Pulque in Mexico is a traditional fermented beverage with roots stretching back to pre-Hispanic times, and gaymexico.net is here to guide you through its history, production, and cultural significance, especially for the LGBTQ+ traveler and Mexico enthusiast. This milky, slightly acidic drink offers a taste of Mexican heritage and a unique experience for those seeking authentic cultural immersion. Explore the depths of this beverage and unlock its secrets, accompanied by insights into the LGBTQ+ friendly destinations and experiences Mexico has to offer.
1. What Is Pulque?
Pulque is a traditional Mexican alcoholic beverage crafted from the fermented sap of the maguey plant, also known as agave. This milky, viscous drink has been enjoyed in Mexico for centuries, dating back to pre-Hispanic times. Its production and consumption are deeply rooted in Mexican culture, especially in central Mexico.
Expanding on Pulque’s Definition
Pulque, often dubbed the “drink of the gods,” is more than just an alcoholic beverage; it’s a cultural icon. The fermentation process gives pulque its distinctive slightly sour and yeasty flavor. It typically has an alcohol content ranging from 4 to 7%. The aguamiel, or sap, is extracted from mature maguey plants. Gaymexico.net provides insights into the cultural significance of pulque, highlighting its role in traditional ceremonies and social gatherings. The drink is associated with various deities, and its consumption was once restricted to religious rituals.
 Tlachiquero extracting aguamiel with an acocote
Tlachiquero extracting aguamiel with an acocote
Why Should You Care About Pulque?
For LGBTQ+ travelers and culture enthusiasts, pulque offers a unique opportunity to connect with Mexico’s rich heritage. Sampling pulque allows you to explore the flavors of Mexico while engaging with local traditions. Gaymexico.net offers recommendations for experiencing pulque in LGBTQ+ friendly environments, ensuring a safe and welcoming experience.
2. What Are The Historical Origins Of Pulque?
Pulque’s history is intertwined with the ancient civilizations of Mexico, dating back to around 2000 BC. The Otomi civilization is believed to be the originators of pulque production. Archaeological evidence shows that maguey plants were used by hunters and gatherers thousands of years ago.
Delving Deeper into Pulque’s Historical Significance
In Aztec culture, pulque, known as metoctli, was a sacred beverage used in religious ceremonies and rituals. Consumption was often restricted to priests and the elderly, with strict rules governing its use. Excessive consumption was severely punished. The god Ometochtli was associated with pulque and drunkenness. According to Fray Bernardino de Sahagún, numerous gods were involved in the Mayahuel‘s gift to humanity. Upon the fall of the Aztec empire, pulque became more accessible to the general population, evolving into a popular beverage.
 Agave species used for aguamiel extraction and pulque production
Agave species used for aguamiel extraction and pulque production
Recent Archaeological Evidence
Recent lipid biomarker analysis of ceramic vessels found in La Ventilla around 200–550 AD detected Zymomonas mobilis, a bacteria known for fermenting pulque. This suggests pulque production existed at the height of Teotihuacan culture.
Pulque During the Spanish Colony
During the Spanish colonial period (1521–1821), pulque production flourished. Haciendas pulqueras (large farms dedicated to agave cultivation and pulque production) emerged in the central Mexican Plateau. Despite attempts to ban pulque due to social and health concerns, its economic importance led to the lifting of the prohibition in 1786.
Pulque in the 19th and 20th Centuries
The late 19th century saw a peak in pulque production, with the introduction of railways facilitating its transportation to major cities. By the early 20th century, production reached approximately 500 million liters per year. However, the Mexican Revolution and subsequent anti-alcohol policies led to a decline in pulque’s popularity, with beer becoming the preferred alcoholic beverage.
3. What Is The Traditional Pulque Production Process?
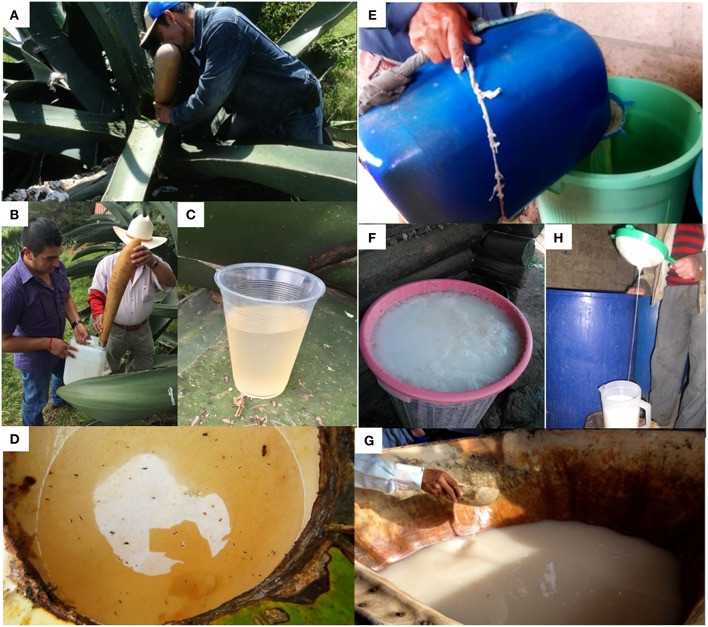
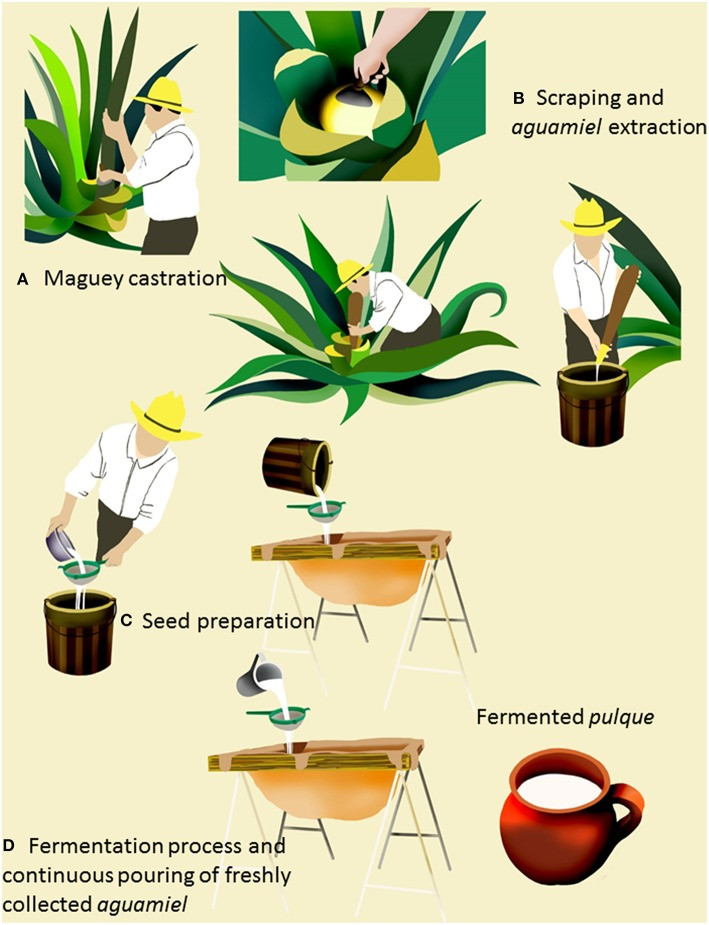
The traditional pulque production process has remained relatively unchanged since pre-Hispanic times. It involves four main steps: maguey castration, pit scraping and aguamiel extraction, seed preparation, and fermentation.
Step 1: Maguey Castration
Mature maguey plants (6 to 15 years old) are selected. The tlachiquero (pulque producer) destroys the embryonic floral peduncle, creating a cavity called a cajete. The cavity is covered to protect it from animals and the environment.
Step 2: Pit Scraping and Aguamiel Extraction
The cajete‘s walls are scraped to induce sap outflow. Aguamiel is collected twice daily using a dried gourd called an acocote. Freshly collected aguamiel is stored in plastic containers and transported to fermentation vats. A mature agave plant can produce aguamiel for 3 to 6 months, yielding 4–6 liters daily.
 Tlachiquero extracting aguamiel with an acocote
Tlachiquero extracting aguamiel with an acocote
Step 3: Seed Preparation
A small amount of previously fermented pulque (“seed”) is mixed with fresh aguamiel in a vat. This mixture undergoes spontaneous fermentation, which takes 1 to 4 weeks.
Step 4: Pulque Fermentation
Fermentation occurs in vats made of leather, fiberglass, plastic, or wood. Freshly collected aguamiel is filtered and added to the vat containing the seed. Fermentation time varies from 3 to 6 hours, although it can sometimes last longer. The final product is either consumed natural or curado (mixed with fruits, vegetables, nuts, or spices).
LGBTQ+ Considerations
Visiting a traditional tinacal or pulqueria can be an immersive experience but assess the environment for LGBTQ+ friendliness. Gaymexico.net can help you identify establishments known for their inclusive atmosphere.
4. What Are The Key Microorganisms Involved In Pulque Fermentation?
Pulque fermentation involves a complex array of microorganisms, including bacteria and yeasts. The main players are lactic acid bacteria (LAB), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast), and Zymomonas mobilis (bacteria).
Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB)
LAB, such as Lactobacillus and Leuconostoc, produce lactic acid, which contributes to pulque’s acidic flavor. Lactobacillus acidophilus is often the dominant bacteria. LAB also produce extracellular polysaccharides (EPS), including dextrans, which contribute to pulque’s viscosity.
Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
S. cerevisiae is the primary yeast responsible for alcoholic fermentation, converting sugars into ethanol.
Zymomonas Mobilis
Z. mobilis is another key bacterium that contributes to alcoholic fermentation. It also produces levans, a type of fructan.
Microbial Succession During Fermentation
The microbial community changes during the fermentation process. Freshly collected aguamiel contains a variety of microorganisms. During fermentation, LAB and yeasts become dominant.
5. What Are The Nutritional And Health Benefits Of Pulque?
Pulque has been recognized for its nutritional and health benefits since pre-Hispanic times. It contains vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and probiotics.
Vitamins and Minerals
Pulque is a source of vitamins C, B vitamins (thiamin, riboflavin, niacin), and minerals such as calcium and iron.
Amino Acids
Pulque contains essential amino acids, although the total protein content is relatively low.
Probiotics
The lactic acid bacteria in pulque have probiotic properties, which may promote gut health.
Historical Use
In 1887, pulque was used to treat scurvy in penitentiary inmates due to its vitamin C content.
Studies on Nutritional Benefits
A study in the indigenous Otomi population of the Valle del Mezquital found that daily pulque intake contributed significantly to their intake of calories, protein, vitamins, and minerals.
Considerations
It’s worth noting that pulque contains alcohol, so moderation is key. The health benefits should be weighed against the potential risks of alcohol consumption.
6. What Are The Potential Probiotic Benefits Of LAB Isolated From Pulque?
The LAB found in pulque have potential probiotic properties that could promote gut health.
Specific Strains
Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus plantarum are commonly found in pulque and are known for their probiotic properties.
Research Findings
Studies have shown that LAB isolated from pulque can survive gastrointestinal conditions and exhibit antimicrobial activity against pathogens. Some strains have shown in vitro and in vivo probiotic properties.
Antimicrobial Activity
Some LAB strains produce bacteriocins, which are antimicrobial peptides that can inhibit the growth of other bacteria.
Potential Applications
These LAB could be used in the development of non-dairy-based functional foods with probiotic benefits.
7. What Is “Pulque Curado”?
Pulque curado is pulque that has been flavored with fruits, vegetables, nuts, or spices. This practice adds variety and enhances the flavor of the beverage.
Popular Flavors
Common curado flavors include guava, mango, strawberry, pineapple, and oatmeal. The added ingredients macerate in the pulque, infusing it with their flavor.
Regional Variations
The specific flavors of pulque curado vary by region, reflecting local ingredients and culinary traditions.
How to Enjoy Curado
Many pulquerías offer a variety of curado flavors. It’s a great way to sample different tastes and find your favorite.
LGBTQ+ Friendly Pulquerias
Gaymexico.net can guide you to LGBTQ+ friendly pulquerías where you can safely enjoy pulque curado.
8. Where Can You Find Authentic Pulque in Mexico?
Authentic pulque is primarily found in central Mexico, particularly in Mexico City and the states of Hidalgo, Tlaxcala, and Puebla.
Pulquerías
Pulquerías are traditional establishments that serve pulque. These establishments often have a rustic atmosphere and are frequented by locals.
Mexico City
Mexico City has a number of pulquerías where you can sample different types of pulque. Some popular pulquerías include:
- Las Duelistas: One of the oldest and most famous pulquerías in Mexico City.
- La Nuclear: Known for its strong pulque and lively atmosphere.
- El Salón Casino: A historic pulquería with a wide variety of curados.
Hidalgo, Tlaxcala, and Puebla
These states are major pulque-producing regions, and you can find authentic pulque in local markets and pulquerías.
LGBTQ+ Considerations
When visiting pulquerías, consider the safety and inclusivity of the establishment. Some may be more welcoming to LGBTQ+ individuals than others.
9. What Are The Challenges Facing Pulque Production Today?
Pulque production faces several challenges, including competition from beer, lack of investment in technology, and the perishable nature of the beverage.
Competition from Beer
Beer has become the dominant alcoholic beverage in Mexico, overshadowing pulque’s popularity.
Lack of Investment in Technology
Pulque production has seen limited investment in science and technology, hindering its modernization and scalability.
Perishable Nature
Pulque is a perishable beverage with a short shelf life, making it difficult to transport and store.
Agave Maturation Time
Agave plants take several years to mature, which can limit the supply of aguamiel.
Industrialization Efforts
Efforts to industrialize pulque production have faced challenges in maintaining the quality and authenticity of the beverage.
10. How Is Science And Technology Contributing To Pulque Production?
Despite the challenges, science and technology are playing an increasing role in pulque production.
Microbiology Research
Research is focused on identifying and characterizing the microorganisms involved in pulque fermentation.
Probiotic Studies
Studies are investigating the probiotic properties of LAB isolated from pulque.
Genomics and Metagenomics
Genomic and metagenomic approaches are being used to study the microbial communities in pulque and identify key genes involved in fermentation.
Technological Innovations
Efforts are underway to develop technologies for stabilizing and preserving pulque without compromising its quality.
Efforts to Increase Awareness
Organizations are promoting pulque and its cultural significance.
11. How Can You Enjoy Pulque Responsibly and Respectfully?
To fully appreciate and respect the cultural significance of pulque, it’s important to enjoy it responsibly and respectfully.
Moderation
Pulque contains alcohol, so drink in moderation.
Respect Local Customs
When visiting pulquerías, respect local customs and traditions.
Support Local Producers
Purchase pulque from local producers to support the traditional industry.
Learn About Its History
Take the time to learn about pulque’s history and cultural significance.
LGBTQ+ Considerations
Choose LGBTQ+ friendly establishments where you can feel safe and welcome.
12. What Is The Significance Of Pulque In Modern Mexican Culture?
Pulque, despite facing numerous challenges, remains a significant part of modern Mexican culture.
Cultural Heritage
Pulque is a symbol of Mexican cultural heritage, representing a connection to the country’s ancient civilizations.
Regional Identity
Pulque production is an important part of the regional identity of central Mexico.
Gastronomic Tourism
Pulque is attracting interest from gastronomic tourists who want to experience authentic Mexican cuisine.
Social Gatherings
Pulque continues to be enjoyed in social gatherings and celebrations.
Revival Efforts
Efforts are underway to revive pulque production and promote its cultural significance.
13. How Do Agave Fructans Benefit Health?
Agave fructans are beneficial for health. Aguamiel from A. mapisaga “Blanco” contains inuline-type fructans (10.2% wt in dry matter) and glucooligosaccharides. Due to the high fructan and fructooligosaccharide (FOS) content, agave extracts as well as the sap (consumed directly or concentrated) from different species, have been considered as an alternative source for prebiotic FOS syrups. This type of food additives has received increased attention due to its low glycemic index and, their demonstrated beneficial health effects such as improving calcium absorption in postmenopausal women, iron absorption, and, colon cancer prevention.
14. What Are the Functional Properties of EPS Produced by LAB Detected in Aguamiel and Pulque?
Some EPS produced by LAB isolated from aguamiel and pulque have been purified and characterized. Results include the identification of dextran with a linear backbone linked in α1 → 6 D-Glcp linkages with branching in α1 → 3 D-Glcp produced by a cell-associated glycosyltransferase (GTF) from L. mesenteroides isolated from pulque. In the same context, two EPS LAB identified as L. kimchii were isolated from pulque produced in Huitzilac, in the state of Morelos. EPS and hetero-oligosaccharides produced by diverse LAB species, including those found in pulque, have gained attention because of their use as food additives and potential natural functional ingredients.
15. What Are the Challenges Associated With Pulque Production?
Probably the main challenge associated with the industrialization of pulque is related to the natural substrate availability and the need for the introduction of a stabilization processes of the fermented product. Aguamiel differs from almost all other fermented beverages such as wine, beer or tepache (pineapple wine), in that agave, the raw material, takes 7 years to reach maturity. Furthermore, when ready for production, aguamiel has to be collected from the plant on a daily basis, and not produced by a single extraction, as it is usually the case for fermented beverages.
16. What are Some Safety Tips For LGBTQ+ Travelers in Mexico?
Mexico is generally welcoming to LGBTQ+ travelers, but here are some safety tips to keep in mind:
- Research LGBTQ+-friendly destinations and accommodations.
- Be aware of local laws and customs.
- Avoid public displays of affection in more conservative areas.
- Use reputable transportation services.
- Stay informed about current events and safety advisories.
- Trust your instincts and avoid situations that make you uncomfortable.
- Connect with local LGBTQ+ communities for support and information.
Gaymexico.net provides resources and information to help LGBTQ+ travelers stay safe and informed.
17. Where Can LGBTQ+ Travelers Find Support and Resources in Mexico?
LGBTQ+ travelers can find support and resources from local LGBTQ+ organizations. Gaymexico.net offers a directory of LGBTQ+ resources in Mexico, including:
- Community centers
- Support groups
- Advocacy organizations
- Helplines
- Cultural events
- Businesses that support the LGBTQ+ community
- Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States
- Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177
- Website: gaymexico.net
18. What Are The Ethical Considerations Of Consuming Pulque?
When consuming pulque, it’s important to consider the ethical implications of your choices.
Support Local Producers
By purchasing pulque from local producers, you are supporting their livelihoods and helping to preserve traditional practices.
Sustainable Production
Choose pulque that is produced using sustainable methods to minimize environmental impact.
Fair Trade Practices
Support producers who adhere to fair trade practices, ensuring that workers are treated fairly and receive fair wages.
Environmental Impact
Be mindful of the environmental impact of pulque production, including the use of water and land resources.
19. What Are Some Alternative Beverages To Pulque?
If you are unable to find or consume pulque, here are some alternative Mexican beverages to try:
- Tequila: A distilled spirit made from blue agave.
- Mezcal: A distilled spirit made from various types of agave.
- Beer: Mexico has a thriving craft beer scene.
- Tepache: A fermented beverage made from pineapple.
- Agua Frescas: Non-alcoholic fruit-flavored drinks.
20. What Are Some Frequently Asked Questions About Pulque?
Here are some frequently asked questions about pulque:
- What does pulque taste like? Pulque has a slightly sour, yeasty flavor that is often described as earthy.
- How is pulque made? Pulque is made by fermenting the sap of the maguey plant.
- Is pulque alcoholic? Yes, pulque typically has an alcohol content of 4 to 7%.
- Where can I find pulque? Pulque is primarily found in central Mexico.
- Is pulque safe to drink? Pulque is generally safe to drink if it is produced and stored properly.
- What is pulque curado? Pulque curado is pulque that has been flavored with fruits, vegetables, nuts, or spices.
- What are the health benefits of pulque? Pulque contains vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and probiotics.
- How should I drink pulque? Pulque is traditionally served in a glass or clay cup.
- What is the cultural significance of pulque? Pulque has been a significant part of Mexican culture for centuries, dating back to pre-Hispanic times.
- Where can I find more information about pulque and LGBTQ+ travel in Mexico? Visit gaymexico.net for more information.
Explore Mexico’s LGBTQ+ scene with us, and discover the magic of pulque and the warmth of Mexican culture. We offer safe and reliable information, so you can plan your trip with confidence. From vibrant cities to hidden gems, let gaymexico.net be your trusted companion!
Ready to explore the wonders of Mexico? Visit gaymexico.net to discover LGBTQ+ friendly travel guides, insider tips, and connect with a welcoming community! Plan your adventure today and experience the best of Mexico!