What Percentage Of Produce Comes From Mexico? Gaymexico.net knows that for LGBTQ+ travelers and Mexican diaspora, this is more than a simple question; it’s about understanding cultural connections and supporting communities. Mexico is a major source of fresh produce for the United States, ensuring the availability of diverse fruits and vegetables year-round. By understanding these dynamics, we can appreciate the vital role Mexico plays in the U.S. food supply chain. For reliable resources and support in Mexico, explore LGBTQ+ travel, culture, and community with gaymexico.net.
1. What Percentage of U.S. Vegetable Imports Come From Mexico?
Mexico supplies a significant portion of U.S. vegetable imports; in 2023, 63% of U.S. vegetable imports came from Mexico. This high percentage underscores Mexico’s importance as a key source for fresh vegetables in the United States, with many U.S. consumers relying on the availability of Mexican produce throughout the year. The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) provides detailed data on agricultural trade, affirming Mexico’s leading role in supplying the U.S. market with vegetables. This close trade relationship is crucial for both countries, supporting agricultural jobs and ensuring a consistent supply of fresh produce.
2. What Percentage of U.S. Fruit and Nut Imports Come From Mexico?
Nearly half of U.S. fruit and nut imports come from Mexico, with 47% of these imports originating from Mexico in 2023. This substantial percentage reflects the diversity of agricultural products Mexico exports, including fruits like avocados, berries, and mangoes, as well as nuts. Data from the USDA confirms this significant contribution, highlighting the strong agricultural trade relationship between Mexico and the United States. This partnership benefits consumers by providing a wider variety of fresh produce options and supports the agricultural sectors in both countries.
3. How Has the Volume of U.S. Horticultural Imports From Mexico Changed Over Time?
The volume of U.S. horticultural imports from Mexico has increased dramatically from 2000 to 2023. Annual U.S. horticultural imports from Mexico have risen more than fourfold, from $3.9 billion to $19.7 billion (inflation adjusted to 2023 dollars). This impressive growth, corresponding to a compound annual growth rate of 7.3 percent, demonstrates the increasing demand for Mexican produce in the United States. USDA statistics highlight this trend, emphasizing the strengthening trade ties between the two countries and the growing importance of Mexican agriculture in meeting U.S. consumer needs.
4. Why Is Mexico Such a Significant Source of Produce for the U.S.?
Mexico is a significant source of produce for the U.S. due to several factors, including its favorable climate, proximity, and established trade relationships. Mexico’s diverse climate allows for year-round production of a wide variety of fruits and vegetables, ensuring a consistent supply for the U.S. market. Its close proximity reduces transportation costs and time, making it a cost-effective source compared to more distant countries. Furthermore, long-standing trade agreements and established supply chains facilitate the smooth flow of produce across the border. The USDA Economic Research Service provides insights into these factors, underscoring Mexico’s crucial role in the U.S. food supply.
5. What Regulations Do Mexican Growers Need to Meet to Sell Produce in the U.S.?
Mexican growers must adhere to U.S. regulations, particularly those outlined in the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), to sell produce in the U.S. FSMA, enacted in 2011, aims to ensure the safety of the U.S. food supply chain from production to transportation, regardless of whether it occurs on U.S. or foreign soil. These regulations cover various aspects, including hygiene, sanitation, and traceability, ensuring that produce meets U.S. safety standards. Compliance with FSMA is essential for Mexican growers to maintain access to the U.S. market. The FDA provides comprehensive information on FSMA requirements and compliance procedures.
6. How Has FSMA Impacted Mexico’s Access to the U.S. Horticultural Market?
FSMA does not appear to have disrupted Mexico’s access to the U.S. horticultural market. Instead, it has provided a framework for Mexico’s horticultural sector to address food safety concerns, leading to improved practices and compliance. Following FSMA’s implementation, organizations like SENASICA in Mexico have worked to provide training and outreach to Mexican growers, helping them meet the new requirements. The USDA reports indicate that U.S. horticultural imports from Mexico have continued to grow since FSMA was enacted, suggesting that the law has not hindered trade but rather enhanced the safety and reliability of Mexican produce.
7. What Is SENASICA’s Role in Ensuring the Safety and Competitiveness of Mexico’s Produce Sector?
SENASICA, the governmental entity responsible for food safety in Mexico, plays a crucial role in ensuring both the safety and competitiveness of Mexico’s produce sector. SENASICA works to ensure the sector’s competitiveness as it relates to international trade. Following FSMA’s implementation, organizations within SENASICA worked to provide training and outreach to Mexican growers. Also, the large number of stakeholders were able to share the costs and knowledge of complying with FSMA, across the supply chain and across different crops.
SENASICA’s Key Functions Include:
- Regulatory Oversight: Enforcing food safety standards and regulations to ensure compliance among Mexican growers.
- Training and Outreach: Providing training programs and resources to help growers understand and implement best practices in food safety.
- International Collaboration: Working with international organizations and regulatory bodies to align standards and facilitate trade.
- Certification and Inspection: Conducting inspections and providing certifications to verify that Mexican produce meets U.S. and international safety requirements.
SENASICA’s efforts help maintain the integrity of Mexico’s produce sector, ensuring that it remains a reliable and competitive source for the U.S. market.
8. What Challenges Do Mexican Horticultural Exporters Face Regarding Food Safety?
Mexican horticultural exporters face unique risks related to food safety due to their heavy reliance on the export market. Many of Mexico’s produce companies rely on the export market for most of their earnings, and some supply only the export market. If a producer in Mexico were to sell produce that led to an outbreak of foodborne illness in the United States, all of Mexico’s exporters for that commodity could be affected because of the difficulty in tracking the contamination’s origin.
Key Challenges Include:
- Traceability: Difficulty in tracing the origin of contamination in the event of a foodborne illness outbreak, potentially affecting all exporters of that commodity.
- Compliance Costs: The financial burden of implementing and maintaining food safety programs, including investments in equipment, infrastructure, and training.
- Access to Resources: Ensuring access to accredited laboratories for testing samples and providing adequate training for food safety managers and workers.
Overcoming these challenges is crucial for Mexican exporters to maintain their competitive edge and ensure the continued safety of their produce.
9. How Did Mexican Horticultural Companies Adapt to Meet FSMA’s Requirements?
Mexican horticultural companies adapted to meet FSMA’s requirements by making significant changes to their operations, including investments in new infrastructure and improved monitoring programs.
Adaptations Included:
- Equipment Upgrades: Investing in new equipment to improve hygiene and sanitation.
- Infrastructure Improvements: Building new facilities and upgrading existing ones to meet FSMA standards.
- Monitoring Programs: Implementing enhanced sampling techniques and monitoring programs to ensure a clean water supply throughout the production process.
- Training and Education: Providing training for food safety managers and workers to ensure they are knowledgeable about FSMA requirements and best practices.
These efforts demonstrate the commitment of Mexican horticultural companies to meeting U.S. food safety standards and maintaining access to the U.S. market.
10. How Did the Coronavirus Pandemic Affect Horticultural Exports From Mexico to the U.S.?
Despite the challenges posed by the Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, horticultural exports from Mexico to the U.S. experienced few, if any, major interruptions. This resilience can be attributed to the essential nature of the food supply chain and the efforts made by Mexican growers to comply with food safety standards.
Factors Contributing to Uninterrupted Exports:
- Essential Service Designation: Agriculture and food production were deemed essential services, allowing them to continue operating during lockdowns and restrictions.
- Compliance with FSMA: Mexican growers’ adherence to FSMA standards helped ensure the safety and reliability of their produce, maintaining confidence among U.S. importers.
- Adaptation and Innovation: The sector’s ability to adapt to new challenges and implement innovative solutions to maintain production and supply chains.
This continuity in exports underscores the strength and adaptability of the Mexican horticultural sector in the face of global challenges.
11. What Types of Fruits Are Most Commonly Imported to the U.S. from Mexico?
Several types of fruits are commonly imported to the U.S. from Mexico, reflecting the country’s diverse agricultural production.
Commonly Imported Fruits:
- Avocados: Mexico is the world’s largest producer of avocados, and a significant portion is exported to the U.S.
- Berries: Strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, and blackberries are popular imports, often available year-round.
- Mangoes: Mexico is a major supplier of mangoes to the U.S. market, especially during the off-season for domestic production.
- Tomatoes: While technically a fruit, tomatoes are a significant horticultural import, with Mexico being a major supplier.
These fruits are vital to the U.S. market, providing consumers with a variety of options throughout the year.
12. What Types of Vegetables Are Most Commonly Imported to the U.S. from Mexico?
Many types of vegetables are commonly imported to the U.S. from Mexico, providing a diverse range of options for American consumers.
Commonly Imported Vegetables:
- Tomatoes: Mexico is a major supplier of tomatoes, especially during the winter months when domestic production is limited.
- Peppers: Bell peppers and chili peppers are significant vegetable imports from Mexico.
- Cucumbers: Mexico is a key source of cucumbers for the U.S. market.
- Squash: Various types of squash are imported from Mexico, contributing to the diversity of vegetables available in the U.S.
These vegetables are essential for meeting consumer demand and ensuring a consistent supply throughout the year.
13. What Are the Economic Benefits of U.S. Horticultural Imports From Mexico for Both Countries?
U.S. horticultural imports from Mexico provide significant economic benefits for both countries, fostering trade, supporting jobs, and ensuring a stable food supply.
Economic Benefits for the U.S.:
- Stable Food Supply: Access to a consistent and diverse supply of fresh fruits and vegetables year-round.
- Competitive Pricing: Lower production costs in Mexico can lead to more affordable produce for U.S. consumers.
- Job Creation: The import and distribution of Mexican produce support jobs in the U.S., including transportation, logistics, and retail.
Economic Benefits for Mexico:
- Export Revenue: Horticultural exports are a major source of revenue for Mexico, supporting the country’s economy.
- Job Creation: The agricultural sector provides employment for a significant portion of the Mexican population.
- Economic Growth: Increased trade with the U.S. stimulates economic growth and development in Mexico.
The strong trade relationship between the two countries benefits both economies and ensures a reliable supply of fresh produce for consumers.
14. How Does the Proximity of Mexico to the U.S. Impact the Cost and Freshness of Produce?
The proximity of Mexico to the U.S. significantly impacts the cost and freshness of produce, making it a cost-effective and reliable source.
Impacts of Proximity:
- Reduced Transportation Costs: Shorter transportation distances lower the costs associated with shipping produce to the U.S.
- Faster Delivery Times: Shorter transit times mean that produce arrives in the U.S. more quickly, ensuring greater freshness.
- Lower Spoilage Rates: Reduced transit times also minimize the risk of spoilage during transportation, preserving the quality of the produce.
These factors contribute to the competitiveness of Mexican produce in the U.S. market, providing consumers with fresh, affordable options.
15. What Role Do Trade Agreements Play in Facilitating Horticultural Imports From Mexico to the U.S.?
Trade agreements play a crucial role in facilitating horticultural imports from Mexico to the U.S. by establishing clear rules and reducing trade barriers.
Key Functions of Trade Agreements:
- Reduced Tariffs: Trade agreements often reduce or eliminate tariffs on imported goods, making Mexican produce more competitive in the U.S. market.
- Standardized Regulations: Agreements can help standardize regulations and procedures, streamlining the import process.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanisms: Trade agreements provide mechanisms for resolving trade disputes, ensuring a stable and predictable trading environment.
These factors promote increased trade and investment between the two countries, benefiting both economies.
16. How Do Seasonal Differences Between Mexico and the U.S. Affect Produce Availability?
Seasonal differences between Mexico and the U.S. significantly affect produce availability, allowing for a year-round supply of various fruits and vegetables.
Impact of Seasonal Differences:
- Winter Supply: During the winter months, when domestic production in the U.S. is limited, Mexico provides a crucial source of fresh produce, such as tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers.
- Counter-Seasonal Availability: Mexico’s climate allows for the production of certain fruits and vegetables during the off-season in the U.S., ensuring a consistent supply.
- Year-Round Variety: The combination of domestic production and imports from Mexico ensures that U.S. consumers have access to a wide variety of produce throughout the year.
This complementary relationship between the two countries enhances the availability and diversity of fresh produce for American consumers.
17. What Are Some Examples of Mexican Companies That Export Produce to the U.S.?
Several Mexican companies are prominent exporters of produce to the U.S., contributing to the robust trade relationship between the two countries.
Examples of Exporting Companies:
- Grupo Altex: A major producer and exporter of various fruits and vegetables, including tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers.
- Divemex: Specializes in the production and export of bell peppers and other vegetables.
- Frutas Selectas: Focuses on the export of high-quality fruits, such as avocados and berries.
- Agricola San Isidro: A leading producer and exporter of tomatoes and other vegetables.
These companies play a vital role in supplying the U.S. market with fresh produce and supporting the agricultural sectors in both countries.
18. How Is Technology Being Used to Improve the Safety and Efficiency of Horticultural Exports From Mexico?
Technology plays an increasingly important role in improving the safety and efficiency of horticultural exports from Mexico, enhancing traceability and quality control.
Technological Innovations:
- Traceability Systems: Advanced tracking systems allow for the monitoring of produce from the farm to the consumer, enabling quick identification and response in the event of a food safety issue.
- Precision Agriculture: Technologies such as GPS, sensors, and data analytics are used to optimize farming practices, improving yields and reducing waste.
- Cold Chain Management: Advanced refrigeration and monitoring systems ensure that produce is kept at the optimal temperature during transportation, preserving its quality and freshness.
- Inspection Technologies: Automated inspection systems use cameras and sensors to detect defects and contaminants, improving the safety and quality of exported produce.
These technological advancements contribute to a more efficient and reliable supply chain, benefiting both producers and consumers.
19. What Measures Are Being Taken to Ensure Sustainable Farming Practices in Mexico’s Horticultural Sector?
Measures are being taken to promote sustainable farming practices in Mexico’s horticultural sector, aiming to protect the environment and ensure long-term productivity.
Sustainable Practices:
- Water Conservation: Implementing irrigation technologies and water management practices to reduce water usage and protect water resources.
- Integrated Pest Management: Using biological controls and other methods to minimize the use of chemical pesticides.
- Soil Conservation: Employing techniques such as cover cropping and no-till farming to prevent soil erosion and improve soil health.
- Organic Farming: Encouraging the adoption of organic farming practices to reduce the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
- Certification Programs: Participating in certification programs that promote sustainable farming practices and provide consumers with assurance of environmental stewardship.
These efforts support the long-term sustainability of Mexico’s horticultural sector and contribute to a healthier environment.
20. How Can Consumers Ensure They Are Purchasing Safe and Ethically Sourced Produce From Mexico?
Consumers can ensure they are purchasing safe and ethically sourced produce from Mexico by looking for certifications, understanding labeling, and supporting companies with transparent practices.
Tips for Consumers:
- Look for Certifications: Certifications such as Fair Trade, USDA Organic, and PrimusGFS indicate that produce has been produced according to certain standards for safety, environmental sustainability, and ethical labor practices.
- Read Labels Carefully: Check labels for information about the origin of the produce and any certifications it may have.
- Support Transparent Companies: Choose companies that are transparent about their sourcing practices and committed to ethical and sustainable production.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date on food safety and ethical sourcing issues by consulting reputable sources such as government agencies, consumer organizations, and industry associations.
- Buy Local When Possible: When in season, buying local produce can reduce transportation costs and support local farmers.
By following these tips, consumers can make informed choices that support safe, ethical, and sustainable practices in the horticultural industry.
FAQ: Produce Imports from Mexico
1. What percentage of produce comes from Mexico to the US?
In 2023, Mexico supplied 63% of U.S. vegetable imports and 47% of U.S. fruit and nut imports, making it a major source of produce for the United States.
2. Why does the US import so much produce from Mexico?
The U.S. imports so much produce from Mexico because of Mexico’s favorable climate, proximity, and established trade relationships, allowing for year-round production and cost-effective transportation.
3. Are Mexican fruits and vegetables safe to eat?
Yes, Mexican fruits and vegetables are safe to eat, as Mexican growers must meet U.S. regulations, including those in the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA).
4. How has the volume of U.S. horticultural imports from Mexico changed over time?
From 2000 to 2023, annual U.S. horticultural imports from Mexico have increased more than fourfold, from $3.9 billion to $19.7 billion (inflation adjusted to 2023 dollars).
5. What regulations do Mexican growers need to meet to sell produce in the US?
Mexican growers must adhere to U.S. regulations, particularly those outlined in the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA), to ensure the safety of their produce.
6. How did Mexican horticultural companies adapt to meet FSMA’s requirements?
Mexican horticultural companies adapted by making changes to equipment, investing in new infrastructure, and implementing monitoring programs to meet FSMA’s requirements.
7. What is SENASICA’s role in ensuring the safety and competitiveness of Mexico’s produce sector?
SENASICA, the governmental entity responsible for food safety in Mexico, works to ensure the sector’s competitiveness as it relates to international trade by providing training and regulatory oversight.
8. How did the Coronavirus pandemic affect horticultural exports from Mexico to the US?
Despite the pandemic, horticultural exports from Mexico to the U.S. experienced few major interruptions, thanks to the essential nature of the food supply chain.
9. What types of fruits and vegetables are most commonly imported from Mexico?
Commonly imported fruits include avocados, berries, and mangoes, while vegetables include tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers.
10. How can consumers ensure they are purchasing safe produce from Mexico?
Consumers can look for certifications, read labels carefully, and support companies with transparent practices to ensure they are purchasing safe produce from Mexico.
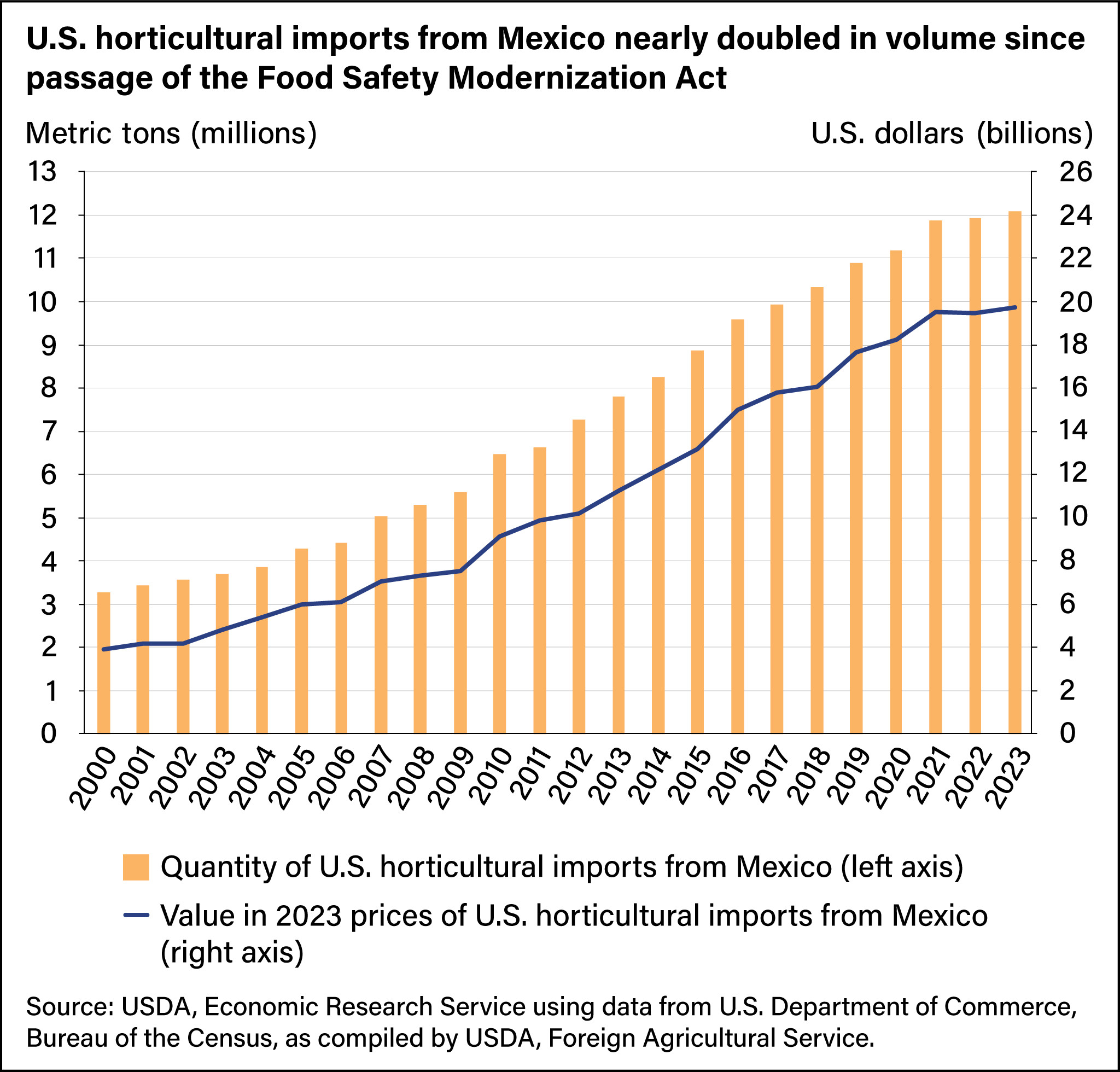 Bar and line chart showing the quantity of U.S. horticultural imports from Mexico and the value in 2023 prices of U.S. horticultural imports from Mexico.
Bar and line chart showing the quantity of U.S. horticultural imports from Mexico and the value in 2023 prices of U.S. horticultural imports from Mexico.
Discover the best of LGBTQ+ travel, culture, and community in Mexico with gaymexico.net. Whether you’re planning a trip or seeking local connections, our comprehensive guides and resources are here to help. Explore top destinations, find LGBTQ+-friendly venues, and stay informed on the latest news and events.
Ready to experience Mexico? Visit gaymexico.net today for everything you need to know, including travel tips, event listings, and community support. Connect with us at Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States. Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177. Let us help you create unforgettable memories in Mexico.
