Did a Mexican president sell Mexico to the US? The question sparks debate, especially within the LGBTQ+ community interested in Mexican history and US-Mexican relations. Gaymexico.net explores the intricacies of the Gadsden Purchase, revealing the historical context and its impact. Discover the truth behind this controversial event and how it shaped the landscapes of both nations.
1. What Was the Gadsden Purchase and Why Was It Significant?
The Gadsden Purchase was an agreement between the United States and Mexico, finalized in 1854, in which the United States paid Mexico $10 million for approximately 29,670 square miles of land that became part of present-day Arizona and New Mexico, and it was significant because it secured land needed for a southern transcontinental railroad and aimed to resolve lingering conflicts after the Mexican-American War. This purchase remains a contentious historical event, particularly when considering the broader history of US-Mexican relations. Let’s explore the details to understand its significance.
- Facilitating Transcontinental Railroad Construction: The primary motivation behind the Gadsden Purchase was the United States’ desire to construct a transcontinental railroad along a southern route. The acquired territory provided the optimal geographical conditions for building this railroad, avoiding the mountainous terrain further north. This railway aimed to connect the eastern states with California, facilitating trade, transportation, and economic growth.
- Resolving Border Disputes and Conflicts: The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, which ended the Mexican-American War in 1848, did not fully resolve border disputes. The Gadsden Purchase sought to clarify and solidify the border between the two nations, particularly concerning the Mesilla Valley, an area claimed by both countries.
- Economic Motivations: For Mexico, selling the land provided much-needed revenue for its struggling economy. Under President Antonio López de Santa Anna, Mexico faced internal rebellions and financial instability. The $10 million from the United States offered a temporary solution to these economic woes.
- Political Ramifications: The Gadsden Purchase had significant political ramifications in both the United States and Mexico. In the U.S., the purchase fueled debates over slavery, as the newly acquired territory could potentially become new slave states. In Mexico, the sale was viewed by many as a further loss of territory to the expansionist United States, leading to criticism of Santa Anna’s government.
- Impact on Indigenous Populations: The purchase affected the indigenous populations living in the region, including the Apaches. The change in sovereignty led to altered relationships with the governing power, impacting their lands, rights, and cultural practices.
The Gadsden Purchase had long-lasting effects, reshaping the geography, economy, and politics of both nations. It facilitated the expansion of the United States, while further diminishing Mexico’s territory. Its legacy continues to be a topic of discussion and analysis, especially when considering its implications for current US-Mexican relations.
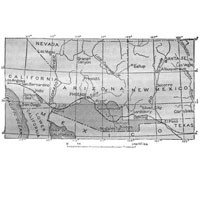 Map Depicting the Gadsden Purchase
Map Depicting the Gadsden Purchase
2. Who Was the Mexican President Involved in the Gadsden Purchase?
Antonio López de Santa Anna, then President of Mexico, was the Mexican president involved in the Gadsden Purchase, and he agreed to sell the territory to the United States for $10 million. His decision was driven by Mexico’s dire financial needs and political instability at the time. Let’s delve deeper into the role of Santa Anna and the context surrounding his decision.
- Political Instability in Mexico: During the mid-19th century, Mexico experienced significant political instability, marked by frequent changes in government and internal conflicts. Santa Anna himself was a dominant figure in Mexican politics, serving multiple terms as president, often marked by authoritarian rule and periods of exile.
- Financial Crisis: Mexico faced a severe financial crisis in the 1850s. The country was burdened by debt from previous wars, including the Mexican-American War, and internal strife. Selling territory to the United States was seen as a way to alleviate some of the financial pressure.
- Santa Anna’s Motivation: Santa Anna’s primary motivation was to secure funds to maintain his army and suppress internal rebellions. He believed that the revenue from the land sale would provide him with the resources necessary to stabilize his government and maintain control over the country.
- Negotiations with James Gadsden: The negotiations for the land sale were conducted between Santa Anna and James Gadsden, the U.S. Minister to Mexico. Gadsden was sent by U.S. President Franklin Pierce to secure a deal that would facilitate the construction of a southern transcontinental railroad.
- Controversy and Criticism: Santa Anna’s decision to sell the territory was met with significant controversy and criticism within Mexico. Many Mexicans viewed the sale as a betrayal of national sovereignty and a further loss of territory to the United States. This decision contributed to Santa Anna’s eventual downfall and exile.
Santa Anna’s involvement in the Gadsden Purchase was a complex mix of political expediency and financial necessity. His decision, though controversial, reflected the challenges Mexico faced during a turbulent period in its history. It also had lasting implications for the relationship between Mexico and the United States, marking another chapter in the ongoing negotiations over territory and sovereignty.
 Mexican President Antonio de Santa Anna
Mexican President Antonio de Santa Anna
3. What Were the Main Reasons Mexico Sold the Territory to the US?
Mexico sold the territory to the US primarily due to severe financial difficulties and internal political instability, necessitating funds to stabilize the government and quell rebellions. These factors made the offer from the United States an appealing, albeit controversial, option for President Santa Anna.
- Financial Crisis: Mexico was in a dire financial situation in the mid-19th century. Years of internal conflict, coupled with the expenses of the Mexican-American War (1846-1848), had left the country heavily indebted. The government struggled to meet its financial obligations and fund essential services.
- Political Instability: The country was plagued by political instability, characterized by frequent changes in leadership and internal rebellions. Santa Anna, who was president at the time of the Gadsden Purchase, needed funds to maintain a strong army to suppress these uprisings and maintain control.
- Economic Incentives: The United States offered $10 million for the territory, which was a significant sum at the time. This money was earmarked to help alleviate Mexico’s financial woes and stabilize its economy, providing short-term relief to the government.
- Strategic Considerations: Some in the Mexican government believed that selling the sparsely populated and difficult-to-defend territory would be strategically advantageous. It would eliminate a potential source of conflict with the United States and allow Mexico to focus on developing its core regions.
- Pressure from the US: The United States had been actively seeking to acquire this territory for several years, primarily to facilitate the construction of a southern transcontinental railroad. The US exerted political and economic pressure on Mexico to sell the land.
- Santa Anna’s Leadership: Santa Anna’s leadership was marked by authoritarian tendencies and a willingness to make controversial decisions to maintain power. His decision to sell the territory was influenced by his desire to secure funds and consolidate his control over Mexico, despite widespread opposition.
- Historical Context: It is important to view this transaction in the context of the broader history of US-Mexican relations, marked by territorial disputes and expansionist ambitions. The Gadsden Purchase was one of several instances where Mexico ceded territory to the United States, reflecting the power dynamics between the two nations.
Mexico’s decision to sell the territory that now comprises part of Arizona and New Mexico was driven by a combination of economic desperation, political instability, and strategic considerations. While the sale provided short-term financial relief, it also resulted in the loss of territory and fueled long-term resentment within Mexico.
4. What Were the Terms of the Gadsden Purchase Agreement?
The terms of the Gadsden Purchase agreement stipulated that the United States would pay Mexico $10 million for approximately 29,670 square miles of land, resolving border disputes and facilitating the construction of a southern transcontinental railroad. This agreement had several key provisions that shaped the future of both nations.
- Land Acquisition: The United States acquired approximately 29,670 square miles (76,840 square kilometers) of land from Mexico. This territory is now part of the states of Arizona and New Mexico.
- Payment: The United States agreed to pay Mexico $10 million for the land. This sum was intended to help alleviate Mexico’s financial difficulties and stabilize its economy.
- Border Resolution: The agreement was intended to resolve lingering border disputes between the two countries, particularly concerning the Mesilla Valley, which both nations claimed as their own.
- Railroad Construction: A primary motivation for the purchase was to secure land that would facilitate the construction of a southern transcontinental railroad. The acquired territory provided a favorable route for the railroad, avoiding the mountainous terrain further north.
- Protection Against Native American Raids: An initial version of the treaty included provisions related to protecting Mexico from Native American raids originating from the United States. However, these provisions were later removed during the U.S. Senate ratification process.
- Release of Claims: The United States was released from any further financial obligations or claims related to Native American attacks along the border.
- Private Claims: Original negotiations included addressing private American claims against Mexico, including those related to the Garay deal (a failed attempt to build a trans-isthmus route across Mexico). However, these provisions were also removed during the U.S. Senate ratification.
- Ratification Process: The treaty faced significant opposition in the U.S. Senate due to sectional tensions over slavery. The Senate ultimately ratified a revised version of the treaty, reducing the amount paid to Mexico and removing some of the original provisions.
- Santa Anna’s Approval: Despite the changes made by the U.S. Senate, Santa Anna approved the revised treaty, primarily because Mexico was in desperate need of funds.
- Impact on Indigenous Populations: The treaty did not adequately address the rights and concerns of the indigenous populations living in the acquired territory, leading to long-term issues related to land rights and sovereignty.
The Gadsden Purchase agreement, while primarily focused on land acquisition and border resolution, had far-reaching consequences for the economies, politics, and societies of both the United States and Mexico. It remains a significant chapter in the history of US-Mexican relations.
5. How Did the Gadsden Purchase Impact US-Mexican Relations?
The Gadsden Purchase further strained US-Mexican relations, adding to existing tensions from the Mexican-American War and contributing to long-term resentment and mistrust between the two nations. It also had domestic political consequences within both countries.
- Increased Resentment: In Mexico, the sale of territory was viewed as another instance of the United States taking advantage of Mexico’s weakness. This fueled resentment and a sense of national humiliation.
- Territorial Loss: The Gadsden Purchase represented another significant loss of Mexican territory to the United States. This further diminished Mexico’s size and resources, contributing to a sense of grievance.
- Political Instability: The sale of territory contributed to political instability in Mexico. Santa Anna was criticized and eventually overthrown for his role in the Gadsden Purchase.
- Economic Impact: While the $10 million payment provided short-term relief, it did not solve Mexico’s underlying economic problems. The loss of territory further limited Mexico’s economic potential.
- Domestic Politics in the US: In the United States, the Gadsden Purchase fueled sectional tensions over slavery. The acquisition of new territory raised the question of whether these lands would become slave states or free states, exacerbating the divide between the North and the South.
- Manifest Destiny: The Gadsden Purchase was seen as another step in the United States’ policy of Manifest Destiny, which held that the US was destined to expand its territory across the North American continent. This expansionist policy was often at the expense of Mexico and other neighboring countries.
- Long-Term Mistrust: The Gadsden Purchase contributed to a long-term sense of mistrust between the two nations. This mistrust has manifested in various ways throughout history, including disputes over immigration, trade, and border security.
- Cultural Impact: The Gadsden Purchase had a cultural impact on the border region, as it altered the demographics and cultural landscape of the area. Mexican culture and heritage remained strong in the region, but it also became a site of cultural mixing and conflict.
- Contemporary Relevance: The legacy of the Gadsden Purchase continues to be relevant in contemporary US-Mexican relations. It is often cited as an example of the unequal power dynamics between the two nations and the historical grievances that shape their relationship.
The Gadsden Purchase had a complex and multifaceted impact on US-Mexican relations. It contributed to resentment, mistrust, and political instability, and its legacy continues to be felt in the relationship between the two countries today.
6. How Did the Gadsden Purchase Affect the Indigenous People of the Region?
The Gadsden Purchase significantly impacted the indigenous people of the region, altering their sovereignty, land rights, and cultural practices without adequate consultation or consideration. This transition led to long-term challenges and displacement for these communities.
- Loss of Sovereignty: The Gadsden Purchase transferred sovereignty over indigenous lands from Mexico to the United States. This change in governance had profound implications for the autonomy and self-determination of indigenous communities.
- Land Rights: The treaty did not adequately address the land rights of indigenous peoples. Many indigenous communities had occupied and utilized these lands for centuries, but their claims were often ignored or dismissed by the U.S. government.
- Displacement: As the United States asserted its control over the territory, many indigenous communities were displaced from their ancestral lands. This displacement led to social, economic, and cultural disruption.
- Cultural Impact: The Gadsden Purchase had a significant cultural impact on indigenous communities. The imposition of U.S. laws and policies undermined traditional cultural practices and institutions.
- Economic Hardship: Many indigenous communities faced economic hardship as a result of the Gadsden Purchase. The loss of land and resources made it difficult for them to sustain their traditional livelihoods.
- Increased Conflict: The arrival of American settlers and the expansion of U.S. military presence in the region led to increased conflict between indigenous peoples and the U.S. government.
- Lack of Consultation: Indigenous communities were not consulted during the negotiation or ratification of the Gadsden Purchase. This lack of consultation reflected a broader pattern of disregard for indigenous rights and concerns.
- Long-Term Consequences: The Gadsden Purchase had long-term consequences for indigenous communities in the region. Many continue to struggle with issues related to land rights, sovereignty, and cultural preservation.
- Resistance: Despite the challenges they faced, indigenous peoples in the region actively resisted U.S. domination and fought to protect their rights and way of life.
The Gadsden Purchase had a devastating impact on the indigenous people of the region. It resulted in the loss of land, sovereignty, and cultural autonomy, and its legacy continues to be felt by indigenous communities today.
7. What Role Did James Gadsden Play in the Purchase?
James Gadsden, as the U.S. Minister to Mexico, played a pivotal role in the Gadsden Purchase by negotiating the agreement with President Santa Anna. His efforts secured the land needed for the southern transcontinental railroad, fulfilling the objectives of the U.S. government.
- Appointment as Minister: James Gadsden was appointed as the U.S. Minister to Mexico by President Franklin Pierce in 1853. His primary mission was to negotiate the purchase of territory from Mexico to facilitate the construction of a southern transcontinental railroad.
- Negotiations with Santa Anna: Gadsden engaged in direct negotiations with Mexican President Antonio López de Santa Anna. These negotiations were complex and challenging, as Mexico was facing political instability and financial difficulties.
- Securing the Agreement: Gadsden successfully negotiated an agreement with Santa Anna for the purchase of approximately 29,670 square miles of land. The United States agreed to pay Mexico $10 million for the territory.
- Advocating for the Railroad: Gadsden was a strong advocate for the construction of a southern transcontinental railroad. He believed that this railroad would promote economic growth and strengthen the United States’ position in the world.
- Overcoming Obstacles: Gadsden faced numerous obstacles during the negotiation process, including opposition from within the U.S. government and resistance from Mexican politicians who opposed the sale of territory.
- Influence on Treaty Terms: Gadsden played a key role in shaping the terms of the Gadsden Purchase treaty. He worked to ensure that the treaty met the strategic and economic objectives of the United States.
- Controversies: Gadsden’s actions were not without controversy. Some critics accused him of using aggressive tactics to pressure Mexico into selling the territory.
- Legacy: James Gadsden is remembered as a key figure in the history of U.S. expansion. His role in the Gadsden Purchase had a lasting impact on the geography and economy of the southwestern United States.
- Background: Prior to his appointment as minister, Gadsden had a military background and had been involved in railroad development, making him well-suited for the task of negotiating the land purchase.
James Gadsden played a crucial role in the Gadsden Purchase through his diplomatic efforts and his advocacy for the southern transcontinental railroad. His negotiations with Santa Anna resulted in an agreement that had significant consequences for both the United States and Mexico.
8. What Were the Domestic Political Consequences in the US?
In the US, the Gadsden Purchase intensified debates over slavery, as the newly acquired territory raised questions about whether it would become slave states or free states, further dividing the nation. This issue contributed to the escalating tensions that eventually led to the Civil War.
- Sectional Tensions: The Gadsden Purchase occurred during a period of intense sectional tensions between the North and the South over the issue of slavery. The acquisition of new territory raised the question of whether these lands would be open to slavery or not, exacerbating the divide between the two regions.
- Slavery Debate: The debate over slavery in the newly acquired territory played out in Congress and in the public sphere. Southern politicians and pro-slavery advocates argued that the new territory should be open to slavery, while Northern politicians and abolitionists argued against the expansion of slavery.
- Compromise Efforts: The Gadsden Purchase further complicated efforts to find a compromise solution to the slavery issue. Previous compromises, such as the Missouri Compromise of 1820 and the Compromise of 1850, had attempted to maintain a balance between slave states and free states, but the acquisition of new territory threatened to upset this balance.
- Political Parties: The Gadsden Purchase also had an impact on the political parties of the time. The Democratic Party, which was the dominant party in the South, generally supported the expansion of slavery. The Whig Party, which had a strong base in the North, was divided over the issue of slavery, leading to its eventual decline.
- Kansas-Nebraska Act: The Gadsden Purchase contributed to the passage of the Kansas-Nebraska Act in 1854. This act allowed the residents of Kansas and Nebraska to decide for themselves whether to allow slavery, through a process known as popular sovereignty. The Kansas-Nebraska Act further inflamed sectional tensions and led to violence in Kansas.
- Rise of the Republican Party: The Gadsden Purchase and the subsequent debates over slavery contributed to the rise of the Republican Party. The Republican Party was founded in 1854 on a platform of opposing the expansion of slavery.
- Civil War: The Gadsden Purchase was one of several factors that contributed to the outbreak of the Civil War in 1861. The war was fought over the issue of slavery and the question of whether the United States would remain a unified nation.
- Manifest Destiny: The Gadsden Purchase was seen by some as a triumph of Manifest Destiny, the belief that the United States was destined to expand its territory across the North American continent. However, the purchase also raised questions about the morality of expansionism and the impact of territorial expansion on the issue of slavery.
The Gadsden Purchase had significant domestic political consequences in the United States, primarily related to the issue of slavery. It intensified sectional tensions, complicated efforts to find a compromise solution, and contributed to the rise of the Republican Party and the outbreak of the Civil War.
9. How Did the Gadsden Purchase Influence the Construction of the Southern Transcontinental Railroad?
The Gadsden Purchase directly enabled the construction of the Southern Transcontinental Railroad by providing the necessary land for a more level and accessible route, avoiding the more challenging terrain further north. This facilitated transportation and economic development in the region.
- Optimal Route: The primary motivation behind the Gadsden Purchase was to secure land that would facilitate the construction of a southern transcontinental railroad. The acquired territory provided a more level and accessible route compared to alternative routes further north.
- Geographical Advantages: The Gadsden Purchase territory offered several geographical advantages for railroad construction, including fewer mountains, more favorable climate conditions, and shorter distances.
- Economic Development: The construction of the Southern Transcontinental Railroad was seen as a way to promote economic development in the southwestern United States. The railroad would facilitate the transportation of goods and people, connecting the region to national and international markets.
- Strategic Importance: The Southern Transcontinental Railroad was also viewed as being of strategic importance. It would provide a vital transportation link between the eastern and western United States, strengthening the country’s position in the world.
- Facilitating Trade: The railroad facilitated trade between the United States and Mexico. It allowed for the efficient transportation of goods across the border, promoting economic integration between the two countries.
- Western Expansion: The Southern Transcontinental Railroad played a key role in the westward expansion of the United States. It encouraged settlement and development in the southwestern region, contributing to the growth of cities and towns.
- Technological Advancement: The construction of the Southern Transcontinental Railroad required significant technological advancements. It spurred innovation in railroad engineering and construction, contributing to the development of the railroad industry.
- Infrastructure Development: The Gadsden Purchase led to significant infrastructure development in the southwestern United States. In addition to the railroad, new roads, bridges, and communication networks were built to support the railroad and facilitate economic development.
The Gadsden Purchase had a direct and significant influence on the construction of the Southern Transcontinental Railroad. It provided the necessary land for a more efficient and cost-effective route, facilitating transportation, economic development, and westward expansion in the United States.
10. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About the Gadsden Purchase?
There are several common misconceptions about the Gadsden Purchase, including beliefs that it involved a much larger portion of Mexico, that it was solely about building a railroad, or that it was universally supported in the US. Addressing these misconceptions provides a more accurate understanding of the historical event.
- Size of the Territory: One common misconception is that the Gadsden Purchase involved a much larger portion of Mexico. In reality, the territory acquired by the United States was approximately 29,670 square miles, which is a relatively small portion of Mexico.
- Solely About the Railroad: While the construction of a southern transcontinental railroad was a primary motivation behind the Gadsden Purchase, it was not the only factor. The United States also sought to resolve border disputes and secure access to valuable resources in the region.
- Unified Support in the US: Another misconception is that the Gadsden Purchase was universally supported in the United States. In fact, the purchase was controversial and faced significant opposition in Congress due to sectional tensions over slavery.
- Mexico Willingly Sold the Land: It is often misconstrued that Mexico willingly sold the land to the United States. The reality is that Mexico was facing severe financial difficulties and political instability, which pressured the government to sell the territory.
- Santa Anna Acted Alone: Some believe that Santa Anna acted alone in selling the territory. While he was the president of Mexico at the time, the decision was influenced by complex political and economic factors and involved negotiations with U.S. representatives.
- Treaty Resolved All Issues: Another misconception is that the Gadsden Purchase treaty resolved all outstanding issues between the United States and Mexico. In reality, the treaty failed to address some key issues, such as Native American raids and private claims.
- Indigenous Peoples Unaffected: A common misconception is that the Gadsden Purchase did not affect the indigenous peoples living in the region. In fact, the purchase had a significant impact on indigenous communities, leading to loss of land, sovereignty, and cultural autonomy.
- Short-Term Impact Only: Some believe that the Gadsden Purchase had only short-term consequences. However, the purchase had long-lasting effects on the geography, economy, and politics of both the United States and Mexico.
- US Paid Fair Value: Another misconception is that the United States paid fair value for the land. Critics argue that the $10 million paid by the United States was far less than the actual value of the territory, especially considering its strategic and economic importance.
- No Impact on US-Mexican Relations: It is often misconstrued that the Gadsden Purchase had no significant impact on US-Mexican relations. In reality, the purchase further strained relations between the two countries and contributed to long-term resentment and mistrust.
Addressing these common misconceptions is essential for a more accurate and nuanced understanding of the Gadsden Purchase and its historical significance.
For further exploration into the relationship between Mexico and the LGBTQ+ community, visit gaymexico.net. There, you’ll discover valuable resources that enhance your travel experiences, provide critical safety guidance, and foster meaningful connections with a supportive community.
Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States
Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177
Website: gaymexico.net
FAQ About The Gadsden Purchase
1. What exactly did the US acquire in the Gadsden Purchase?
The US acquired approximately 29,670 square miles of land from Mexico, which later became part of Arizona and New Mexico, to facilitate a southern transcontinental railroad.
2. How much did the US pay for the Gadsden Purchase territory?
The US paid Mexico $10 million for the Gadsden Purchase territory, aiming to resolve border disputes and facilitate railroad construction.
3. Was the Gadsden Purchase popular in Mexico at the time?
No, the Gadsden Purchase was largely unpopular in Mexico, seen as a further loss of territory and a sign of US expansionism, contributing to political instability.
4. How did the Gadsden Purchase affect Native American tribes in the area?
The Gadsden Purchase negatively impacted Native American tribes by altering their sovereignty, land rights, and cultural practices, leading to displacement and hardship.
5. What was Antonio López de Santa Anna’s role in the Gadsden Purchase?
Antonio López de Santa Anna, as President of Mexico, agreed to sell the territory to the US for $10 million, driven by Mexico’s financial needs and political instability.
6. What were the main benefits of the Gadsden Purchase for the United States?
The main benefits included securing land for a southern transcontinental railroad, resolving border disputes, and promoting economic development in the southwestern US.
7. Did the Gadsden Purchase resolve all tensions between the US and Mexico?
No, the Gadsden Purchase did not resolve all tensions, as it further strained US-Mexican relations, contributing to long-term resentment and mistrust.
8. How did the Gadsden Purchase contribute to the American Civil War?
The Gadsden Purchase intensified debates over slavery, as the newly acquired territory raised questions about whether it would become slave states or free states, further dividing the nation.
9. Was the Gadsden Purchase solely about building a railroad?
While the construction of a southern transcontinental railroad was a primary motivation, the Gadsden Purchase also aimed to resolve border disputes and secure resources.
10. What is the lasting legacy of the Gadsden Purchase today?
The Gadsden Purchase remains a significant event in US-Mexican relations, symbolizing historical power dynamics and territorial disputes, and continues to be a topic of discussion and analysis.