Are you curious about how the United States acquired territory from Mexico? The Gadsden Purchase, a significant event in North American history, involved a transaction where the U.S. bought land from Mexico. Gaymexico.net offers insights into the historical and cultural context of this event, especially relevant for those interested in LGBTQ+ perspectives within Mexican history. Let’s delve into the details of this pivotal moment.
This article explores the intricacies surrounding the Gadsden Purchase and provides historical insights. Key phrases related to this topic include Mexican-American relations, 19th-century history, and Southwestern U.S. history.
1. What Was the Gadsden Purchase?
The Gadsden Purchase was an agreement between the United States and Mexico, finalized in 1854, wherein the U.S. paid Mexico $10 million for approximately 29,670 square miles of land that later became parts of Arizona and New Mexico. This purchase aimed to secure land for a southern transcontinental railroad route and resolve lingering disputes following the Mexican-American War.
The Gadsden Purchase, formally known as the Treaty of La Mesilla, represents a significant chapter in the complex history between the United States and Mexico. This transaction, finalized in 1854, resulted in the United States acquiring nearly 30,000 square miles of Mexican territory for $10 million. This land now forms part of present-day Arizona and New Mexico.
Why Was the Gadsden Purchase Important?
The primary motivation behind the Gadsden Purchase was the United States’ desire to secure a suitable route for a southern transcontinental railroad. The topography of the acquired land was ideal for railroad construction, offering a flatter and more easily navigable path compared to other potential routes further north.
Beyond the railroad, the Gadsden Purchase also aimed to resolve several outstanding issues between the two countries. These included disputes over the border, compensation for Native American raids, and American claims against Mexico. However, the purchase ultimately failed to fully address these complex issues, and tensions between the U.S. and Mexico persisted.
The Gadsden Purchase remains a controversial topic in both the United States and Mexico. Some view it as a pragmatic land deal that facilitated economic development and westward expansion in the U.S. Others see it as an example of American imperialism and exploitation of a weaker neighbor.
2. Who Was Involved in the Gadsden Purchase?
Key figures involved in the Gadsden Purchase included James Gadsden, the U.S. Minister to Mexico, and Antonio López de Santa Anna, the President of Mexico at the time. President Franklin Pierce of the United States also played a crucial role in initiating the negotiations.
Key Players in the Gadsden Purchase Negotiations
- James Gadsden: As the U.S. Minister to Mexico, Gadsden was tasked by President Franklin Pierce to negotiate the land purchase. Gadsden, a railroad promoter himself, was a strong advocate for acquiring the land for the transcontinental railroad.
- Antonio López de Santa Anna: Santa Anna, the President of Mexico during the negotiations, faced immense pressure due to the country’s financial instability and internal conflicts. Selling the land to the U.S. provided much-needed funds for his government.
- President Franklin Pierce: President Pierce, a strong proponent of westward expansion, authorized Gadsden to negotiate the land purchase with Mexico. He saw the acquisition of this territory as crucial for the economic and strategic interests of the United States.
- William Marcy: As the U.S. Secretary of State, Marcy provided guidance to Gadsden during the negotiations. He outlined the specific goals of the U.S. government, including securing a railroad route and resolving outstanding disputes with Mexico.
The negotiations between Gadsden and Santa Anna were complex and fraught with challenges. Santa Anna initially resisted selling a large portion of Mexican territory, but he eventually agreed to the sale due to Mexico’s dire financial situation.
The Gadsden Purchase was met with opposition in both the United States and Mexico. In the U.S., some politicians argued that the price paid for the land was too high. In Mexico, many viewed the sale as a betrayal of national sovereignty.
3. Why Did Mexico Sell the Territory to the USA?
Mexico sold the territory primarily due to severe financial difficulties and internal political instability. President Antonio López de Santa Anna needed funds to stabilize the government and quell ongoing rebellions.
Financial Pressures on Mexico
Following the Mexican-American War, Mexico faced significant economic challenges. The war had drained the country’s resources, disrupted trade, and left Mexico deeply in debt.
The government struggled to maintain its finances and fund essential services. This financial instability made Mexico vulnerable and susceptible to external pressures.
Santa Anna saw the sale of the territory as a way to alleviate Mexico’s financial woes. The $10 million from the U.S. provided much-needed revenue for his government.
However, this decision was controversial and faced opposition from those who believed that selling Mexican land to the United States was a betrayal of national interests.
- Economic Hardship: The Mexican-American War (1846-1848) left Mexico financially devastated.
- Political Instability: Internal rebellions and political strife weakened the government’s control.
- Need for Revenue: Santa Anna sought funds to rebuild the army and maintain power.
4. What Were the Terms of the Gadsden Purchase?
The Gadsden Purchase stipulated that the United States would pay Mexico $10 million for 29,670 square miles of land. Additionally, the U.S. was released from certain financial obligations related to Native American attacks, and discussions were held regarding American claims against Mexico.
Key Provisions of the Treaty
The treaty outlining the Gadsden Purchase contained several key provisions:
- Land Acquisition: The United States acquired approximately 29,670 square miles of land from Mexico, encompassing parts of present-day Arizona and New Mexico.
- Payment: The United States agreed to pay Mexico $10 million for the land.
- Release of Obligations: The treaty included a provision releasing the U.S. from certain financial obligations related to Native American attacks along the border.
- American Claims: The treaty addressed American claims against Mexico, including those related to the Garay deal, a failed attempt to build a transcontinental railroad across the Isthmus of Tehuantepec.
- Border Security: The United States committed to preventing American raids along Mexico’s border.
- Ratification: The treaty required ratification by both the U.S. Senate and the Mexican government.
The terms of the Gadsden Purchase were controversial and subject to debate in both countries. Some in the U.S. felt that the price paid for the land was excessive, while others in Mexico viewed the sale as a national humiliation.
Despite the controversy, the Gadsden Purchase ultimately reshaped the border between the United States and Mexico and had a lasting impact on the history of both countries.
| Provision | Description |
|---|---|
| Land Area Acquired | 29,670 square miles (parts of Arizona and New Mexico) |
| Payment Amount | $10 million |
| Obligations | U.S. released from financial responsibilities related to Native American attacks |
| Border Security | U.S. committed to preventing American raids along Mexico’s border |
| Ratification | Required by both U.S. Senate and Mexican government |
5. How Did the Gadsden Purchase Impact the United States?
The Gadsden Purchase enabled the construction of a southern transcontinental railroad, facilitating trade and westward expansion. It also finalized the southern border of the present-day United States.
Economic and Strategic Benefits for the U.S.
- Transcontinental Railroad: The Gadsden Purchase provided the ideal terrain for building a southern transcontinental railroad. This railroad facilitated trade and transportation, connecting the East and West coasts of the United States.
- Economic Growth: The railroad spurred economic growth in the Southwest, leading to the development of towns, industries, and agriculture.
- Territorial Expansion: The Gadsden Purchase added valuable territory to the United States, expanding its borders and resources.
- Strategic Importance: The acquired land held strategic importance, providing access to valuable resources and strengthening the U.S.’s position in the region.
The construction of the southern transcontinental railroad had a transformative impact on the United States. It facilitated the movement of goods and people across the country, contributing to economic growth and national integration.
The Gadsden Purchase also had significant implications for the Native American populations living in the acquired territory. The expansion of the United States into this region led to increased conflict and displacement of Native American tribes.
While the Gadsden Purchase brought economic and strategic benefits to the United States, it also came at a cost, both in terms of financial investment and the impact on Native American communities.
6. What Were the Consequences of the Gadsden Purchase for Mexico?
The Gadsden Purchase resulted in the loss of significant territory for Mexico, further diminishing its land after the Mexican-American War. It also deepened resentment towards the United States and contributed to ongoing political instability.
Loss of Territory and National Humiliation
- Territorial Loss: The Gadsden Purchase resulted in Mexico losing nearly 30,000 square miles of territory, further diminishing its land after the Mexican-American War.
- Economic Impact: While the $10 million received from the U.S. provided short-term relief, it did not address Mexico’s long-term economic problems.
- Political Instability: The sale of the territory fueled political instability in Mexico, leading to criticism of Santa Anna’s government and contributing to his eventual downfall.
- National Humiliation: Many Mexicans viewed the Gadsden Purchase as a national humiliation, a reminder of their country’s weakness and vulnerability to the United States.
The Gadsden Purchase had a lasting impact on Mexico’s relationship with the United States. It deepened resentment and mistrust between the two countries, contributing to a history of conflict and tension.
The loss of territory also had a significant impact on the people living in the affected region. Many Mexican citizens were forced to choose between becoming U.S. citizens or relocating to Mexico.
The Gadsden Purchase remains a sensitive topic in Mexico, a symbol of the country’s unequal relationship with its powerful neighbor to the north.
7. How Did the Gadsden Purchase Affect Native American Tribes?
The Gadsden Purchase significantly impacted Native American tribes living in the region, leading to further displacement, loss of land, and increased conflicts with the U.S. government and settlers.
Displacement and Loss of Land
- Displacement: The Gadsden Purchase led to the displacement of numerous Native American tribes, including the Apaches and the Tohono O’odham.
- Loss of Land: Native American tribes lost significant portions of their ancestral lands, disrupting their traditional way of life and livelihoods.
- Increased Conflicts: The influx of American settlers and the expansion of U.S. military presence led to increased conflicts between Native Americans and the U.S. government.
- Broken Treaties: The Gadsden Purchase often resulted in the violation of existing treaties between the U.S. government and Native American tribes.
The impact of the Gadsden Purchase on Native American tribes was devastating. They faced displacement, loss of land, and increased violence and oppression.
The U.S. government often disregarded the rights and interests of Native Americans in the region, prioritizing westward expansion and economic development.
The legacy of the Gadsden Purchase continues to affect Native American communities in the Southwest today. Many tribes are still fighting to reclaim their ancestral lands and protect their cultural heritage.
8. What Was the Controversy Surrounding the Gadsden Purchase?
The Gadsden Purchase was controversial due to disagreements over the price, the perceived legitimacy of the sale, and the ethical implications of exploiting Mexico’s weakened state.
Ethical and Political Disagreements
- Price Disagreement: Some in the U.S. believed that the $10 million paid for the land was excessive, while others felt it was a fair price for the strategic and economic benefits it provided.
- Legitimacy of the Sale: The sale was questioned by some in Mexico, who viewed it as an illegitimate transaction forced upon a weakened nation.
- Ethical Concerns: The purchase raised ethical concerns about the U.S. exploiting Mexico’s vulnerable state for its own gain.
- Sectional Tensions: In the United States, the Gadsden Purchase fueled sectional tensions between the North and the South. Some Northerners feared that the acquisition of new territory would lead to the expansion of slavery.
The controversy surrounding the Gadsden Purchase reflected the complex political and ethical issues of the time. It highlighted the tensions between westward expansion, national interests, and the rights of other nations and peoples.
The Gadsden Purchase remains a subject of debate and interpretation today. Some view it as a pragmatic land deal that benefited the United States, while others see it as an example of American imperialism and exploitation.
9. How Did the Gadsden Purchase Shape the U.S.-Mexico Border?
The Gadsden Purchase finalized the southern border of the contiguous United States, establishing the boundary line between the U.S. and Mexico in the Southwest.
Establishing the Modern Border
- Finalization of the Border: The Gadsden Purchase established the modern border between the United States and Mexico in the Southwest, defining the boundary line between the two countries.
- Impact on Border Communities: The new border divided communities and families, creating unique challenges for those living in the region.
- Ongoing Border Issues: The Gadsden Purchase did not resolve all border issues between the U.S. and Mexico. Disputes over water rights, immigration, and drug trafficking continue to plague the border region.
- Cultural Exchange: Despite the challenges, the border region has also become a site of vibrant cultural exchange, with a blend of Mexican and American traditions.
The Gadsden Purchase had a profound and lasting impact on the U.S.-Mexico border. It shaped the physical landscape, the demographics of the region, and the relationship between the two countries.
The border established by the Gadsden Purchase remains a complex and contested space, a site of both conflict and cooperation.
10. What Is the Legacy of the Gadsden Purchase Today?
The legacy of the Gadsden Purchase continues to be felt today, influencing U.S.-Mexico relations, border issues, and the cultural landscape of the Southwestern United States.
Enduring Impact on U.S.-Mexico Relations
- Lingering Resentment: The Gadsden Purchase continues to be a source of resentment in Mexico, a reminder of past territorial losses and perceived injustices.
- Border Security Concerns: The border established by the Gadsden Purchase remains a focus of border security concerns, including immigration, drug trafficking, and cross-border crime.
- Economic Ties: Despite the challenges, the U.S. and Mexico have strong economic ties, with significant trade and investment between the two countries.
- Cultural Intermingling: The border region is characterized by a rich cultural intermingling, with a blend of Mexican and American traditions.
The legacy of the Gadsden Purchase is complex and multifaceted. It is a reminder of the historical tensions between the U.S. and Mexico, but also of the enduring ties that bind the two countries together.
The Gadsden Purchase continues to shape the political, economic, and cultural landscape of the Southwestern United States and the relationship between the U.S. and Mexico.
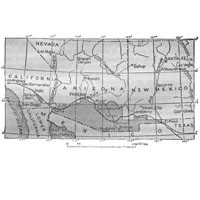 Map Depicting the Gadsden Purchase
Map Depicting the Gadsden Purchase
A historical map illustrating the boundaries defined by the Gadsden Purchase in 1853, showcasing the land acquired by the United States from Mexico which later became part of Arizona and New Mexico, crucial for facilitating the construction of the southern transcontinental railroad.
 Mexican President Antonio de Santa Anna
Mexican President Antonio de Santa Anna
A historical portrait of Antonio López de Santa Anna, the President of Mexico during the Gadsden Purchase, who negotiated the sale of Mexican territory to the United States in 1853 amidst financial instability and internal conflicts.
These complexities underscore the importance of understanding the historical context when discussing LGBTQ+ perspectives within Mexican history, as explored on gaymexico.net.
FAQ about the Gadsden Purchase
-
What were the main reasons behind the Gadsden Purchase?
The Gadsden Purchase was primarily driven by the United States’ need for land to build a southern transcontinental railroad and to resolve lingering border disputes with Mexico after the Mexican-American War.
-
How much land did the U.S. acquire in the Gadsden Purchase?
The U.S. acquired approximately 29,670 square miles of land from Mexico, which later became parts of present-day Arizona and New Mexico.
-
Who were the key figures involved in negotiating the Gadsden Purchase?
Key figures included James Gadsden, the U.S. Minister to Mexico, and Antonio López de Santa Anna, the President of Mexico. President Franklin Pierce of the United States also played a crucial role.
-
Why was Mexico willing to sell territory to the United States?
Mexico was facing severe financial difficulties and internal political instability. President Santa Anna needed funds to stabilize the government and quell ongoing rebellions, making the sale of land a viable option.
-
What were the main terms of the Gadsden Purchase agreement?
The United States agreed to pay Mexico $10 million for the land. Additionally, the U.S. was released from certain financial obligations related to Native American attacks.
-
How did the Gadsden Purchase affect the border between the U.S. and Mexico?
The Gadsden Purchase finalized the southern border of the contiguous United States, establishing the boundary line between the U.S. and Mexico in the Southwest.
-
What impact did the Gadsden Purchase have on Native American tribes in the region?
The Gadsden Purchase led to further displacement, loss of land, and increased conflicts for Native American tribes living in the region, as their ancestral lands were disrupted.
-
What were some of the controversies surrounding the Gadsden Purchase?
The Gadsden Purchase was controversial due to disagreements over the price, the perceived legitimacy of the sale, and the ethical implications of exploiting Mexico’s weakened state.
-
How did the Gadsden Purchase influence the construction of railroads in the U.S.?
The Gadsden Purchase provided the necessary land for the construction of a southern transcontinental railroad, facilitating trade and westward expansion in the United States.
-
What is the lasting legacy of the Gadsden Purchase today?
The legacy of the Gadsden Purchase continues to influence U.S.-Mexico relations, border issues, and the cultural landscape of the Southwestern United States, shaping political and cultural dynamics.
Explore LGBTQ+ Mexico with Gaymexico.net
Discover the vibrant LGBTQ+ scene in Mexico with gaymexico.net. Plan your trip with our comprehensive guides to the most welcoming destinations, find LGBTQ+ friendly venues, and connect with the local community. Visit gaymexico.net for the latest information and resources.
Ready to experience the best of LGBTQ+ Mexico? Explore our travel guides, event listings, and community resources at gaymexico.net today! Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States. Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177. Website: gaymexico.net.
