Navigating the complexities of immigration can be challenging, but at gaymexico.net, we’re here to provide clarity. So, what percentage of illegal immigrants are Mexican? While this number fluctuates, recent data suggests Mexicans no longer constitute the majority. Let’s delve deeper into the trends, factors, and related aspects of Mexican immigration to the U.S., offering resources and support for our LGBTQ+ community and allies interested in understanding these dynamics, remember, at gaymexico.net we are here to support you.
1. Understanding the Demographics of Unauthorized Immigration: An Overview
The demographics of unauthorized immigration in the United States have undergone significant shifts in recent years. Understanding these changes is crucial for informed discussions.
1.1. What Is the Current Percentage of Mexican Unauthorized Immigrants in the U.S.?
Mexicans constituted 47% of the unauthorized immigrant population in the U.S. in 2017, according to Pew Research Center estimates. This marks the first time since the surge in illegal immigration began half a century ago that Mexicans have made up less than half of this population.
1.2. Why Has the Percentage of Mexican Unauthorized Immigrants Changed?
Several factors have contributed to this demographic shift:
- Decreased Arrivals: Fewer Mexicans are arriving in the U.S. without authorization.
- Increased Departures: More Mexicans are leaving the U.S. than arriving.
- Growth from Other Regions: Unauthorized immigration from other regions, such as Asia and Central America, has increased.
1.3. What Were the Peak Numbers of Mexican Unauthorized Immigrants?
In 2007, the number of Mexican unauthorized immigrants in the U.S. peaked at 6.9 million. By 2017, this number had fallen to 4.9 million, a decrease of 2 million.
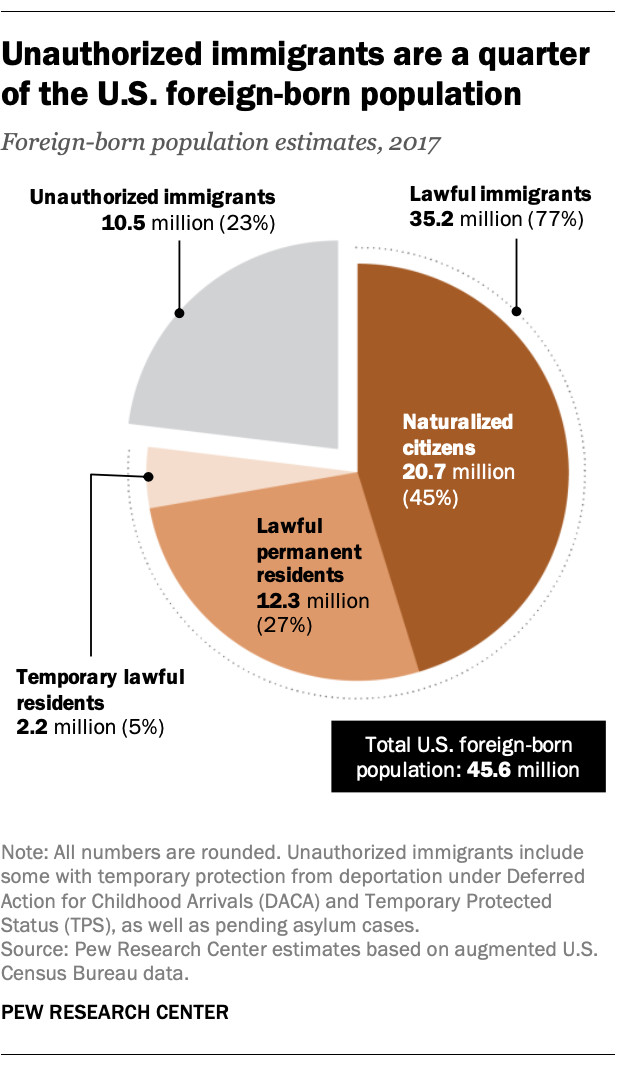 An illustration of how unauthorized immigrants make up a quarter of the U.S. foreign-born population, showcasing the demographic breakdown.
An illustration of how unauthorized immigrants make up a quarter of the U.S. foreign-born population, showcasing the demographic breakdown.
2. Key Trends in Mexican Immigration
To fully grasp the current landscape, it’s essential to examine the key trends that have shaped Mexican immigration over the past few decades.
2.1. How Has the Number of Mexican Apprehensions at the Border Changed?
The number of apprehensions of Mexicans at the U.S. border has decreased over the past decade. In recent years, apprehensions of non-Mexicans have outnumbered those of Mexicans, according to federal statistics.
2.2. What Is the Significance of the 1965 Immigration Policy Overhaul?
The 1965 immigration policy overhaul imposed the first limits on immigration from Western Hemisphere countries, including Mexico. This policy coincided with the end of the Bracero program, which had allowed temporary farm workers from Mexico to work legally in the U.S. These changes contributed to the rise in unauthorized immigration.
2.3. How Does the Decline in Mexican Unauthorized Immigrants Affect the Overall Population?
The decline in Mexican unauthorized immigrants has been the major factor driving down the overall population of unauthorized immigrants in the U.S. While the total number of unauthorized immigrants in the U.S. has decreased from its peak in 2007, the rise in unauthorized immigrants from other parts of the world has partially offset this decline.
3. Factors Influencing Mexican Immigration Patterns
Various economic, social, and political factors influence Mexican immigration patterns. Understanding these factors is key to interpreting the trends.
3.1. What Economic Factors Drive Mexican Immigration?
- Job Opportunities: The availability of jobs in the U.S., particularly in agriculture, construction, and service industries, has historically attracted Mexican immigrants.
- Wage Differentials: Higher wages in the U.S. compared to Mexico provide an economic incentive for migration.
- Economic Conditions in Mexico: Economic downturns, lack of opportunities, and poverty in Mexico can push people to seek better prospects in the U.S.
3.2. How Do Social Factors Influence Mexican Immigration?
- Family Networks: Established immigrant communities in the U.S. provide support and resources for new arrivals.
- Social Networks: Social connections and networks facilitate migration by providing information, assistance, and a sense of community.
- Educational Opportunities: Access to better educational opportunities for children can motivate families to migrate to the U.S.
3.3. What Role Do Political Factors Play?
- Immigration Policies: U.S. immigration policies, including border enforcement, deportation policies, and pathways to legal status, significantly impact immigration patterns.
- Political Instability: Political instability and violence in certain regions of Mexico can lead to increased migration.
- Government Programs: Government programs and policies in both the U.S. and Mexico can influence migration flows.
4. Regional Changes in Unauthorized Immigration
The changes in unauthorized immigration are not uniform across all regions. Some areas have seen increases, while others have experienced declines.
4.1. Which Regions Have Seen an Increase in Unauthorized Immigrants?
From 2007 to 2017, the number of unauthorized immigrants increased from Asia and Central America. The Northern Triangle nations of El Salvador, Guatemala, and Honduras saw significant increases, as did India and Venezuela.
4.2. Which Regions Have Seen a Decrease in Unauthorized Immigrants?
During the same period, the number of unauthorized immigrants decreased from South America and the combined regions of Europe and Canada. Mexico experienced the most significant decline.
4.3. What Are the State-Level Changes in Unauthorized Immigrant Populations?
Some states have seen growth in their unauthorized immigrant populations, while others have experienced declines:
- States with Growth: Louisiana, Maryland, Massachusetts, North Dakota, and South Dakota.
- States with Declines: Arizona, California, Colorado, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Michigan, Nevada, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, and Oregon.
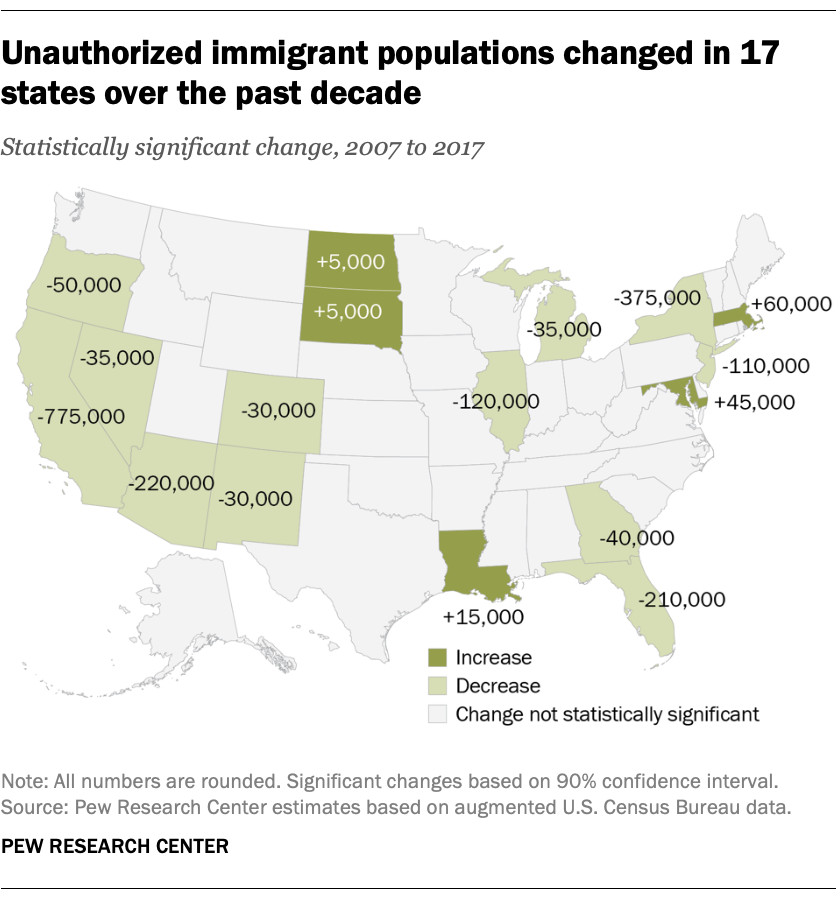 A map highlighting the changes in unauthorized immigrant populations across different states from 2007 to 2017, illustrating regional variations.
A map highlighting the changes in unauthorized immigrant populations across different states from 2007 to 2017, illustrating regional variations.
5. Demographic Characteristics of Unauthorized Immigrants
Understanding the demographic characteristics of unauthorized immigrants provides insights into their integration, contributions, and challenges.
5.1. How Long Have Unauthorized Immigrants Lived in the U.S.?
The unauthorized immigrant population in the U.S. is increasingly made up of longer-term residents. In 2017, the typical unauthorized immigrant adult had lived in the U.S. for 15 years, the longest median duration of residence since 1995.
5.2. What Percentage of Unauthorized Immigrants Have Been in the U.S. for Five Years or Less?
In 2017, only 20% of unauthorized immigrant adults had lived in the U.S. for five years or less, down from 30% a decade earlier.
5.3. How Has the Composition of New Arrivals Changed?
Mexicans accounted for 20% of unauthorized immigrants who came to the U.S. in the previous five years in 2017, compared to 52% in 2007. This represents a significant decrease in the average annual inflow of Mexican unauthorized immigrants.
6. Unauthorized Immigrants in the U.S. Workforce
The role of unauthorized immigrants in the U.S. workforce is a critical aspect of the immigration debate.
6.1. How Has the Number of Unauthorized Immigrants in the Workforce Changed?
The number of unauthorized immigrants in the labor force declined to 7.6 million in 2017, down from 8.2 million in 2007.
6.2. What Percentage of the Labor Force Do Unauthorized Immigrants Constitute?
Unauthorized immigrants made up 4.6% of the labor force in 2017, down from 5.4% in 2007.
6.3. What Sectors Employ a Significant Number of Unauthorized Immigrants?
Unauthorized immigrants are often employed in sectors such as agriculture, construction, hospitality, and domestic services. Their labor is essential in these industries.
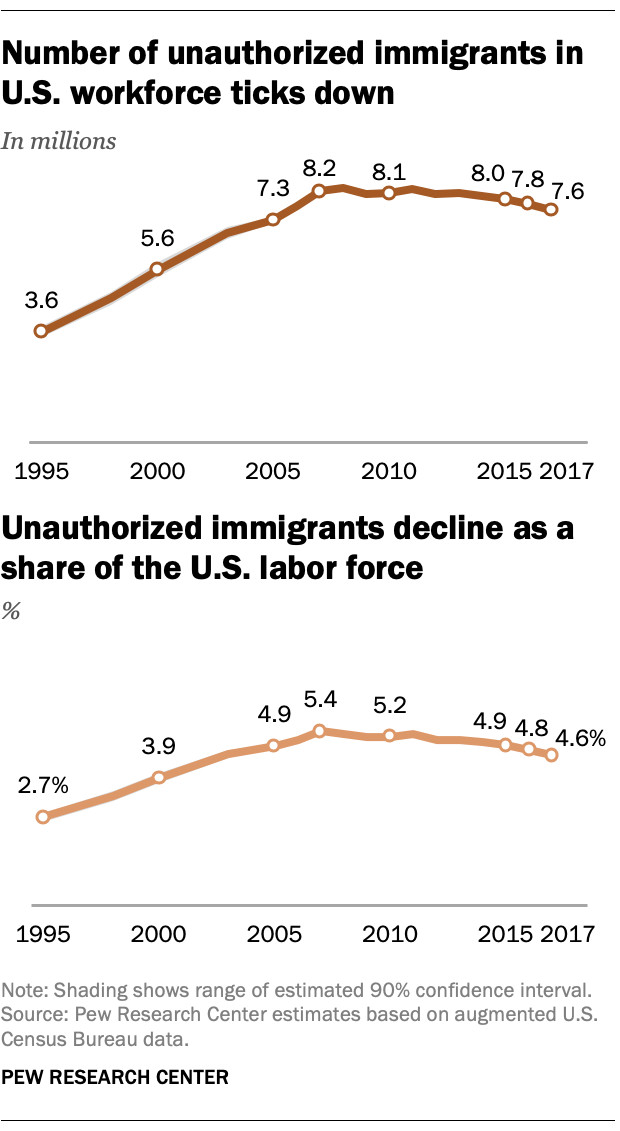 A graph showing the number of unauthorized immigrants in the U.S. workforce over time, highlighting the decline in recent years.
A graph showing the number of unauthorized immigrants in the U.S. workforce over time, highlighting the decline in recent years.
7. The LGBTQ+ Community and Immigration
Immigration issues often intersect with the experiences of the LGBTQ+ community, particularly for those seeking asylum or facing discrimination.
7.1. How Do Immigration Policies Affect LGBTQ+ Individuals?
LGBTQ+ individuals may face unique challenges in the immigration system, including discrimination, lack of recognition of same-sex relationships, and persecution in their home countries.
7.2. What Resources Are Available for LGBTQ+ Immigrants?
Various organizations provide legal assistance, advocacy, and support services for LGBTQ+ immigrants. These resources can help individuals navigate the complex immigration system and access the protections they need.
7.3. How Can the LGBTQ+ Community Support Immigrant Rights?
The LGBTQ+ community can advocate for comprehensive immigration reform that protects the rights and dignity of all immigrants, regardless of their sexual orientation or gender identity. Supporting organizations that provide direct services to immigrants and raising awareness about the challenges they face are also important steps.
8. Methodology for Estimating Unauthorized Immigrant Populations
Understanding the methodology used to estimate unauthorized immigrant populations is essential for interpreting the data.
8.1. What Is the “Residual Method”?
The “residual method” is a common approach used to estimate the unauthorized immigrant population. It involves calculating the total number of immigrants living in the U.S. and then subtracting the number of lawful immigrants to arrive at an estimate of the unauthorized immigrant population.
8.2. How Does Pew Research Center Estimate the Unauthorized Immigrant Population?
Pew Research Center uses the residual method, relying on U.S. census counts and government surveys to calculate the total number of immigrants in the U.S. They then use official counts of immigrant admissions and other demographic data to determine the number of lawful immigrants. The difference between these two figures is their estimate of the unauthorized immigrant population.
8.3. What Adjustments Are Made for Undercounting?
Pew Research Center makes adjustments for potential undercounting in census counts and surveys, as unauthorized immigrants are especially likely to be missed. These adjustments are based on experience and research to ensure the most accurate estimate possible.
9. The Impact of Temporary Protected Status (TPS) and Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA)
Temporary Protected Status (TPS) and Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA) are programs that provide temporary legal status to certain immigrants. Changes in these programs can significantly impact the unauthorized immigrant population.
9.1. How Many People Are Affected by TPS?
In 2017, about 320,000 people from 10 nations with Temporary Protected Status were included in the estimate of unauthorized immigrants. Changes in TPS policies can subject these individuals to deportation.
9.2. What Is the Impact of DACA?
Approximately 700,000 beneficiaries of Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals were included in the estimate of unauthorized immigrants in 2017. The future of DACA remains uncertain, and changes in the program could also lead to deportation for many of these individuals.
9.3. How Do Asylum Applications Affect the Unauthorized Immigrant Population?
A rising number of people who have applied for asylum and are awaiting a ruling are also included in the estimate of unauthorized immigrants. The outcome of their asylum cases will determine their legal status in the U.S.
10. Addressing Common Misconceptions About Mexican Immigration
Addressing common misconceptions about Mexican immigration is crucial for fostering informed and respectful dialogue.
10.1. Are Most Unauthorized Immigrants Mexican?
While Mexicans have historically been the largest group of unauthorized immigrants in the U.S., they no longer constitute the majority. In 2017, Mexicans made up 47% of the unauthorized immigrant population.
10.2. Are Unauthorized Immigrants Primarily Recent Arrivals?
The unauthorized immigrant population in the U.S. is increasingly made up of longer-term residents. In 2017, the typical unauthorized immigrant adult had lived in the U.S. for 15 years.
10.3. Do Unauthorized Immigrants Take Jobs Away from U.S. Citizens?
The economic impact of unauthorized immigration is complex and debated. Some studies suggest that unauthorized immigrants fill jobs that U.S. citizens are unwilling to do, while others raise concerns about wage depression and job displacement.
11. Gaymexico.net: Your Resource for LGBTQ+ Information and Support
At gaymexico.net, we are committed to providing accurate and up-to-date information on a wide range of topics, including immigration. We strive to create a welcoming and inclusive community for LGBTQ+ individuals and their allies.
11.1. What Resources Does Gaymexico.net Offer?
Gaymexico.net offers a variety of resources, including:
- Travel Guides: Information on LGBTQ+-friendly destinations in Mexico.
- Event Listings: Details on LGBTQ+ events and festivals.
- Community Forums: A platform for connecting with other LGBTQ+ individuals.
- News and Articles: Coverage of issues affecting the LGBTQ+ community.
11.2. How Can Gaymexico.net Help LGBTQ+ Individuals Interested in Immigration?
Gaymexico.net can provide information and resources to help LGBTQ+ individuals understand their rights and options under U.S. immigration law. We can also connect you with organizations that offer legal assistance and support services.
11.3. How Can I Get Involved with Gaymexico.net?
There are many ways to get involved with Gaymexico.net, including:
- Contributing Articles: Share your stories and insights on LGBTQ+ issues.
- Participating in Forums: Engage in discussions and connect with other members of the community.
- Volunteering: Help us create and maintain our resources.
- Donating: Support our work and help us continue to provide valuable services.
12. Exploring LGBTQ+ Culture and Travel in Mexico
Mexico is a vibrant and diverse country with a rich LGBTQ+ culture. Exploring Mexico can be a rewarding and enriching experience for LGBTQ+ travelers.
12.1. What Are Some LGBTQ+-Friendly Destinations in Mexico?
Some popular LGBTQ+-friendly destinations in Mexico include:
- Puerto Vallarta: Known for its thriving gay scene and beautiful beaches.
- Mexico City: A cosmopolitan city with a diverse LGBTQ+ community and numerous gay bars and clubs.
- Cancun: A popular resort destination with LGBTQ+-friendly hotels and activities.
12.2. What LGBTQ+ Events Take Place in Mexico?
Mexico hosts a variety of LGBTQ+ events throughout the year, including:
- Puerto Vallarta Pride: A week-long celebration of LGBTQ+ culture.
- Mexico City Pride: One of the largest Pride celebrations in Latin America.
- Guadalajara International Film Festival: Features LGBTQ+ films from around the world.
12.3. What Should LGBTQ+ Travelers Know Before Visiting Mexico?
While Mexico is generally becoming more accepting of LGBTQ+ individuals, it is important to be aware of local laws and customs. Researching destinations and seeking advice from LGBTQ+ travel resources can help ensure a safe and enjoyable trip.
13. Understanding the Bracero Program
The Bracero Program was a significant factor in shaping Mexican immigration to the United States.
13.1. What Was the Bracero Program?
The Bracero Program was a series of laws and diplomatic agreements between the United States and Mexico that permitted Mexican citizens to take temporary agricultural work in the United States. It operated from 1942 to 1964.
13.2. How Did the Bracero Program Impact Mexican Immigration?
The Bracero Program brought millions of Mexican workers to the United States, particularly to work in agriculture. While intended to be temporary, it established patterns of migration and labor that continued after the program’s end.
13.3. Why Was the Bracero Program Ended?
The Bracero Program was ended due to a combination of factors, including concerns about labor conditions, low wages, and the exploitation of Mexican workers. There were also concerns about the program’s impact on domestic labor markets.
14. The Role of the Northern Triangle Countries
The Northern Triangle countries of El Salvador, Guatemala, and Honduras have become increasingly significant in discussions about immigration to the United States.
14.1. What Are the Northern Triangle Countries?
The Northern Triangle countries are El Salvador, Guatemala, and Honduras, located in Central America.
14.2. Why Are People Leaving the Northern Triangle Countries?
People are leaving the Northern Triangle countries due to a combination of factors, including:
- Violence: High levels of gang violence and organized crime.
- Poverty: Widespread poverty and lack of economic opportunities.
- Political Instability: Corruption and weak governance.
14.3. How Does Immigration from the Northern Triangle Affect U.S. Immigration Policy?
The increase in asylum seekers and unauthorized immigrants from the Northern Triangle countries has put pressure on U.S. immigration policies and resources. It has also led to debates about border security, asylum procedures, and humanitarian assistance.
15. Asylum and Refugee Status for LGBTQ+ Individuals
LGBTQ+ individuals who face persecution in their home countries may be eligible for asylum or refugee status in the United States.
15.1. What Is Asylum?
Asylum is a form of protection granted to individuals who are already in the United States and are unable or unwilling to return to their home country due to a well-founded fear of persecution.
15.2. What Is Refugee Status?
Refugee status is a form of protection granted to individuals who are outside of the United States and are unable or unwilling to return to their home country due to a well-founded fear of persecution.
15.3. How Can LGBTQ+ Individuals Apply for Asylum or Refugee Status?
LGBTQ+ individuals can apply for asylum or refugee status by demonstrating that they have a well-founded fear of persecution based on their sexual orientation or gender identity. They may need to provide evidence of discrimination, violence, or threats they have experienced or are likely to experience if they return to their home country.
16. Resources for Immigrants and Their Families
There are many organizations and resources available to support immigrants and their families in the United States.
16.1. What Legal Resources Are Available?
- Immigration Attorneys: Provide legal representation and advice on immigration matters.
- Nonprofit Legal Organizations: Offer free or low-cost legal services to immigrants.
- Immigration Courts: Adjudicate immigration cases and determine whether individuals are eligible for relief from deportation.
16.2. What Social Services Are Available?
- Community Centers: Provide a range of services, including English classes, job training, and cultural programs.
- Religious Organizations: Offer assistance to immigrants, including food, shelter, and counseling.
- Social Service Agencies: Provide support services such as healthcare, housing, and education.
16.3. What Educational Resources Are Available?
- English Classes: Help immigrants learn English and improve their communication skills.
- GED Programs: Provide opportunities for immigrants to earn a high school equivalency diploma.
- College and University Programs: Offer higher education opportunities to immigrants.
17. The Future of Mexican Immigration
The future of Mexican immigration to the United States is uncertain and will depend on a variety of factors.
17.1. What Factors Will Influence Future Immigration Patterns?
- Economic Conditions: The economic conditions in both the United States and Mexico will play a significant role.
- Immigration Policies: U.S. immigration policies will continue to shape immigration flows.
- Political Stability: Political stability and security in Mexico will influence migration decisions.
17.2. What Are the Potential Scenarios for Mexican Immigration?
- Continued Decline: Mexican immigration could continue to decline if economic conditions in Mexico improve and U.S. immigration policies become more restrictive.
- Stabilization: Mexican immigration could stabilize at current levels if economic and political conditions remain relatively unchanged.
- Increase: Mexican immigration could increase if economic conditions in Mexico worsen or if U.S. immigration policies become more lenient.
17.3. How Can the U.S. and Mexico Work Together on Immigration Issues?
The U.S. and Mexico can work together on immigration issues by:
- Addressing Root Causes: Investing in economic development and security in Mexico and Central America to address the root causes of migration.
- Strengthening Border Security: Enhancing cooperation on border security to prevent unauthorized immigration.
- Creating Legal Pathways: Expanding legal pathways for Mexican workers to come to the United States.
- Protecting Immigrant Rights: Ensuring that the rights of all immigrants are protected, regardless of their legal status.
18. Conclusion: Understanding and Supporting the Immigrant Community
Understanding the complexities of immigration is essential for creating a more inclusive and welcoming society. By addressing misconceptions, supporting immigrant rights, and providing resources and services, we can help immigrants and their families thrive. Remember to visit gaymexico.net, your ultimate guide for your LGBTQ+ travel and community needs in Mexico.
Explore Mexico safely and enjoyably as an LGBTQ+ individual! Visit gaymexico.net for detailed travel guides, event listings, and connections to the LGBTQ+ community in Mexico. Discover welcoming destinations, find local resources, and plan your next adventure with confidence. Connect with us today and start your journey!
Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States.
Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177.
Website: gaymexico.net.
19. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
19.1. What Percentage Of Illegal Immigrants Are Mexican?
In 2017, Mexicans constituted 47% of the unauthorized immigrant population in the U.S., marking the first time they’ve been less than half since the rise of illegal immigration began.
19.2. Why Has the Number Of Mexican Illegal Immigrants Decreased?
The decrease is due to fewer arrivals from Mexico, increased departures, and a rise in unauthorized immigration from other regions.
19.3. How Does the U.S. Government Estimate The Number Of Illegal Immigrants?
The U.S. government uses the “residual method,” subtracting the number of legal immigrants from the total immigrant population.
19.4. What Are The Main Factors That Influence Mexican Immigration Patterns?
The primary factors include economic opportunities, wage differentials, social networks, and U.S. immigration policies.
19.5. Which U.S. States Have Seen An Increase In Illegal Immigrants?
States like Louisiana, Maryland, Massachusetts, North Dakota, and South Dakota have seen increases in illegal immigrant populations.
19.6. How Long Have Most Illegal Immigrants Lived In The U.S.?
As of 2017, the typical unauthorized immigrant adult had lived in the U.S. for 15 years, the longest median duration since 1995.
19.7. What Percentage Of The U.S. Labor Force Do Illegal Immigrants Represent?
In 2017, unauthorized immigrants made up 4.6% of the labor force, down from 5.4% in 2007.
19.8. How Do Temporary Protected Status (TPS) and DACA Impact Illegal Immigration Numbers?
Changes in TPS and DACA policies can significantly affect the unauthorized immigrant population, as these programs provide temporary legal status to certain immigrants.
19.9. How Can LGBTQ+ Individuals Seek Asylum In The U.S.?
LGBTQ+ individuals can apply for asylum by demonstrating a well-founded fear of persecution based on their sexual orientation or gender identity.
19.10. What Resources Are Available For Immigrants And Their Families In The U.S.?
Resources include legal aid, community centers, religious organizations, and educational programs such as English classes and GED programs.