopochtli commanded them to leave their ancestral homeland, Aztlán, and seek a new home.
1.1. The Divine Sign
The prophecy stated that the Aztecs would find their destined location when they saw an eagle perched on a nopal cactus, devouring a serpent. This iconic image would signify the place where they were meant to build their great city.
1.2. The Wandering Tribe
Driven by this divine mandate, the Aztecs embarked on a long and arduous journey. This pilgrimage took them through various regions of Mexico, where they faced numerous challenges and hardships.
1.3. Finding the Sign
Around 1325 CE, after centuries of wandering, the Aztecs finally witnessed the prophesied sign on a small, swampy island in Lake Texcoco. This marked the end of their pilgrimage and the beginning of their new chapter.
2. Strategic Advantages of the Valley of Mexico
The Valley of Mexico, despite its initial uninviting appearance, offered several strategic advantages that made it an ideal location for the Aztecs to settle.
2.1. Natural Defenses
The island in Lake Texcoco provided natural defenses. Surrounded by water, it was difficult for potential enemies to launch attacks. This isolation allowed the Aztecs to develop their society and military strength without constant threats.
2.2. Abundant Resources
The Valley of Mexico was rich in natural resources. The lake provided fish, waterfowl, and other aquatic life, which served as important food sources. The surrounding land was fertile, allowing for agriculture and cultivation.
2.3. Central Location
The valley’s central location facilitated trade and communication with other regions. The Aztecs could easily access resources and markets, which contributed to their economic growth and political influence.
3. The Economic Opportunities in the Valley
The Valley of Mexico presented significant economic opportunities for the Aztecs, which they skillfully exploited to build a thriving society.
3.1. Chinampa Agriculture
One of the most important economic factors was the development of chinampas, or “floating gardens.” These artificial islands were created by piling up mud and vegetation in the shallow waters of the lake, creating fertile plots for agriculture.
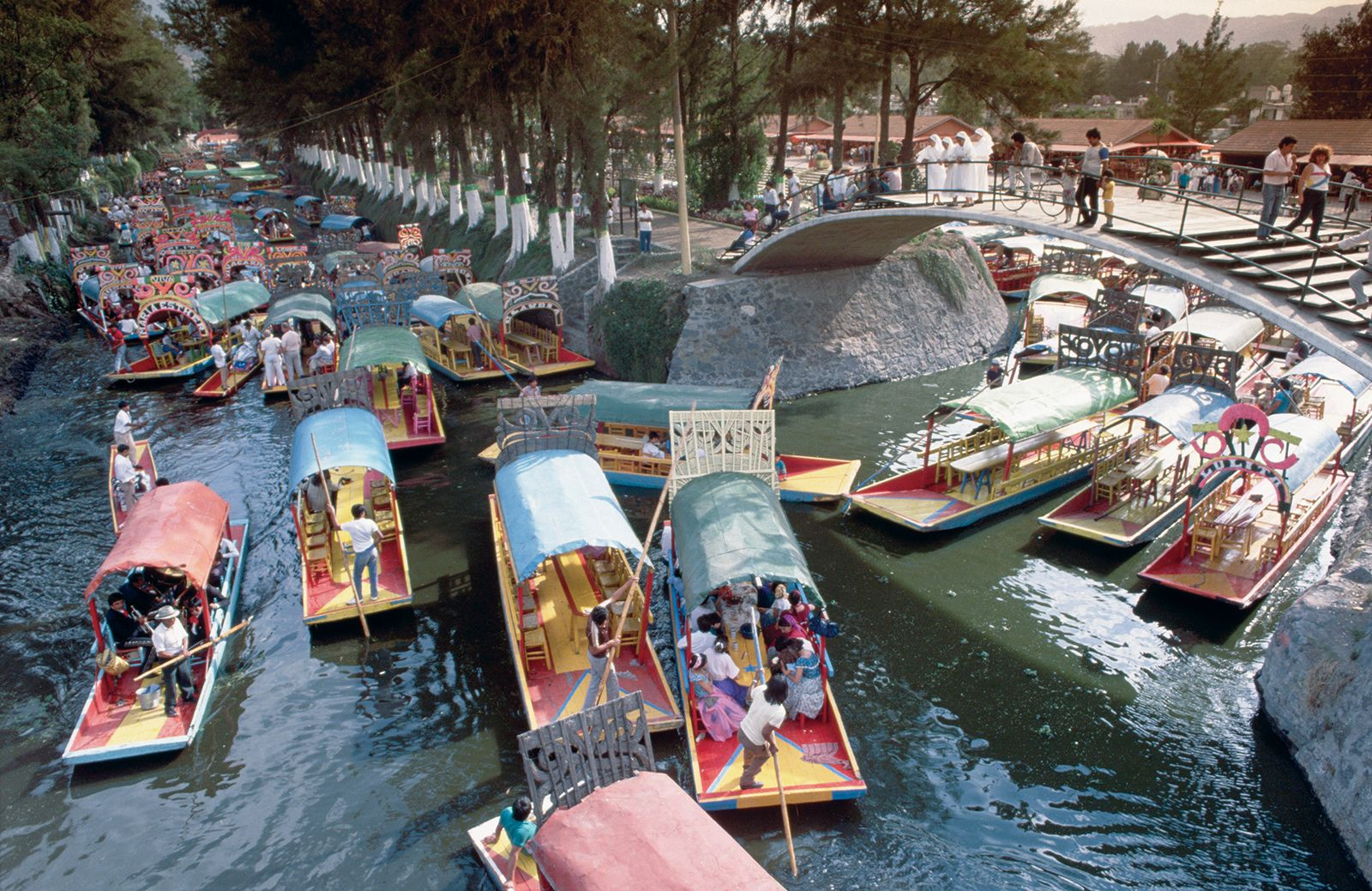 Chinampas Xochimilco
Chinampas Xochimilco
3.2. High Productivity
Chinampas were incredibly productive, allowing the Aztecs to grow multiple crops each year. This agricultural surplus supported a large population and fueled the growth of their urban centers.
3.3. Trade and Commerce
The Aztecs also developed a sophisticated system of trade and commerce. They established markets and trade routes that extended throughout the Valley of Mexico and beyond, exchanging goods such as food, textiles, and crafts.
4. Political Landscape and Alliances
The political situation in the Valley of Mexico played a crucial role in the Aztecs’ decision to settle there and their subsequent rise to power.
4.1. Peripheral Location
When the Aztecs arrived, the island in Lake Texcoco was located at the edge of the lands controlled by the major powers in the valley: the Chichimec of Texcoco, the Toltec of Culhuacán, and the Tepanec of Atzcapotzalco. This peripheral location meant that no one had claimed it, giving the Aztecs an opportunity to establish themselves without immediate conflict.
4.2. Strategic Alliances
The Aztecs initially allied themselves with the Tepanec, helping them in their wars of expansion. This alliance allowed the Aztecs to gain military experience and build their own power base.
4.3. Overthrowing the Overlords
By 1428, the Aztecs, under their ruler Itzcoatl and his chief advisor Tlacaelel, were strong enough to conquer their former allies and overlords. This marked a turning point in Aztec history, as they became the dominant power in the Valley of Mexico.
5. Aztec Religion and Ideology
Aztec religion and ideology played a central role in their decision-making and their success in the Valley of Mexico.
5.1. Huitzilopochtli and Warfare
The Aztecs worshipped Huitzilopochtli, the god of war and the sun. They believed that they were the “people of the sun” and had a sacred duty to nourish him with human blood. This belief led to a culture of constant warfare and the practice of human sacrifice.
5.2. Religious Justification for Expansion
War was not only a religious obligation but also a means of acquiring resources and expanding their territory. The Aztecs used their religious beliefs to justify their conquests and maintain their control over their empire.
5.3. Integration of Conquered Peoples
While the Aztecs were fierce warriors, they also had a sophisticated system of integrating conquered peoples into their empire. They allowed local rulers to maintain their positions, as long as they paid tribute and recognized Aztec authority. This helped to maintain stability and prevent rebellions.
6. Sociopolitical Organization of the Aztecs
The complex sociopolitical organization of the Aztecs was another key factor in their success in the Valley of Mexico.
6.1. Calpulli System
Aztec society was organized into calpulli, or “big houses,” which were pseudo-family units based in Tenochtitlán. These units played a crucial role in organizing labor, distributing resources, and providing social support.
6.2. Social Stratification
Despite the communal nature of the calpulli, Aztec society was highly stratified. There was a hereditary nobility, a class of priests and warriors, and a large class of commoners. This social hierarchy helped to maintain order and stability.
6.3. Bureaucracy and Administration
The Aztecs developed a sophisticated bureaucracy to administer their empire. They had governors, tax collectors, courts of justice, military garrisons, and a system of mail and messenger services. This allowed them to effectively control their vast territory and extract tribute from conquered peoples.
7. The Rise of Tenochtitlán
The settlement in the Valley of Mexico led to the rise of Tenochtitlán, one of the most impressive cities in the ancient world.
7.1. Urban Planning
Tenochtitlán was carefully planned and designed. It was built on a grid system, with canals and causeways connecting different parts of the city. The city had impressive temples, palaces, and public buildings.
7.2. Engineering Achievements
The Aztecs were skilled engineers. They built aqueducts to bring fresh water to the city, and they constructed dikes to control flooding. They also developed a system of waste management and sanitation.
7.3. Cultural and Religious Center
Tenochtitlán became the cultural and religious center of the Aztec empire. It was a place of great beauty and splendor, attracting artists, scholars, and religious leaders from all over the region.
8. The Impact on the Valley of Mexico
The Aztecs’ settlement in the Valley of Mexico had a profound impact on the region, transforming its landscape, economy, and culture.
8.1. Environmental Changes
The Aztecs’ agricultural practices, such as the construction of chinampas, significantly altered the environment of the Valley of Mexico. They created new habitats for plants and animals and changed the flow of water in the lake.
8.2. Population Growth
The Aztecs’ successful economy and political dominance led to a significant increase in the population of the Valley of Mexico. This put pressure on resources and led to further environmental changes.
8.3. Cultural Exchange
The Aztecs were not only conquerors but also cultural borrowers. They adopted and adapted many of the customs and traditions of the peoples they conquered, creating a unique and syncretic culture.
9. Legacy and Modern Relevance
The legacy of the Aztecs continues to resonate in Mexico today, influencing its culture, identity, and even its national symbols.
9.1. National Symbolism
The image of the eagle, cactus, and serpent, which guided the Aztecs to their new home, is prominently featured on the Mexican flag. This serves as a constant reminder of the Aztecs’ origins and their role in shaping the nation.
9.2. Cultural Heritage
The ruins of Tenochtitlán, now located in Mexico City, are a major tourist attraction. Visitors can explore the remains of the Templo Mayor, the main temple of the Aztecs, and learn about their history and culture.
9.3. Lessons for Today
The story of the Aztecs offers valuable lessons for today. It demonstrates the importance of adaptability, innovation, and strategic thinking in overcoming challenges and building a successful society. It also highlights the complex relationship between religion, politics, and economics in shaping human history.
10. LGBTQ+ Considerations and Mexico’s Cultural Landscape
For LGBTQ+ travelers interested in exploring Mexico’s rich history and culture, it’s essential to consider the country’s evolving social landscape. While Mexico has made significant strides in LGBTQ+ rights, attitudes can vary widely depending on the region.
10.1. LGBTQ+ Rights in Mexico
Mexico City, in particular, is known for its progressive stance on LGBTQ+ issues, with same-sex marriage legal and a vibrant LGBTQ+ community. However, in more rural areas, traditional values may prevail, and it’s advisable to exercise caution and respect local customs.
10.2. LGBTQ+ Friendly Destinations
Popular tourist destinations like Puerto Vallarta and Cancun also offer welcoming environments for LGBTQ+ travelers, with numerous gay-friendly hotels, bars, and clubs. These cities often host LGBTQ+ events and festivals, providing opportunities to connect with the local community and celebrate diversity.
10.3. Cultural Sensitivity
When exploring historical sites like Tenochtitlán, it’s important to be mindful of the cultural significance of these places and to dress and behave respectfully. Engaging with local guides and learning about the history and traditions of the Aztec civilization can enhance your understanding and appreciation of Mexico’s heritage.
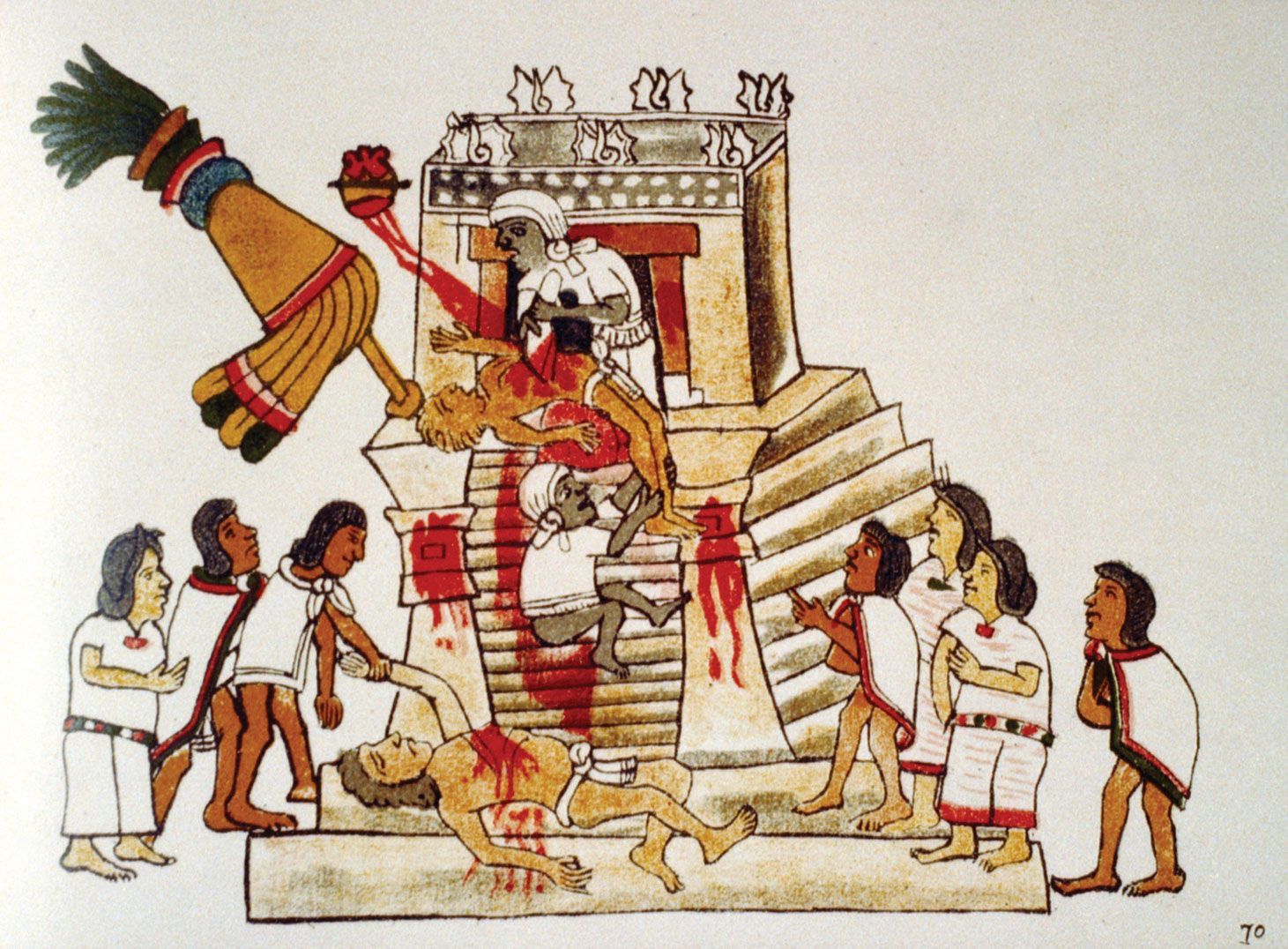 Aztec Sacrifice
Aztec Sacrifice
In conclusion, the Aztecs settled in the Valley of Mexico due to a confluence of factors, including religious prophecy, strategic advantages, economic opportunities, and political considerations. Their decision transformed the region and led to the rise of one of the most impressive civilizations in the ancient world. For those interested in exploring Mexico’s rich history and culture, understanding the story of the Aztecs is essential.
FAQ: The Aztecs in the Valley of Mexico
1. What was the main reason the Aztecs settled in the Valley of Mexico?
The main reason was fulfilling a prophecy from their god Huitzilopochtli, who instructed them to find a place marked by an eagle perched on a cactus eating a serpent.
2. How did the Valley of Mexico’s environment help the Aztecs?
The Valley of Mexico offered strategic advantages like natural defenses from Lake Texcoco and fertile land for agriculture, supporting their growth.
3. What were chinampas, and how did they benefit the Aztecs?
Chinampas were “floating gardens,” artificial islands created for agriculture. They provided high productivity, allowing the Aztecs to grow multiple crops annually.
4. How did the Aztecs rise to power after settling in the Valley of Mexico?
Initially, they formed alliances with groups like the Tepanec, gaining military experience. By 1428, they were strong enough to conquer their allies and dominate the valley.
5. How did Aztec religion influence their settlement and expansion?
Their religion, centered on Huitzilopochtli, required human sacrifices, leading to warfare for prisoners. This religious justification fueled their expansion and control.
6. What was the social structure of the Aztec civilization in the Valley of Mexico?
Aztec society was organized into calpulli (pseudo-family units) with social stratification, including nobility, priests, warriors, and commoners.
7. How did the Aztecs transform the Valley of Mexico?
They altered the environment through agricultural practices like chinampas, increased the population, and integrated various cultural traditions.
8. What is the legacy of the Aztecs in modern Mexico?
The Aztec legacy is seen in Mexico’s national symbolism, such as the eagle on the flag, and in the cultural heritage preserved in ruins like Templo Mayor.
9. How did the Aztecs handle conquered peoples?
The Aztecs allowed local rulers to maintain their positions if they paid tribute and recognized Aztec authority, helping maintain stability.
10. Why is understanding the Aztecs important for LGBTQ+ travelers in Mexico?
Understanding Aztec history enriches the travel experience, offering a deeper appreciation of Mexico’s cultural roots while being mindful of the country’s evolving social landscape and LGBTQ+ rights.
Interested in learning more about the captivating history and vibrant culture of Mexico? Visit gaymexico.net to explore comprehensive travel guides, discover LGBTQ+-friendly destinations, and connect with a welcoming community that celebrates diversity and inclusion. Whether you’re planning a trip or simply seeking to expand your knowledge, gaymexico.net is your go-to resource for all things LGBTQ+ in Mexico.
