Are you curious about what food the US imports from Mexico, especially if you’re part of the LGBTQ+ community and planning a trip? At gaymexico.net, we’ve got the answers! Mexico is a major source of fresh produce for the United States, offering a wide variety of delicious and essential ingredients. Let’s explore the flavorful world of Mexican imports, catering to your adventurous palate and travel interests, complete with details on cultural significance and travel tips for the discerning LGBTQ+ traveler.
1. Why Does the US Import Food From Mexico?
The US imports a significant amount of food from Mexico due to factors like favorable climate, lower labor costs, and trade agreements. This allows for a consistent supply of fresh produce year-round, enhancing culinary experiences and travel opportunities, especially for the LGBTQ+ community exploring Mexico’s diverse food scene.
Climate and Growing Seasons
Mexico’s diverse climate allows for year-round growing seasons for many fruits and vegetables. This contrasts with the seasonal limitations in many parts of the United States, particularly during winter months. The warm climate provides ideal conditions for crops such as tomatoes, avocados, peppers, and berries, ensuring a consistent supply for the US market.
Cost-Effectiveness
Lower labor costs in Mexico make it more economical to produce certain crops compared to the United States. This cost advantage allows Mexican farmers to offer produce at competitive prices, benefiting both consumers and businesses in the US. According to a report by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), labor costs in Mexico can be significantly lower, contributing to the overall affordability of imported produce.
Trade Agreements
Trade agreements such as the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) facilitate the smooth exchange of goods between the two countries. These agreements reduce tariffs and trade barriers, making it easier and more affordable for US companies to import food from Mexico. The USMCA has played a crucial role in strengthening the agricultural trade relationship between the US and Mexico.
Consumer Demand
US consumers have a growing demand for a variety of fresh produce year-round. This demand cannot always be met by domestic production alone, especially for certain fruits and vegetables that thrive in Mexico’s climate. Imports from Mexico help to fill this gap and provide consumers with a wider selection of fresh and healthy options. This trend is supported by data from the USDA’s Economic Research Service, which shows a steady increase in the volume of fresh vegetable imports over the past two decades.
Proximity and Logistics
Mexico’s geographical proximity to the United States makes it an ideal trading partner. The relatively short distance reduces transportation costs and ensures that produce arrives fresh and in good condition. Efficient logistics and transportation networks facilitate the quick and reliable delivery of goods across the border. This logistical advantage is particularly important for perishable items that require timely delivery to maintain their quality and freshness.
2. What are the Top Food Imports from Mexico to the US?
Mexico exports a wide range of food products to the US, with fresh produce being a significant component. The top imports include avocados, tomatoes, bell peppers, cucumbers, berries, and mangoes. These products enrich the US culinary scene and offer diverse options for consumers, aligning with the preferences of LGBTQ+ travelers seeking authentic flavors and experiences in Mexico.
Avocados
Avocados are one of the most popular and valuable food imports from Mexico. The US has a high demand for avocados, driven by their nutritional benefits and versatility in various dishes, from guacamole to salads. Mexico is the world’s largest producer of avocados, and a significant portion of its production is exported to the US. According to data from the USDA, avocado imports from Mexico have steadily increased over the years, making it a staple in American households and restaurants.
 Avocados are one of the most popular and valuable food imports from Mexico, perfect for guacamole and salads.
Avocados are one of the most popular and valuable food imports from Mexico, perfect for guacamole and salads.
Tomatoes
Tomatoes are another major food import from Mexico. They are used extensively in the US food industry, appearing in everything from sauces and salsas to salads and sandwiches. Mexico’s climate allows for year-round tomato production, ensuring a consistent supply to meet US demand. Both field-grown and greenhouse tomatoes are imported, providing consumers with a variety of options. The USDA reports that Mexico is a leading supplier of tomatoes to the US market, contributing significantly to the overall availability of this essential vegetable.
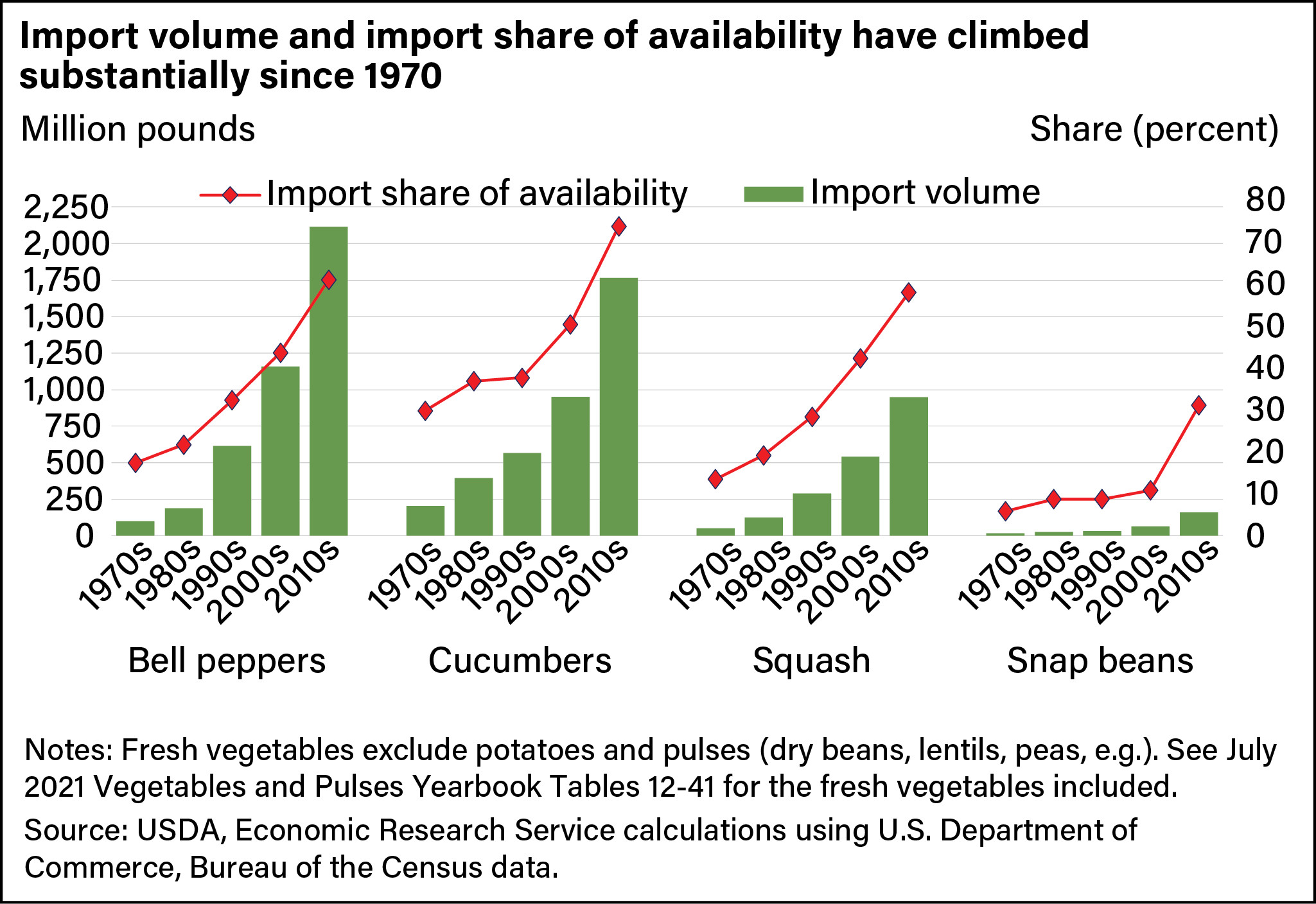
Bell Peppers
Bell peppers are also among the top food imports from Mexico. They are popular in American cuisine for their color, flavor, and versatility. Mexico’s growing regions provide ideal conditions for bell pepper cultivation, and the country exports significant quantities to the US. Bell peppers are used in a wide range of dishes, including stir-fries, salads, and stuffed peppers. Data from the USDA indicates that bell pepper imports from Mexico have been on the rise, reflecting the increasing demand for this vegetable in the US market.
Cucumbers
Cucumbers are another key vegetable import from Mexico. They are widely used in salads, pickles, and other culinary applications. Mexico’s climate and growing practices allow for a consistent supply of cucumbers to the US market throughout the year. Both conventional and greenhouse-grown cucumbers are imported, catering to different consumer preferences. The USDA reports that cucumber imports from Mexico have been steadily increasing, contributing to the overall availability of this refreshing vegetable in the US.
Berries
Berries, including strawberries, blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries, are a significant category of food imports from Mexico. The US has a high demand for berries, driven by their nutritional benefits and popularity as a snack and ingredient in various dishes. Mexico’s climate and growing regions provide ideal conditions for berry cultivation, and the country exports significant quantities to the US. According to data from the USDA, berry imports from Mexico have been on the rise, reflecting the increasing consumer demand for these healthy and delicious fruits.
Mangoes
Mangoes are a popular tropical fruit import from Mexico. They are enjoyed in the US for their sweet flavor and versatility in various dishes, from smoothies to salads. Mexico is a major producer of mangoes, and a significant portion of its production is exported to the US. The USDA reports that mango imports from Mexico have been steadily increasing, contributing to the overall availability of this tropical fruit in the US market.
3. How Does Importing Food From Mexico Affect the US Economy?
Importing food from Mexico has both positive and negative effects on the US economy. It provides consumers with access to a wider variety of affordable produce, but it can also create competition for domestic farmers. Understanding these economic impacts is crucial for informed travel and supporting sustainable practices, especially for LGBTQ+ travelers who value ethical consumption.
Benefits
- Access to Affordable Produce: Importing food from Mexico often leads to lower prices for consumers, as production costs in Mexico are generally lower than in the US. This affordability allows households, especially those with lower incomes, to access a wider variety of fresh fruits and vegetables. According to a report by the Economic Research Service (ERS) of the USDA, the increased availability of Mexican produce helps stabilize food prices and ensures a consistent supply for consumers.
- Year-Round Availability: Mexico’s diverse climate allows for year-round cultivation of many crops, ensuring that US consumers have access to fresh produce even during the off-season in domestic production areas. This continuous supply is particularly important for fruits and vegetables like tomatoes, avocados, and berries, which are in high demand throughout the year.
- Meeting Consumer Demand: The US has a high demand for certain types of produce that cannot be entirely met by domestic production. Importing food from Mexico helps to fill this gap, ensuring that consumers have access to the variety and quantity of produce they desire. This is especially true for specialty items and tropical fruits that are not commonly grown in the US.
- Supporting US Businesses: The import of food from Mexico supports various US businesses involved in transportation, distribution, and retail. These businesses benefit from the increased volume of trade and contribute to the overall economic activity in the US. Additionally, many US companies have investments in Mexican agriculture, further strengthening the economic ties between the two countries.
Challenges
- Competition for Domestic Farmers: One of the main concerns is the increased competition faced by US farmers. Lower production costs in Mexico can make it difficult for US farmers to compete, potentially leading to reduced market share and lower profits. This is particularly challenging for small and medium-sized farms that may not have the resources to compete with large-scale Mexican agricultural operations.
- Job Displacement: As US farmers face increased competition, there is a risk of job displacement in the agricultural sector. Reduced production can lead to fewer employment opportunities for farmworkers and related industries. This can have a significant impact on rural communities that rely heavily on agriculture for their economic stability.
- Environmental Concerns: The increased demand for imported produce can lead to unsustainable agricultural practices in Mexico, such as overuse of water resources and deforestation. These environmental issues can have long-term consequences for the region and can indirectly affect the US through environmental degradation and resource depletion.
- Food Safety Regulations: Ensuring that imported food meets US safety standards can be challenging. While there are regulations in place to monitor food safety, there is always a risk of contaminated or unsafe produce entering the US market. This requires ongoing vigilance and investment in food safety inspections and monitoring programs.
4. Which Regions in Mexico Export the Most Food to the US?
Several regions in Mexico are major exporters of food to the US, including Baja California, Sinaloa, and Michoacán. These regions have favorable climates and well-developed agricultural industries. Exploring these regions can offer LGBTQ+ travelers unique insights into Mexican culture and sustainable tourism opportunities.
Baja California
Baja California is a key agricultural region in Mexico, known for its production of tomatoes, strawberries, and various vegetables. Its proximity to the US border and favorable climate make it an ideal location for export-oriented agriculture.
- Tomatoes: Baja California is a significant producer of tomatoes, both for domestic consumption and export. The region’s mild climate and advanced agricultural techniques allow for year-round tomato production.
- Strawberries: Strawberries are another important crop in Baja California. The region’s climate is well-suited for strawberry cultivation, and the state exports a significant quantity of strawberries to the US.
- Vegetables: In addition to tomatoes and strawberries, Baja California also produces a variety of other vegetables for export, including bell peppers, cucumbers, and squash.
Sinaloa
Sinaloa is another major agricultural region in Mexico, known as the “Granary of Mexico.” It produces a wide range of crops, including tomatoes, cucumbers, bell peppers, and mangoes.
- Tomatoes: Sinaloa is one of Mexico’s largest tomato-producing regions. The state’s extensive irrigation systems and favorable climate allow for large-scale tomato cultivation.
- Cucumbers: Sinaloa is also a significant producer of cucumbers, both for domestic consumption and export. The region’s agricultural practices are well-suited for cucumber cultivation.
- Bell Peppers: Bell peppers are another important crop in Sinaloa. The state’s growing regions provide ideal conditions for bell pepper cultivation, and the state exports significant quantities to the US.
- Mangoes: Sinaloa is also a major producer of mangoes. The state’s tropical climate is ideal for mango cultivation, and the state exports a significant quantity of mangoes to the US.
Michoacán
Michoacán is best known for its avocado production, but it also produces a variety of other crops, including berries and limes.
- Avocados: Michoacán is the world’s largest avocado-producing region. The state’s climate and soil conditions are ideal for avocado cultivation, and the state exports a significant quantity of avocados to the US.
- Berries: Michoacán is also a significant producer of berries, including strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries. The region’s climate is well-suited for berry cultivation, and the state exports a growing quantity of berries to the US.
- Limes: Michoacán is also a major producer of limes. The state’s tropical climate is ideal for lime cultivation, and the state exports a significant quantity of limes to the US.
Other Key Regions
- Guanajuato: Known for its broccoli, lettuce, and cauliflower production.
- Jalisco: Famous for its agave (used to make tequila) and berries.
- Sonora: Produces grapes, watermelons, and other fruits.
5. What are the Food Safety Regulations for Mexican Food Imports to the US?
The US has strict food safety regulations for all imported foods, including those from Mexico. These regulations are enforced by agencies like the FDA and USDA to protect public health. Staying informed about these regulations can enhance your travel experiences and ensure responsible consumption, aligning with the values of many LGBTQ+ travelers.
Regulatory Agencies
The primary agencies responsible for overseeing food safety regulations for Mexican food imports to the US are the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA): The FDA is responsible for regulating most food products imported into the US, including fruits, vegetables, seafood, and processed foods. The FDA ensures that these products meet US safety standards and are properly labeled.
- United States Department of Agriculture (USDA): The USDA is responsible for regulating meat, poultry, and certain egg products. The USDA ensures that these products meet US safety standards and are properly inspected.
Key Regulations
Several key regulations govern the safety of Mexican food imports to the US.
- Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA): The FSMA is a landmark law that aims to prevent foodborne illnesses by shifting the focus from responding to food safety problems to preventing them. The FSMA includes several key provisions that affect food imports, including:
- Preventive Controls for Human Food: Requires food facilities to implement preventive controls to minimize the risk of food safety hazards.
- Produce Safety Rule: Establishes science-based standards for the safe growing, harvesting, packing, and holding of fruits and vegetables.
- Foreign Supplier Verification Program (FSVP): Requires importers to verify that their foreign suppliers are producing food in a manner that meets US safety standards.
- Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) Measures: These measures are used to protect human, animal, and plant health from pests and diseases. The USDA’s Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (APHIS) works to prevent the introduction and spread of pests and diseases that could harm US agriculture.
- Country of Origin Labeling (COOL): COOL requires retailers to inform consumers of the country of origin of certain food products, including fruits, vegetables, and meats. This allows consumers to make informed choices about the food they purchase.
Inspection and Enforcement
The FDA and USDA conduct inspections of food facilities and imported food products to ensure compliance with US safety standards.
- FDA Inspections: The FDA conducts inspections of foreign food facilities that export to the US. These inspections are designed to verify that the facilities are meeting US safety standards and are implementing preventive controls.
- USDA Inspections: The USDA conducts inspections of meat, poultry, and egg products imported into the US. These inspections are designed to ensure that the products meet US safety standards and are properly labeled.
- Port of Entry Inspections: Both the FDA and USDA conduct inspections of food products at US ports of entry. These inspections are designed to detect and prevent the entry of unsafe or non-compliant food products.
Challenges and Improvements
Despite the robust regulatory framework, there are ongoing challenges in ensuring the safety of Mexican food imports to the US.
- Complexity of Supply Chains: The complexity of modern food supply chains makes it difficult to trace food products back to their source. This can make it challenging to identify and address food safety problems.
- Resource Constraints: Both the FDA and USDA face resource constraints that can limit their ability to conduct inspections and enforce regulations.
- Evolving Food Safety Risks: New and emerging food safety risks, such as antibiotic-resistant bacteria and novel food technologies, require ongoing vigilance and adaptation of regulatory strategies.
6. How Do Trade Agreements Like USMCA Affect Food Imports From Mexico?
Trade agreements like the USMCA significantly impact food imports from Mexico by reducing tariffs and facilitating trade. This can lead to increased availability of Mexican produce in the US but also raises concerns about competition for domestic farmers. Understanding these impacts can inform your travel decisions and support local economies, aligning with the values of many LGBTQ+ travelers.
Overview of USMCA
The United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) is a trade agreement between the three countries that replaced the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) in 2020. The USMCA aims to modernize trade relations and address some of the concerns raised under NAFTA.
Impact on Food Imports
The USMCA has several key provisions that affect food imports from Mexico.
- Reduced Tariffs: The USMCA maintains the zero-tariff policy for most agricultural products traded between the US and Mexico. This means that there are no tariffs on the vast majority of food imports from Mexico, making it more affordable for US businesses to import these products.
- Streamlined Customs Procedures: The USMCA includes provisions to streamline customs procedures and reduce red tape. This makes it easier and faster for food products to cross the border, reducing transportation costs and ensuring that produce arrives fresh.
- Increased Market Access: The USMCA includes provisions to increase market access for certain agricultural products. For example, the agreement includes provisions to increase US access to the Canadian dairy market and to address concerns about Canadian wheat grading practices.
- Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures: The USMCA includes provisions to strengthen sanitary and phytosanitary (SPS) measures. These measures are designed to protect human, animal, and plant health from pests and diseases. The agreement includes provisions to enhance cooperation and information sharing on SPS issues, which can help to prevent the spread of foodborne illnesses.
Benefits for US Consumers
The USMCA has several potential benefits for US consumers.
- Increased Availability of Affordable Produce: The USMCA is likely to lead to increased availability of affordable produce from Mexico. The zero-tariff policy and streamlined customs procedures make it more affordable for US businesses to import Mexican produce, which can lead to lower prices for consumers.
- Year-Round Availability of Fresh Produce: Mexico’s climate allows for year-round cultivation of many crops, ensuring that US consumers have access to fresh produce even during the off-season in domestic production areas. The USMCA helps to facilitate this year-round availability by reducing trade barriers and promoting efficient supply chains.
- Greater Variety of Food Products: The USMCA is likely to lead to a greater variety of food products available to US consumers. The agreement makes it easier for US businesses to import specialty items and tropical fruits from Mexico, which can enhance the culinary experiences of US consumers.
Concerns for US Farmers
Despite the potential benefits for consumers, the USMCA has raised concerns among US farmers.
- Increased Competition: The USMCA is likely to lead to increased competition for US farmers. The zero-tariff policy and streamlined customs procedures make it easier for Mexican farmers to export their products to the US, which can put downward pressure on prices and reduce market share for US farmers.
- Labor Costs: Lower labor costs in Mexico can make it difficult for US farmers to compete. Mexican farmers often pay lower wages and have fewer labor regulations than US farmers, which can give them a cost advantage.
- Environmental Regulations: Some US farmers have raised concerns about the environmental regulations in Mexico. They argue that Mexican farmers may not be subject to the same environmental standards as US farmers, which can give them a competitive advantage.
Potential Solutions
To address these concerns, several potential solutions have been proposed.
- Strengthening Domestic Support Programs: The US government could strengthen domestic support programs for US farmers, such as crop insurance and price supports. These programs can help to level the playing field and ensure that US farmers can compete effectively.
- Enforcing Environmental Regulations: The US government could work with the Mexican government to enforce environmental regulations and ensure that Mexican farmers are meeting the same environmental standards as US farmers.
- Promoting Fair Trade Practices: The US government could promote fair trade practices and ensure that Mexican farmers are paying fair wages and providing safe working conditions for their workers.
7. What is the Impact of Climate Change on Food Production in Mexico and its Exports to the US?
Climate change poses significant challenges to food production in Mexico, potentially affecting the availability and quality of its exports to the US. Droughts, floods, and extreme weather events can disrupt agricultural practices and reduce crop yields. Supporting sustainable farming practices can mitigate these impacts, aligning with the values of environmentally conscious LGBTQ+ travelers.
Climate Change Impacts
Climate change is expected to have several significant impacts on food production in Mexico.
- Increased Temperatures: Rising temperatures can reduce crop yields and increase water demand for irrigation. Many crops are sensitive to high temperatures, and even a small increase in temperature can have a significant impact on production.
- Changes in Precipitation Patterns: Climate change is expected to alter precipitation patterns, leading to more frequent and severe droughts in some areas and increased flooding in others. These changes can disrupt agricultural practices and reduce crop yields.
- Extreme Weather Events: Climate change is expected to increase the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, heatwaves, and cold snaps. These events can damage crops and infrastructure, leading to significant economic losses for farmers.
Impacts on Food Production
These climate change impacts are expected to have several effects on food production in Mexico.
- Reduced Crop Yields: Rising temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events are all expected to reduce crop yields for many important crops, such as corn, beans, and wheat.
- Increased Water Scarcity: Climate change is expected to exacerbate water scarcity in many parts of Mexico, making it more difficult to irrigate crops and raise livestock.
- Shifts in Growing Seasons: Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns are expected to shift growing seasons for many crops, making it more difficult for farmers to plan their planting and harvesting schedules.
- Increased Pest and Disease Pressure: Climate change is expected to increase pest and disease pressure on crops, making it more difficult for farmers to control pests and diseases and reducing crop yields.
Impacts on Exports to the US
These changes in food production are likely to have several impacts on Mexico’s exports to the US.
- Reduced Export Volumes: Reduced crop yields and increased water scarcity are likely to reduce the volume of food that Mexico is able to export to the US.
- Increased Prices: Reduced export volumes are likely to lead to increased prices for Mexican food products in the US.
- Changes in Crop Quality: Climate change is likely to affect the quality of Mexican food products. For example, rising temperatures can reduce the sugar content of fruits and vegetables, making them less desirable to consumers.
- Increased Food Safety Risks: Climate change is expected to increase food safety risks, such as the spread of foodborne illnesses and the contamination of food products with pesticides and other chemicals.
Potential Solutions
To address these challenges, several potential solutions have been proposed.
- Investing in Climate-Resilient Agriculture: The Mexican government could invest in climate-resilient agriculture practices, such as drought-resistant crops, water-efficient irrigation techniques, and soil conservation measures.
- Promoting Sustainable Agriculture: The Mexican government could promote sustainable agriculture practices, such as organic farming and integrated pest management. These practices can help to reduce the environmental impacts of agriculture and improve the resilience of food production systems.
- Strengthening Food Safety Regulations: The Mexican government could strengthen food safety regulations to ensure that Mexican food products meet US safety standards.
- Investing in Research and Development: The Mexican government could invest in research and development to develop new technologies and practices that can help farmers adapt to climate change.
8. Are There Ethical Concerns Related to Importing Food From Mexico?
Yes, there are ethical concerns related to importing food from Mexico, including labor practices, environmental sustainability, and the impact on small-scale farmers. Supporting fair trade and responsible sourcing can address these concerns, aligning with the values of many LGBTQ+ travelers who prioritize ethical and sustainable tourism.
Labor Practices
One of the primary ethical concerns related to importing food from Mexico is the labor practices used in the agricultural sector.
- Low Wages: Agricultural workers in Mexico often earn very low wages, which can make it difficult for them to support their families.
- Poor Working Conditions: Agricultural workers in Mexico often work in harsh conditions, with long hours, exposure to pesticides, and limited access to healthcare and other benefits.
- Child Labor: Child labor is a problem in some agricultural regions of Mexico. Children are often employed in hazardous jobs, such as harvesting crops and applying pesticides.
Environmental Sustainability
Another ethical concern is the environmental sustainability of agricultural practices in Mexico.
- Deforestation: Deforestation is a problem in some agricultural regions of Mexico. Forests are often cleared to make way for new agricultural land, which can lead to soil erosion, loss of biodiversity, and climate change.
- Water Pollution: Agriculture can contribute to water pollution through the use of pesticides, fertilizers, and other chemicals. These chemicals can contaminate surface water and groundwater, harming aquatic ecosystems and human health.
- Soil Erosion: Agriculture can contribute to soil erosion, which can reduce soil fertility and lead to sedimentation of waterways.
Impact on Small-Scale Farmers
The import of food from Mexico can have a negative impact on small-scale farmers in both Mexico and the US.
- Competition: Small-scale farmers often struggle to compete with large-scale agricultural operations, which can produce food at lower costs due to economies of scale.
- Loss of Livelihoods: The import of food from Mexico can lead to the loss of livelihoods for small-scale farmers, who may be forced to sell their land or abandon farming altogether.
- Dependence on Global Markets: The import of food from Mexico can make small-scale farmers dependent on global markets, which can be volatile and unpredictable.
Potential Solutions
To address these ethical concerns, several potential solutions have been proposed.
- Promoting Fair Trade: Promoting fair trade practices can help to ensure that agricultural workers in Mexico are paid fair wages and have safe working conditions.
- Supporting Sustainable Agriculture: Supporting sustainable agriculture practices can help to reduce the environmental impacts of agriculture and improve the livelihoods of small-scale farmers.
- Enforcing Labor and Environmental Regulations: Enforcing labor and environmental regulations can help to protect workers and the environment.
- Supporting Local Food Systems: Supporting local food systems can help to reduce the dependence on global markets and promote the livelihoods of small-scale farmers.
9. What are Some Sustainable Options for Consuming Food Imported from Mexico?
Choosing sustainable options for consuming food imported from Mexico can reduce your environmental impact and support ethical practices. Look for certifications like Fair Trade and organic labels, and prioritize seasonal produce. Supporting local farmers’ markets and community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs can also make a difference, aligning with the values of environmentally conscious LGBTQ+ travelers.
Fair Trade Certification
Fair Trade certification ensures that farmers and workers in developing countries receive fair prices for their products and have safe working conditions. When you purchase Fair Trade certified products, you are supporting ethical labor practices and helping to improve the lives of farmers and workers.
Organic Certification
Organic certification ensures that food products are produced without the use of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Organic farming practices are more environmentally sustainable and can help to protect soil and water resources.
Seasonal Produce
Eating seasonal produce can reduce your environmental impact by reducing the need for long-distance transportation and energy-intensive storage. When you eat seasonal produce, you are supporting local farmers and reducing your carbon footprint.
Local Farmers’ Markets
Shopping at local farmers’ markets is a great way to support local farmers and reduce your environmental impact. Farmers’ markets offer fresh, seasonal produce that is often grown using sustainable farming practices.
Community Supported Agriculture (CSA)
Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) programs allow you to purchase a share of a local farm’s harvest. By joining a CSA, you are supporting local farmers and receiving fresh, seasonal produce throughout the growing season.
Reducing Food Waste
Reducing food waste is an important way to reduce your environmental impact. When you waste food, you are wasting the resources that were used to produce, transport, and store that food. You can reduce food waste by planning your meals, storing food properly, and composting food scraps.
Supporting Sustainable Agriculture Initiatives
Supporting sustainable agriculture initiatives can help to promote more environmentally friendly and ethical farming practices. You can support these initiatives by donating to organizations that promote sustainable agriculture, volunteering on local farms, and advocating for policies that support sustainable agriculture.
10. How Can LGBTQ+ Travelers Support Sustainable and Ethical Food Consumption in Mexico?
LGBTQ+ travelers can support sustainable and ethical food consumption in Mexico by choosing restaurants that source local and organic ingredients, visiting farmers’ markets, and supporting LGBTQ+-owned businesses committed to sustainability. You can also educate yourself about local food systems and advocate for responsible tourism practices, aligning with the values of community and sustainability.
Choose Restaurants that Source Local and Organic Ingredients
One of the best ways to support sustainable and ethical food consumption in Mexico is to choose restaurants that prioritize local and organic ingredients. These restaurants are committed to supporting local farmers and reducing their environmental impact. Look for restaurants that advertise their use of local and organic ingredients on their menus or websites.
Visit Farmers’ Markets
Farmers’ markets are a great place to find fresh, seasonal produce that is grown by local farmers. By visiting farmers’ markets, you are supporting local agriculture and reducing your carbon footprint. Farmers’ markets also offer a unique opportunity to interact with local farmers and learn about their farming practices.
Support LGBTQ+-Owned Businesses Committed to Sustainability
Supporting LGBTQ+-owned businesses that are committed to sustainability is another great way to promote ethical food consumption in Mexico. These businesses are often committed to using sustainable practices and supporting local communities. Look for LGBTQ+-owned restaurants, cafes, and food shops that prioritize sustainability.
Educate Yourself About Local Food Systems
Educating yourself about local food systems is an important step in supporting sustainable and ethical food consumption. Learn about the challenges and opportunities facing local farmers and food producers. This knowledge will help you make more informed choices about the food you eat and the businesses you support.
Advocate for Responsible Tourism Practices
As a traveler, you can advocate for responsible tourism practices that support sustainable food consumption. Encourage hotels, tour operators, and other tourism businesses to prioritize local and organic ingredients, reduce food waste, and support local communities.
Reduce Food Waste
Reducing food waste is an important way to minimize your environmental impact while traveling. Be mindful of portion sizes, store food properly, and compost food scraps whenever possible.
Support Local Initiatives
Look for opportunities to support local initiatives that promote sustainable agriculture and food security. This could include donating to local food banks, volunteering on local farms, or participating in community gardening projects.
Choose Eco-Friendly Accommodations
When booking accommodations, opt for eco-friendly hotels or guesthouses that prioritize sustainability. These accommodations often source local and organic food, reduce waste, and conserve resources.
Participate in Cooking Classes
Participating in cooking classes that focus on traditional Mexican cuisine can provide valuable insights into local food systems and sustainable cooking practices. You’ll learn how to prepare delicious meals using fresh, seasonal ingredients and support local culinary traditions.
At gaymexico.net, we’re dedicated to providing you with the best information for your travels, ensuring you can explore Mexico safely and ethically. Discover more about LGBTQ+ friendly destinations, sustainable practices, and connect with the community. Join us to make your travel experiences unforgettable. Contact us at Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States. Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177. Website: gaymexico.net, and start planning your adventure today!