The Gulf of Mexico is a vital body of water bordering the southeastern coast of North America, offering numerous opportunities for LGBTQ+ travelers, and gaymexico.net is your ultimate guide to exploring its wonders. This article will dive into its location, significance, and how you can make the most of your visit, focusing on LGBTQ+ friendly destinations. Ready to explore this gem of North America? Let’s dive in.
1. What Is The Geographical Location Of The Gulf Of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is situated on the southeastern periphery of the North American continent. It is connected to the Atlantic Ocean through the Straits of Florida, which lie between Florida and Cuba, and to the Caribbean Sea via the Yucatán Channel, positioned between the Yucatán Peninsula and Cuba. These connections make it a significant body of water for trade, tourism, and ecological balance.
1.1 Borders And Boundaries
The Gulf of Mexico is bordered by the United States to the northwest, north, and northeast, and by Mexico to the west, south, and southeast. This strategic location makes it a hub for diverse cultures and economies. According to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the Gulf spans approximately 600,000 square miles, making it a substantial body of water with varied ecosystems.
1.2 Key Geographical Features
The Gulf’s geographical features include the continental shelf, coastal zones, and the abyssal plain. The continental shelf varies in width, extending up to 200 miles in some areas. Coastal zones feature tidal marshes, sandy beaches, and mangrove-covered regions. The abyssal plain, the deepest part of the Gulf, reaches depths of over 17,000 feet at the Sigsbee Deep.
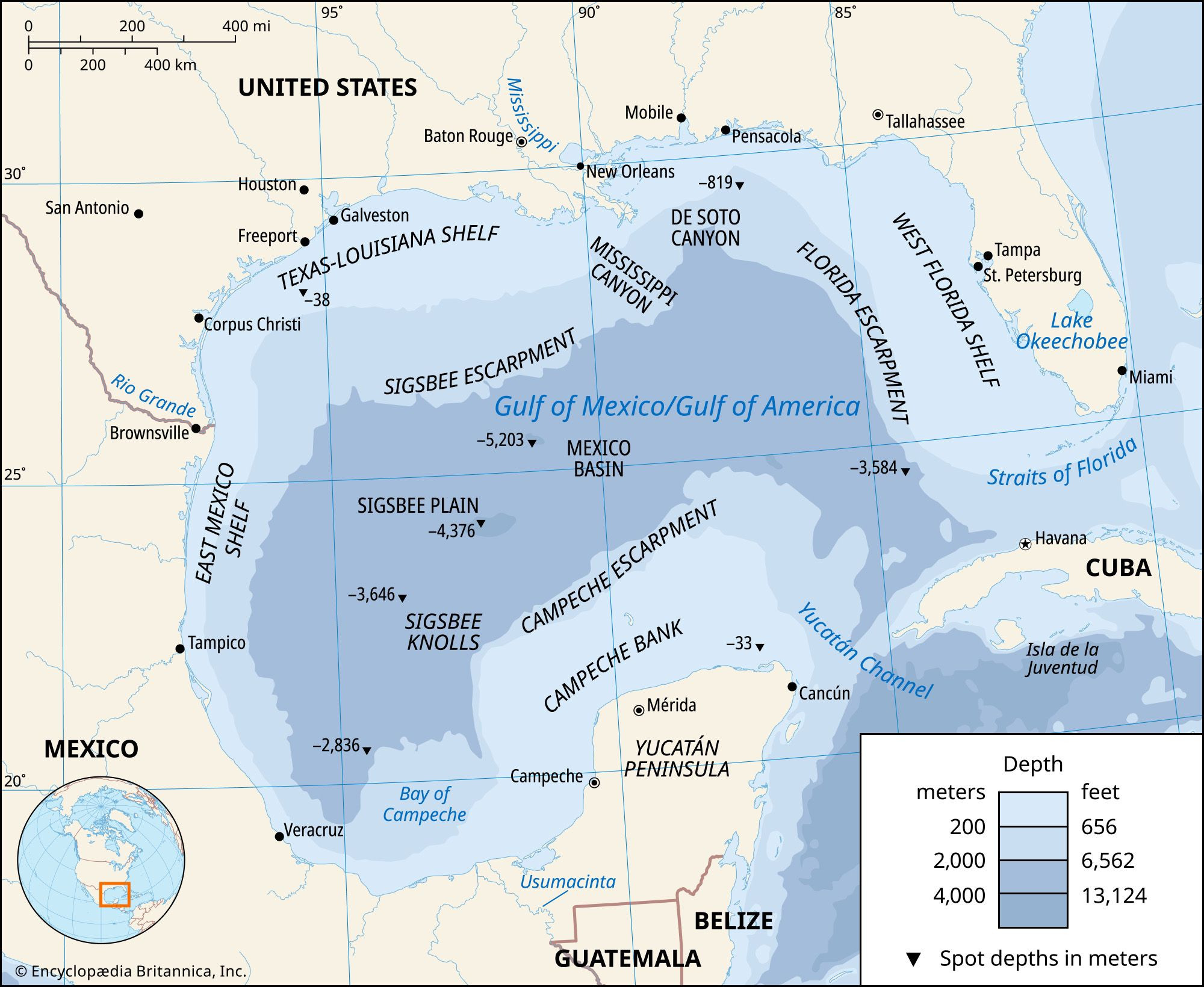 Map of the Gulf of Mexico and surrounding areas
Map of the Gulf of Mexico and surrounding areas
This image depicts the Gulf of Mexico’s location, nestled between North America and the Caribbean, showcasing its connection to the Atlantic Ocean.
1.3 Importance Of Its Location
The Gulf of Mexico’s location is crucial for several reasons. It supports extensive marine biodiversity, facilitates international trade, and plays a significant role in weather patterns. Its location also makes it a prime destination for tourism, particularly for those interested in beach vacations, fishing, and exploring diverse cultures.
2. What Is The Geological Composition Of The Gulf Of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is composed of diverse geological features, including coastal zones, continental shelves, slopes, and abyssal plains. These components contribute to the region’s ecological and economic significance.
2.1 Coastal Zone
The coastal zone features tidal marshes, sandy beaches, and mangrove-covered areas. These zones are vital habitats for numerous species and serve as natural buffers against storms. Estuaries and lagoons also dot the coastline, providing breeding grounds for marine life.
2.2 Continental Shelf
The continental shelf is a continuous terrace around the Gulf, varying in width from 25 to over 200 miles. It primarily consists of carbonate material off Florida and the Yucatán Peninsula, while other areas are composed of sand, silt, and clay sediments. This shelf is crucial for supporting marine ecosystems and fisheries.
2.3 Continental Slope
The continental slope dips downward from the shelf to the abyssal plain. Buried salt domes, associated with significant deposits of oil and natural gas, are found on the shelf and slope. These resources contribute significantly to the region’s economy.
2.4 Abyssal Plain
The abyssal plain forms the floor of the Gulf, characterized by its flatness and a gentle gradient. The deepest point, Sigsbee Deep, is 17,070 feet below sea level. Rising from the plain are the Sigsbee Knolls, surface expressions of buried salt domes.
2.5 Impact On The Ecosystem
The geological composition profoundly impacts the Gulf’s ecosystem. Salt domes influence marine habitats, while the varied sediments support diverse benthic communities. Understanding these geological features is essential for managing and conserving the Gulf’s natural resources.
3. How Does The Hydrology Of The Gulf Of Mexico Work?
The hydrology of the Gulf of Mexico is characterized by a complex system of currents, salinity variations, and temperature gradients that influence its marine environment.
3.1 Major Currents
The Gulf is traversed by currents that contribute to the North Atlantic Gulf Stream. Water enters through the Yucatán Channel and flows clockwise, exiting via the Straits of Florida. Loop currents, meandering masses of water, break off from the main stream, affecting the northeastern part of the Gulf.
3.2 Salinity Levels
The salinity of the Gulf varies, with open waters comparable to the North Atlantic at about 36 parts per thousand. However, coastal waters, particularly near the Mississippi River delta, experience significant fluctuations. During peak flow, salinity can drop to 14-20 parts per thousand up to 30 miles offshore.
3.3 Temperature Variations
Sea surface temperatures in February range from 64°F (18°C) in the northern Gulf to 76°F (24°C) off the Yucatán coast. Summer temperatures can reach 90°F (32°C). Bottom-water temperatures near the Yucatán Channel can be as low as 43°F (6°C).
3.4 Tidal Range
The tidal range in the Gulf is generally small, averaging less than two feet. Diurnal tides, with one high and one low water period each day, are the norm.
3.5 Hydrological Impact On Marine Life
These hydrological factors significantly influence marine life. Current patterns affect nutrient distribution, salinity levels impact species distribution, and temperature variations dictate breeding seasons and migration patterns. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for conservation efforts.
4. What Kind Of Climate Does The Gulf Of Mexico Have?
The Gulf of Mexico experiences a climate that ranges from tropical to subtropical, characterized by warm temperatures and significant humidity. The region is also prone to hurricanes, which can have devastating impacts.
4.1 Temperature And Humidity
The Gulf region generally enjoys warm temperatures throughout the year. Summers are hot and humid, with average temperatures hovering around 90°F (32°C). Winters are mild, with temperatures rarely dropping below 60°F (15°C). Humidity levels are consistently high, contributing to the tropical feel of the area.
4.2 Hurricane Season
The hurricane season officially runs from June 1 to November 30. During this period, meteorological and oceanographic conditions are conducive to the formation and intensification of hurricanes. The Gulf has been hit by numerous devastating hurricanes, including the Galveston hurricane of 1900 and Hurricane Katrina in 2005.
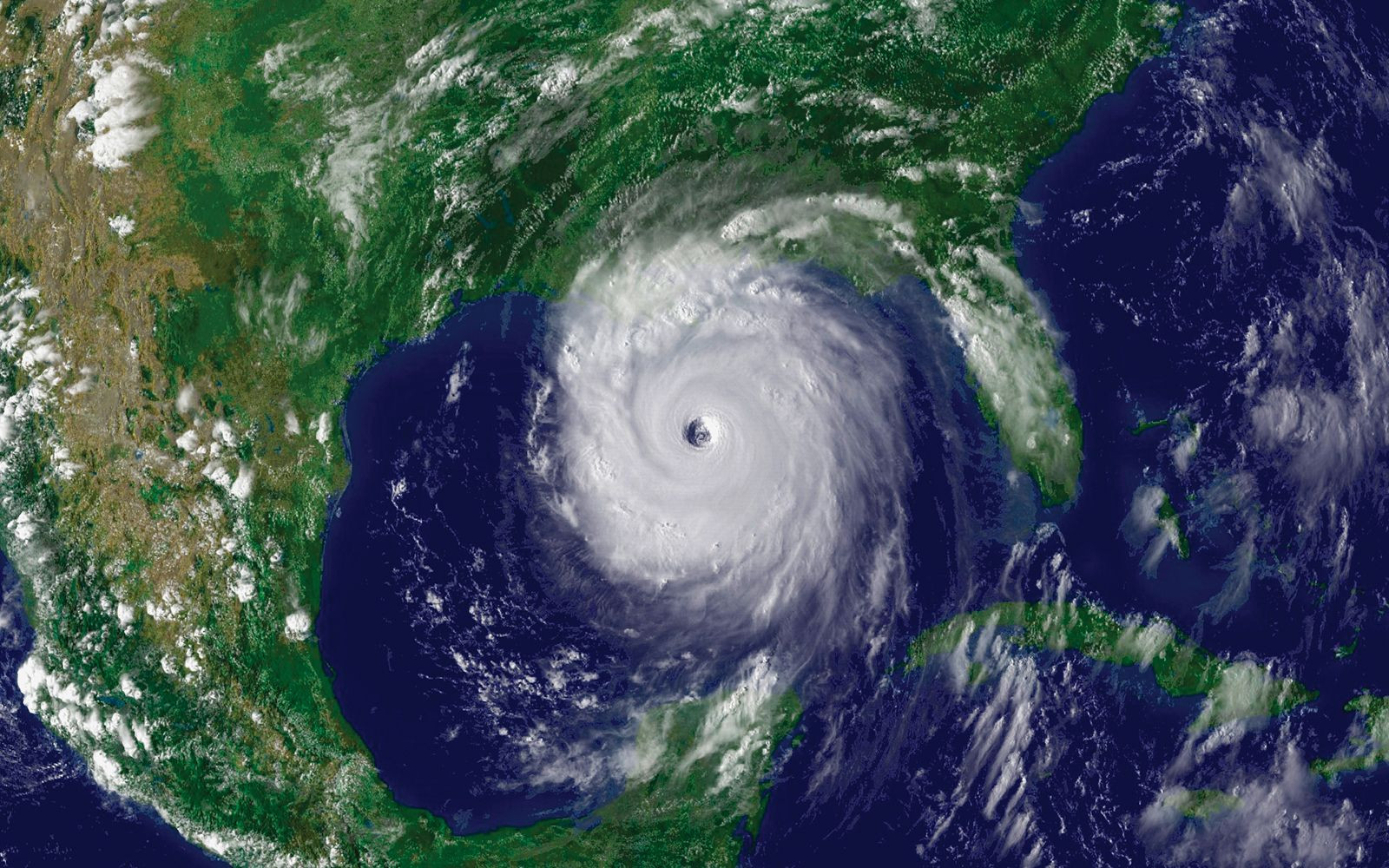 Satellite image of Hurricane Katrina
Satellite image of Hurricane Katrina
This image captures Hurricane Katrina from space, illustrating the power of these storms and their potential impact on the Gulf region.
4.3 Rainfall Patterns
Rainfall is abundant in the Gulf region, particularly during the summer months. Thunderstorms are common, and tropical storms can bring torrential rain and flooding. The average annual rainfall ranges from 40 to 60 inches, depending on the specific location.
4.4 Impact Of Climate On Tourism
The climate significantly impacts tourism. The warm temperatures and sunny skies attract visitors year-round, but the threat of hurricanes necessitates careful planning. Many tourists visit during the spring and fall to avoid the peak of hurricane season while still enjoying pleasant weather.
5. What Types Of Plants And Animals Live In The Gulf Of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is home to a rich variety of plant and animal life, supported by its diverse habitats ranging from coastal wetlands to deep-sea environments.
5.1 Plant Life
Coastal areas are characterized by mangroves, seagrass beds, and marsh grasses. Mangroves provide crucial habitat for many species and protect coastlines from erosion. Seagrass beds serve as nurseries for fish and other marine life. Marsh grasses help filter pollutants and stabilize sediments.
5.2 Fish Species
The Gulf is teeming with fish, including commercially important species like red snapper, grouper, and tuna. Other common fish include flounder, mullet, and various reef fish. The abundance of fish supports a thriving fishing industry and recreational angling.
5.3 Marine Mammals
While marine mammals are not as abundant as fish, the Gulf is home to dolphins, whales, and the endangered Caribbean manatee. Dolphins are frequently seen along the coast, while whales migrate through the Gulf during certain times of the year. Conservation efforts are in place to protect the manatee population.
5.4 Birdlife
The shores of the Gulf are a major habitat for waterfowl and shorebirds. Substantial colonies of noddies, boobies, pelicans, and other seabirds winter along the coasts of Mexico and Cuba, as well as on offshore islands.
5.5 Invertebrates
The Gulf is home to a wide range of invertebrates, including shrimp, crabs, oysters, and various species of coral. Shrimp and crabs are commercially important, while oysters play a crucial role in filtering water and creating habitat. Coral reefs provide shelter and food for numerous marine species.
5.6 Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts are essential to protect the Gulf’s biodiversity. These include habitat restoration, pollution control, and sustainable fishing practices. Organizations like the Gulf of Mexico Alliance work to address environmental issues and promote responsible stewardship of the region’s resources.
6. What Mineral Resources Are Found In The Gulf Of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is rich in mineral resources, including petroleum, natural gas, and sulfur. These resources contribute significantly to the region’s economy but also pose environmental challenges.
6.1 Petroleum And Natural Gas
The Gulf contains large deposits of petroleum and natural gas, primarily associated with buried salt domes on the continental shelf and slope. These resources are extracted through offshore drilling, providing a significant portion of the United States’ energy supply.
6.2 Sulfur
Sulfur is extracted from wells drilled on the continental shelf off Louisiana. This sulfur is used in various industrial processes, including the production of sulfuric acid and fertilizers.
6.3 Oyster Shells
Oyster shells are obtained from shallow waters and used in the chemical industry as a source of calcium carbonate. They also provide material for building roads.
6.4 Environmental Impact
The extraction of mineral resources can have significant environmental impacts, including oil spills, habitat destruction, and pollution. The Deepwater Horizon oil spill in 2010 highlighted the risks associated with offshore drilling.
6.5 Sustainable Practices
Efforts are being made to promote sustainable practices in the extraction of mineral resources. These include implementing stricter safety regulations, investing in spill prevention technologies, and restoring damaged habitats.
7. How Did European Exploration Impact The Gulf Of Mexico?
European exploration significantly impacted the Gulf of Mexico, bringing about cultural, economic, and environmental changes.
7.1 Early Exploration
After Christopher Columbus first made contact with the region in 1492, waves of Spanish explorers entered the Gulf and penetrated into the North American interior. By 1600, the major physical features had been discovered, and a system of towns, silver mines, and missions had been established around the Gulf shore.
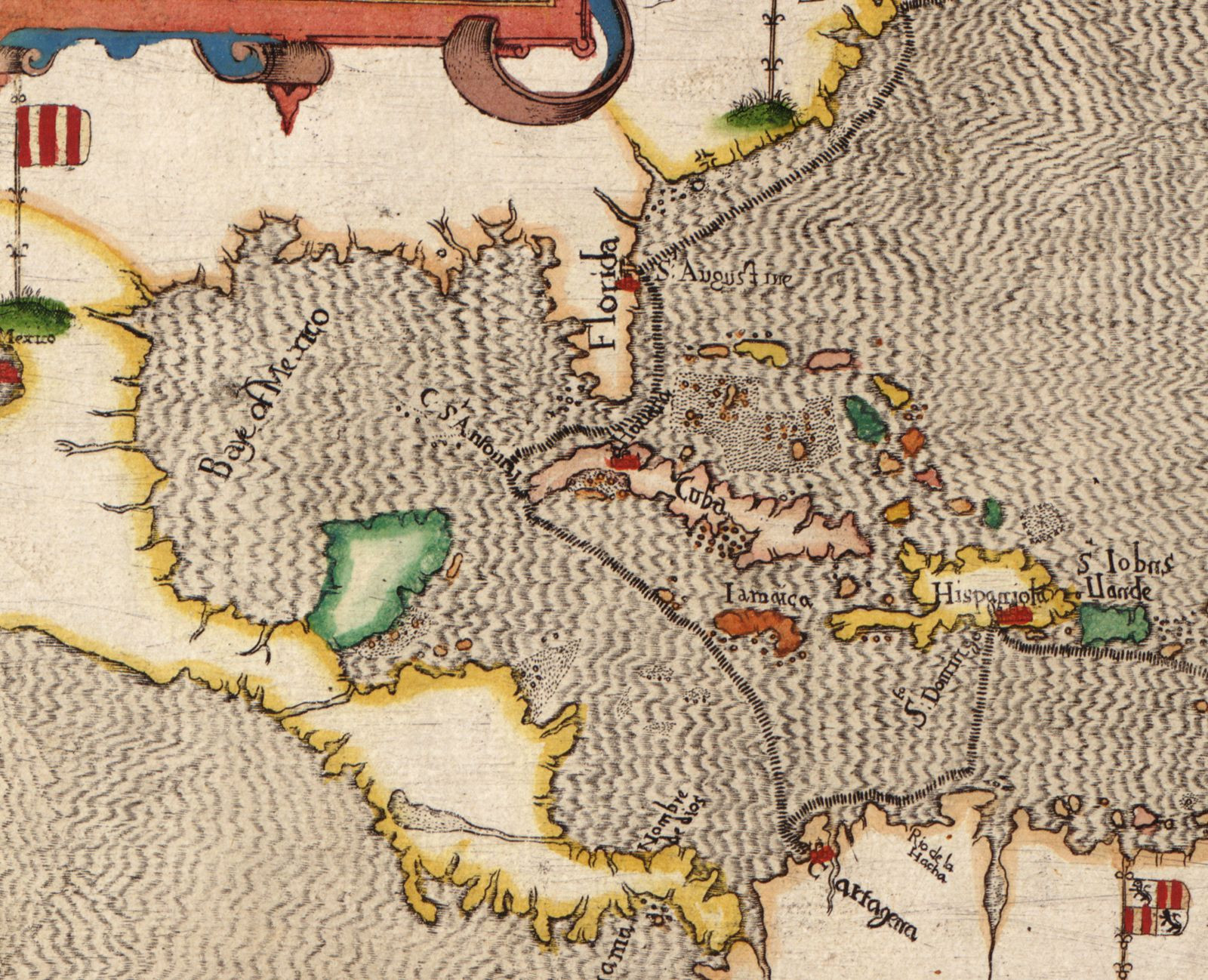 Historical map of the Gulf of Mexico
Historical map of the Gulf of Mexico
This map offers a glimpse into how the Gulf of Mexico was perceived during the age of exploration, highlighting its strategic importance to European powers.
7.2 Cultural Exchange
European exploration led to cultural exchange between Europeans and Native Americans. This exchange included the introduction of new technologies, crops, and livestock. However, it also resulted in the spread of diseases that devastated Native American populations.
7.3 Economic Development
The discovery of mineral resources, such as silver and gold, spurred economic development in the Gulf region. European powers established trade routes and exploited natural resources, transforming the region’s economy.
7.4 Environmental Changes
European exploration brought about significant environmental changes. Deforestation, overfishing, and the introduction of invasive species altered the Gulf’s ecosystems.
7.5 Legacy Of Exploration
The legacy of European exploration continues to shape the Gulf of Mexico today. The region’s cultural diversity, economic structure, and environmental challenges are all influenced by this historical period.
8. What Are The Major Ports And Cities Around The Gulf Of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is surrounded by several major ports and cities that play a crucial role in trade, tourism, and economic development.
8.1 New Orleans, Louisiana
New Orleans is a major port city located on the Mississippi River near the Gulf of Mexico. It is a hub for trade, tourism, and culture. The city’s port handles a large volume of cargo, including agricultural products, chemicals, and manufactured goods.
8.2 Houston, Texas
Houston is a major industrial and shipping center located near Galveston Bay. The Port of Houston is one of the busiest in the United States, handling a large volume of petroleum, petrochemicals, and other goods.
8.3 Tampa, Florida
Tampa is a major port city located on the west coast of Florida. It is a hub for trade, tourism, and finance. The Port of Tampa handles a variety of cargo, including phosphate, petroleum, and citrus products.
8.4 Mobile, Alabama
Mobile is a historic port city located on Mobile Bay. It is a hub for shipbuilding, trade, and manufacturing. The Port of Mobile handles a variety of cargo, including coal, steel, and forest products.
8.5 Veracruz, Mexico
Veracruz is a major port city located on the Gulf Coast of Mexico. It is a hub for trade, tourism, and industry. The Port of Veracruz handles a variety of cargo, including petroleum, automobiles, and agricultural products.
8.6 Impact On The Economy
These ports and cities significantly impact the economy of the Gulf region. They facilitate trade, create jobs, and attract investment. They also serve as gateways for tourism, bringing visitors and revenue to the area.
9. What Are The Environmental Concerns Affecting The Gulf Of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico faces numerous environmental concerns, including pollution, habitat loss, and climate change.
9.1 Pollution
Pollution is a major threat to the Gulf’s ecosystem. Sources of pollution include oil spills, industrial discharges, agricultural runoff, and plastic waste. These pollutants can harm marine life, contaminate seafood, and degrade water quality.
9.2 Habitat Loss
Habitat loss is another significant concern. Coastal development, dredging, and destructive fishing practices have destroyed or degraded vital habitats such as mangroves, seagrass beds, and coral reefs.
9.3 Climate Change
Climate change is exacerbating many of the Gulf’s environmental problems. Rising sea levels, ocean acidification, and warmer water temperatures are threatening marine life and coastal communities.
9.4 Dead Zones
Dead zones, areas of low oxygen, are a recurring problem in the Gulf. These zones are caused by nutrient pollution from agricultural runoff, which leads to algal blooms and oxygen depletion.
9.5 Conservation Efforts
Numerous organizations are working to address these environmental concerns. These efforts include habitat restoration, pollution control, and sustainable resource management. The Gulf of Mexico Alliance is a regional partnership that promotes collaboration among states, federal agencies, and other stakeholders.
10. What Opportunities Does The Gulf Of Mexico Offer For LGBTQ+ Travelers?
The Gulf of Mexico offers diverse opportunities for LGBTQ+ travelers, ranging from vibrant city life to relaxing beach getaways. At gaymexico.net, we strive to provide inclusive and up-to-date information for the LGBTQ+ community.
10.1 LGBTQ+ Friendly Destinations
Several cities and towns along the Gulf Coast are known for their LGBTQ+ friendly atmosphere. These destinations offer a welcoming environment, gay-friendly accommodations, and thriving LGBTQ+ scenes.
10.2 Key LGBTQ+ Destinations in Mexico
- Puerto Vallarta: Renowned for its vibrant gay scene with numerous gay bars, clubs, and beaches.
- Mexico City: Offers a diverse cultural experience with a lively LGBTQ+ community.
- Cancun: Known for its beautiful beaches and gay-friendly resorts.
10.3 Activities And Attractions
LGBTQ+ travelers can enjoy a variety of activities and attractions in the Gulf region. These include beach vacations, water sports, cultural events, and nightlife. Many destinations offer LGBTQ+ specific events and festivals.
10.4 Safety And Inclusion
While the Gulf region is generally welcoming, LGBTQ+ travelers should be aware of local laws and customs. Researching destinations and seeking advice from LGBTQ+ travel resources can help ensure a safe and enjoyable trip.
10.5 Resources For LGBTQ+ Travelers
Gaymexico.net provides resources and information for LGBTQ+ travelers planning a trip to the Gulf of Mexico. Our website offers guides to LGBTQ+ friendly destinations, event listings, and travel tips. We also highlight accommodations and businesses that support the LGBTQ+ community.
A vibrant image of a Pride parade in Mexico City, symbolizing the inclusivity and support for the LGBTQ+ community in this region.
10.6 Connecting With The Community
Gaymexico.net also provides opportunities for LGBTQ+ travelers to connect with the local community. We feature profiles of LGBTQ+ organizations and businesses, as well as forums for travelers to share their experiences and tips.
By utilizing gaymexico.net, LGBTQ+ travelers can confidently explore the wonders of the Gulf of Mexico, knowing they have access to reliable and inclusive information.
FAQ: Your Questions About The Gulf Of Mexico Answered
1. Where exactly is the Gulf of Mexico located?
The Gulf of Mexico is located on the southeastern edge of North America, bordered by the United States and Mexico, connected to the Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea.
2. How deep is the deepest part of the Gulf of Mexico?
The deepest point in the Gulf of Mexico is the Sigsbee Deep, which reaches a depth of 17,070 feet (5,203 meters).
3. What are some major cities located on the Gulf of Mexico?
Major cities include New Orleans, Houston, Tampa, Mobile, and Veracruz, all playing key roles in trade and tourism.
4. What kind of climate does the Gulf of Mexico region have?
The climate ranges from tropical to subtropical, characterized by warm temperatures, high humidity, and a hurricane season from June to November.
5. What are some popular activities for LGBTQ+ travelers in the Gulf of Mexico?
Popular activities include visiting LGBTQ+ friendly beaches, bars, clubs, and participating in cultural events and festivals, especially in cities like Puerto Vallarta and Mexico City.
6. What mineral resources can be found in the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf contains significant deposits of petroleum, natural gas, and sulfur, contributing substantially to the regional economy.
7. How did European exploration impact the Gulf of Mexico region?
European exploration led to cultural exchange, economic development through resource extraction, and environmental changes such as deforestation and the introduction of invasive species.
8. What are some environmental concerns affecting the Gulf of Mexico today?
Major concerns include pollution from oil spills and agricultural runoff, habitat loss, climate change, and the occurrence of dead zones due to nutrient pollution.
9. How can LGBTQ+ travelers find safe and welcoming places in the Gulf of Mexico?
LGBTQ+ travelers can use resources like gaymexico.net to find gay-friendly accommodations, events, and destinations, ensuring a safe and enjoyable travel experience.
10. What is the role of the Gulf of Mexico in the broader ocean ecosystem?
The Gulf serves as a crucial habitat for diverse marine life, influences regional weather patterns, and connects the Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea, making it vital for global marine biodiversity.
The Gulf of Mexico is a treasure trove of natural beauty, economic opportunity, and cultural diversity, especially for the LGBTQ+ community. Whether you’re looking to explore its vibrant cities, relax on its stunning beaches, or connect with the local LGBTQ+ community, gaymexico.net is here to guide you every step of the way.
Ready to start your adventure? Visit gaymexico.net today to discover LGBTQ+ friendly destinations, events, and resources in the Gulf of Mexico. Let us help you create unforgettable travel experiences!
Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States
Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177
Website: gaymexico.net
