Are you curious about the countries that share a border with Mexico, a nation known for its vibrant culture, delicious cuisine, and welcoming LGBTQ+ scene? At gaymexico.net, we’re here to provide you with not only that answer but also insights into the unique relationships and cultural exchanges that define these borders, offering a comprehensive guide for LGBTQ+ travelers and enthusiasts alike. Explore the bordering nations, understand the nuances of these connections, and discover how gaymexico.net can be your ultimate resource for exploring Mexico’s diversity and inclusivity.
1. What Countries Share a Border with Mexico?
Mexico shares its borders with three countries: the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the south. Each border presents unique geographical, cultural, and social landscapes that contribute to Mexico’s diverse identity.
- United States: Stretching over 1,954 miles (3,145 kilometers), this is the most extensive border, characterized by bustling cities, vast deserts, and significant economic and cultural exchange.
- Guatemala: To the southeast, this border is approximately 541 miles (871 kilometers) long, marked by lush rainforests, ancient Mayan sites, and shared indigenous cultures.
- Belize: The smallest border, at about 176 miles (283 kilometers), is a tropical paradise of turquoise waters, vibrant coral reefs, and a blend of Caribbean and Central American influences.
2. How Does the U.S.-Mexico Border Impact Migration Patterns?
The U.S.-Mexico border is a major focal point for migration, influenced by a complex interplay of economic, social, and political factors.
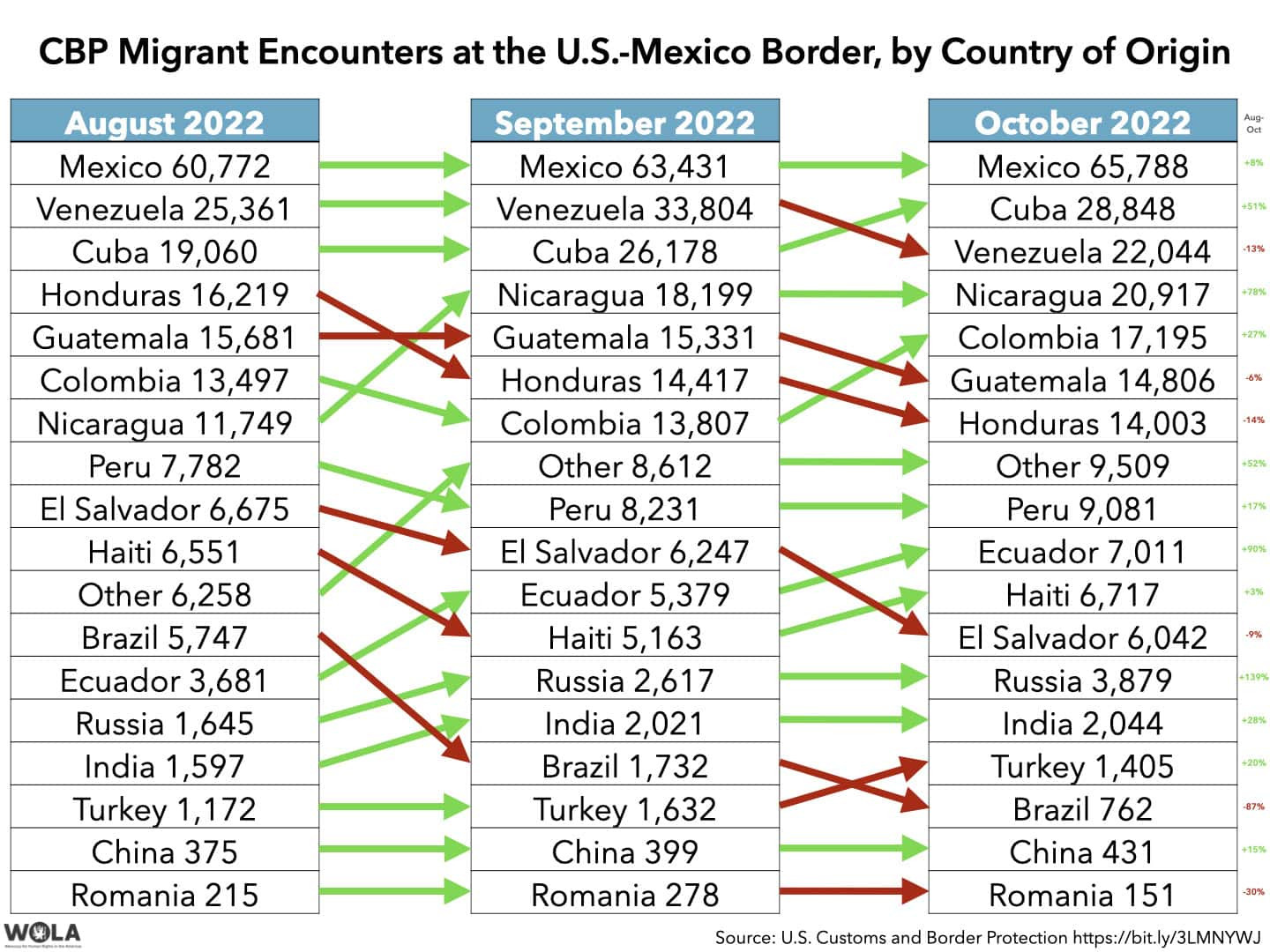 Migrant encounters at the U.S.-Mexico border show shifts in origin countries, with Mexico remaining a significant source but facing Title 42 expulsions.
Migrant encounters at the U.S.-Mexico border show shifts in origin countries, with Mexico remaining a significant source but facing Title 42 expulsions.
- Economic Opportunities: The promise of better economic opportunities in the United States drives many Mexicans and Central Americans to attempt crossing the border. According to a report by the Pew Research Center, economic disparities between the U.S. and Mexico continue to be a significant factor in migration patterns.
- Political Instability and Violence: Many individuals from Central American countries, such as Honduras, Guatemala, and El Salvador, seek asylum in the U.S. due to political instability, gang violence, and lack of security in their home countries.
- U.S. Policy Impacts: U.S. immigration policies, such as Title 42 (which allowed for the swift expulsion of migrants during the COVID-19 pandemic) and the Migrant Protection Protocols (MPP), significantly affect migration patterns, creating bottlenecks and humanitarian challenges at the border. As noted by Human Rights Watch, these policies have been criticized for limiting access to asylum and increasing the vulnerability of migrants.
- LGBTQ+ Asylum Seekers: The border is also a route for LGBTQ+ individuals fleeing persecution in their home countries. Mexico, while generally more tolerant than some of its neighbors, still presents challenges. Resources like gaymexico.net are essential for LGBTQ+ migrants seeking information and support.
3. What is the Significance of the Mexico-Guatemala Border?
The Mexico-Guatemala border is significant for its cultural exchange, environmental importance, and migration dynamics.
- Cultural Exchange: The border region is home to numerous indigenous communities with shared cultural and linguistic ties, fostering ongoing exchange and interaction. This is especially true for the Mayan communities, who traverse the border for cultural and religious events.
- Environmental Concerns: The area is rich in biodiversity, including the Maya Biosphere Reserve. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect the rainforests and wildlife in this region.
- Migration Transit: The border serves as a transit point for migrants from Central America heading north to the United States. Many face significant risks, including human trafficking and violence, while crossing this stretch.
- Trade and Commerce: Legal and informal trade activities occur along the border, contributing to the local economies. Small-scale commerce, particularly agricultural products, is common in border towns.
4. What Makes the Mexico-Belize Border Unique?
The Mexico-Belize border is characterized by its unique blend of Caribbean and Central American cultures, ecotourism opportunities, and distinct environmental features.
- Cultural Fusion: Belize’s English-speaking Caribbean culture contrasts with Mexico’s Spanish-speaking, primarily mestizo culture, creating a fascinating cultural interface. This is evident in the music, cuisine, and traditions found in the border region.
- Ecotourism: The border region is known for its ecotourism, with opportunities to explore the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef, rainforests, and Mayan ruins. Tourists often cross the border to experience the diverse attractions on both sides.
- Environmental Diversity: The border area includes diverse ecosystems, from coastal wetlands to dense jungles. Conservation efforts are essential to protect the region’s biodiversity and natural resources.
- Economic Activities: Trade and tourism are significant economic drivers along the border. The Santa Elena Free Zone in Belize attracts shoppers from Mexico seeking tax-free goods.
5. How Does Mexico’s Border Policy Affect LGBTQ+ Migrants?
Mexico’s border policy can significantly impact LGBTQ+ migrants, who often face unique challenges and vulnerabilities.
- Asylum Claims: LGBTQ+ individuals fleeing persecution in their home countries may seek asylum in Mexico. However, the asylum process can be complex and lengthy, requiring legal assistance and documentation.
- Discrimination and Violence: LGBTQ+ migrants may face discrimination and violence from both state and non-state actors while in transit or residing in border areas. This can include harassment, extortion, and physical attacks.
- Access to Resources: Access to resources such as shelter, healthcare, and legal aid can be limited for LGBTQ+ migrants, especially in remote border regions. Organizations like the UNHCR and local LGBTQ+ groups provide some support, but the need often outweighs the available resources.
- Safe Havens: Finding safe havens and supportive communities is crucial for LGBTQ+ migrants. Cities like Tijuana and Ciudad Juarez have emerging LGBTQ+ scenes, but safety can still be a concern. Gaymexico.net provides valuable information on LGBTQ+ friendly locations and resources.
6. What are the Key Border Cities Between Mexico and the United States?
Key border cities between Mexico and the United States include Tijuana, Ciudad Juarez, and El Paso.
- Tijuana, Baja California: Located across from San Diego, California, Tijuana is one of the busiest border crossings in the world. It is known for its vibrant cultural scene, medical tourism, and significant economic activity.
- Ciudad Juarez, Chihuahua: Across from El Paso, Texas, Ciudad Juarez has a complex history marked by periods of violence and resilience. It is an important manufacturing hub and a major crossing point for migrants.
- El Paso, Texas: El Paso is a major U.S. city on the border, with a strong Hispanic culture and a significant military presence. It serves as a key entry point into the United States and a hub for trade and commerce.
7. What Role Does Title 42 Play at the U.S.-Mexico Border?
Title 42, a public health order invoked during the COVID-19 pandemic, has played a controversial role at the U.S.-Mexico border.
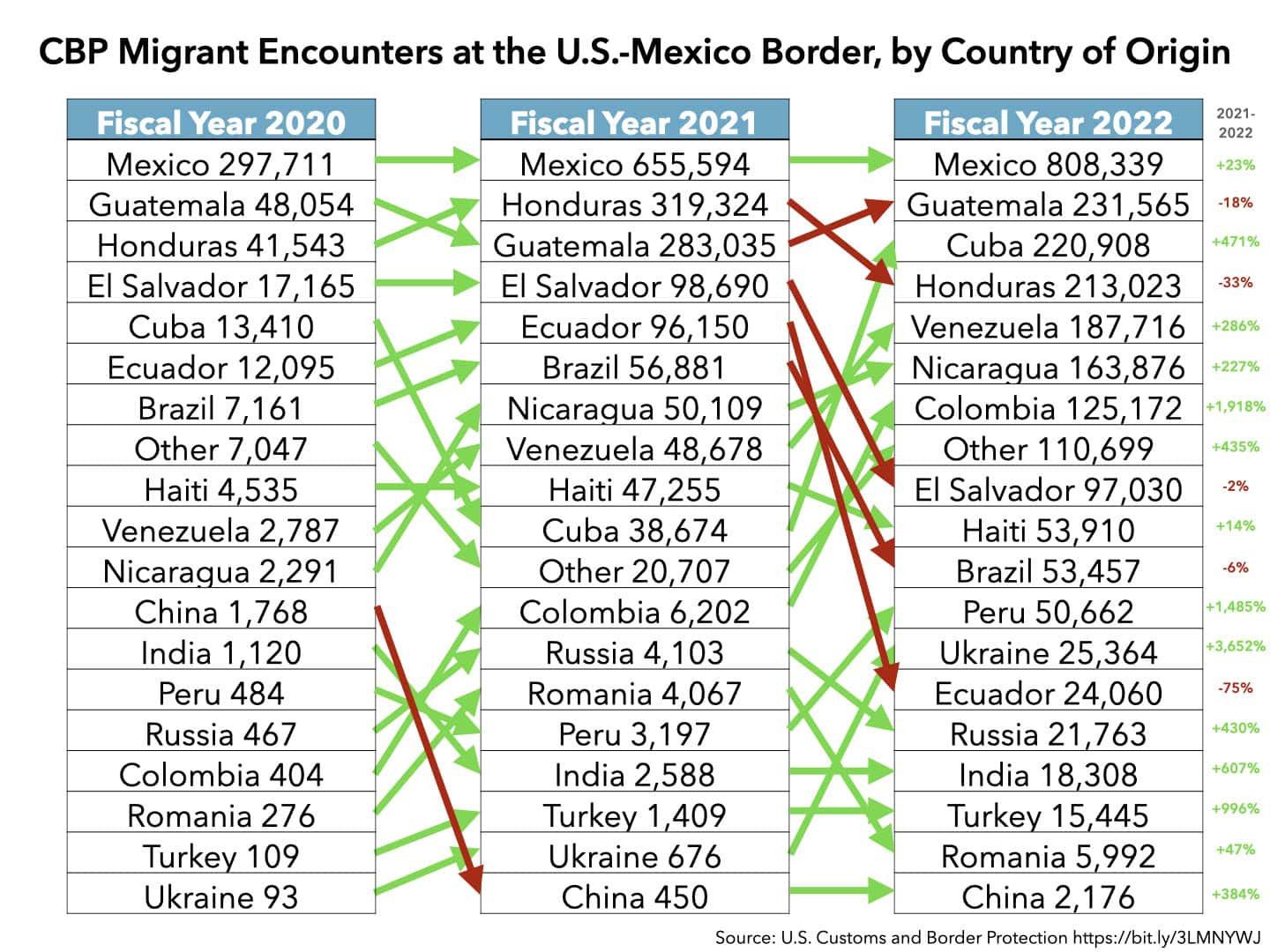 Migrant encounters at the U.S.-Mexico border show an increase from 2021 to 2022, highlighting the impact of policies on various nationalities and demographics.
Migrant encounters at the U.S.-Mexico border show an increase from 2021 to 2022, highlighting the impact of policies on various nationalities and demographics.
- Expulsions: Title 42 allowed U.S. authorities to quickly expel migrants without allowing them to seek asylum, citing public health concerns. This policy disproportionately affected asylum seekers from Central America, Haiti, and other countries.
- Limited Access to Asylum: Human Rights Watch and other organizations criticized Title 42 for undermining international refugee law and limiting access to asylum for vulnerable individuals.
- Impact on LGBTQ+ Migrants: LGBTQ+ asylum seekers were particularly vulnerable under Title 42, as they were often denied the opportunity to present their claims for protection and faced increased risks of violence and discrimination in Mexico.
- End of Title 42: The Biden administration ended Title 42 in May 2023, leading to significant shifts in border management policies. However, the long-term effects of the policy on migration patterns and asylum processes are still being assessed.
8. How Can LGBTQ+ Travelers Find Safe and Welcoming Spaces in Mexico’s Border Regions?
LGBTQ+ travelers can find safe and welcoming spaces in Mexico’s border regions by seeking out LGBTQ+-friendly establishments and resources.
- LGBTQ+ Friendly Cities: Cities like Tijuana and Ciudad Juarez have growing LGBTQ+ communities and offer gay bars, clubs, and cultural events. Researching local LGBTQ+ scenes and support networks can help travelers find safe spaces.
- Online Resources: Websites like gaymexico.net provide valuable information on LGBTQ+-friendly destinations, accommodations, and activities in Mexico, including border regions.
- Community Support: Connecting with local LGBTQ+ organizations and activists can provide insights into safe spaces and resources. These groups often offer support services and advocacy for LGBTQ+ individuals in the region.
- Travel Tips: Being aware of local customs and laws, avoiding risky areas, and traveling with trusted companions can enhance safety and comfort for LGBTQ+ travelers.
9. What are Some Cultural Similarities and Differences Along Mexico’s Borders?
Cultural similarities and differences along Mexico’s borders create a rich tapestry of traditions and identities.
- U.S.-Mexico Border: Shared culinary traditions, such as Tex-Mex and Baja Med cuisine, reflect the cultural fusion along this border. Music genres like norteño and banda are popular on both sides, reflecting a shared heritage.
- Mexico-Guatemala Border: Mayan languages and traditions are prevalent on both sides, fostering cultural continuity. Traditional textiles, music, and dance reflect shared indigenous roots.
- Mexico-Belize Border: A blend of Caribbean and Central American cultures is evident, with influences from Creole, Garifuna, and Mayan traditions. English is widely spoken in Belize, contrasting with the Spanish dominance in Mexico.
10. What Challenges Do Migrants Face When Crossing Mexico’s Borders?
Migrants face numerous challenges when crossing Mexico’s borders, including legal, physical, and social obstacles.
- Legal Hurdles: Complex immigration laws and asylum processes can be difficult to navigate, especially for those without legal representation. The requirements for documentation and evidence can be onerous.
- Physical Dangers: The journey across Mexico can be perilous, with risks of dehydration, exhaustion, and exposure to harsh weather conditions. Remote border regions are particularly dangerous.
- Violence and Exploitation: Migrants are often targeted by criminal organizations, who may subject them to extortion, kidnapping, and human trafficking. Women and LGBTQ+ individuals are particularly vulnerable to sexual violence.
- Social Stigma: Migrants may face discrimination and xenophobia from local communities, making it difficult to access housing, employment, and other essential services.
11. How Are Environmental Issues Addressed Along Mexico’s Borders?
Addressing environmental issues along Mexico’s borders requires international cooperation and community involvement.
- Transboundary Conservation: Collaborative efforts between Mexico and its neighbors aim to protect shared ecosystems, such as the Maya Biosphere Reserve and the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef.
- Pollution Control: Initiatives to reduce air and water pollution are crucial, especially in industrialized border cities like Tijuana and Ciudad Juarez.
- Sustainable Development: Promoting sustainable tourism and agriculture can help balance economic development with environmental protection.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in conservation efforts is essential for ensuring the long-term sustainability of border regions.
12. What Impact Does Drug Trafficking Have on Mexico’s Border Regions?
Drug trafficking has a profound and destabilizing impact on Mexico’s border regions, contributing to violence, corruption, and social disruption.
- Violence and Insecurity: Cartels and criminal organizations engage in violent conflicts to control drug trafficking routes, resulting in high levels of homicide and insecurity in border cities.
- Corruption: Drug money corrupts government officials and law enforcement agencies, undermining the rule of law and hindering efforts to combat organized crime.
- Human Rights Abuses: Cartels commit widespread human rights abuses, including kidnapping, extortion, and forced recruitment. Migrants are often targeted by these criminal groups.
- Economic Impact: Drug trafficking distorts local economies, diverting resources away from legitimate businesses and creating a climate of fear and instability.
13. What Role Do Indigenous Communities Play in Mexico’s Border Regions?
Indigenous communities play a vital role in Mexico’s border regions, preserving cultural traditions, advocating for land rights, and contributing to local economies.
- Cultural Preservation: Indigenous communities maintain their languages, customs, and traditional practices, enriching the cultural diversity of border regions.
- Land Rights: Indigenous communities often struggle to protect their ancestral lands from development projects and resource extraction. Advocacy for land rights is a key focus of indigenous organizations.
- Economic Contributions: Indigenous communities contribute to local economies through agriculture, tourism, and traditional crafts. Sustainable development initiatives can support these economic activities.
- Political Participation: Indigenous communities are increasingly engaged in political processes, seeking representation and advocating for their rights and interests.
14. How Does Trade Influence the Economies of Mexico’s Border Cities?
Trade significantly influences the economies of Mexico’s border cities, driving economic growth, creating jobs, and fostering cross-border commerce.
- Manufacturing and Assembly: Border cities like Tijuana and Ciudad Juarez are major manufacturing hubs, with maquiladoras (assembly plants) producing goods for export to the United States.
- Cross-Border Commerce: Retail trade and tourism benefit from the flow of goods and people across the border. Mexican consumers often shop in U.S. border cities, while American tourists visit Mexico for cultural experiences and medical services.
- Logistics and Transportation: The border region is a key transportation corridor, with trucking companies and logistics providers facilitating the movement of goods between Mexico and the United States.
- Economic Development: Government policies and investment incentives aim to promote economic development in border cities, attracting foreign investment and creating jobs.
15. What Are Some Popular Tourist Destinations Along Mexico’s Borders?
Popular tourist destinations along Mexico’s borders include Tijuana, San Cristobal de las Casas, and the Riviera Maya.
- Tijuana, Baja California: Known for its vibrant nightlife, culinary scene, and cultural attractions, Tijuana attracts tourists from Southern California and beyond.
- San Cristobal de las Casas, Chiapas: This colonial city is a gateway to the indigenous cultures of Chiapas, offering opportunities to explore Mayan ruins, traditional markets, and natural landscapes.
- Riviera Maya, Quintana Roo: While not directly on the border, the Riviera Maya is easily accessible from Belize and offers stunning beaches, Mayan ruins, and ecotourism attractions.
16. How Does Mexico Cooperate with its Neighbors on Border Security?
Mexico cooperates with its neighbors on border security through various agreements and initiatives aimed at combating drug trafficking, human smuggling, and other transnational crimes.
- Bilateral Agreements: Mexico has bilateral agreements with the United States, Guatemala, and Belize on border security, outlining cooperation on law enforcement, intelligence sharing, and joint operations.
- Joint Operations: Joint operations involve coordinated efforts by law enforcement agencies from Mexico and its neighbors to patrol border areas, intercept drug shipments, and apprehend criminals.
- Intelligence Sharing: Intelligence sharing is crucial for identifying and disrupting criminal networks operating along the border. Mexico cooperates with its neighbors to exchange information on drug trafficking routes, smuggling operations, and gang activities.
- Capacity Building: Mexico provides training and technical assistance to its neighbors to enhance their capacity to secure their borders and combat transnational crime.
17. What Resources Are Available for Migrants Seeking Assistance at Mexico’s Borders?
Various resources are available for migrants seeking assistance at Mexico’s borders, including government agencies, international organizations, and non-profit groups.
- Government Agencies: The Mexican government provides assistance to migrants through agencies such as the National Migration Institute (INM) and the Mexican Commission for Refugee Assistance (COMAR).
- International Organizations: The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) and the International Organization for Migration (IOM) provide humanitarian assistance and support to migrants in Mexico.
- Non-Profit Groups: Numerous non-profit organizations operate along Mexico’s borders, providing shelter, food, medical care, legal aid, and other essential services to migrants. Examples include Al Otro Lado, the Border Angels, and the Kino Border Initiative.
18. How Can LGBTQ+ Individuals Contribute to Positive Change in Mexico’s Border Regions?
LGBTQ+ individuals can contribute to positive change in Mexico’s border regions through activism, advocacy, and community engagement.
- Activism: LGBTQ+ activists can raise awareness about issues affecting the LGBTQ+ community, advocate for policy changes, and organize protests and demonstrations.
- Advocacy: LGBTQ+ advocates can work with government officials, community leaders, and other stakeholders to promote LGBTQ+ rights and inclusion.
- Community Engagement: LGBTQ+ individuals can volunteer with local organizations, support LGBTQ+-owned businesses, and participate in community events to build a more inclusive and welcoming society.
19. What Legal Rights Do LGBTQ+ Individuals Have in Mexico’s Border States?
The legal rights of LGBTQ+ individuals in Mexico’s border states vary depending on the state, but significant progress has been made in recent years.
- Same-Sex Marriage: Same-sex marriage is legal in all of Mexico’s border states, providing LGBTQ+ couples with the same rights and protections as heterosexual couples.
- Anti-Discrimination Laws: Some border states have anti-discrimination laws that protect LGBTQ+ individuals from discrimination in employment, housing, and other areas. However, enforcement of these laws can be inconsistent.
- Gender Identity Recognition: Some border states allow transgender individuals to change their legal gender on identification documents. However, the process can be complex and may require a court order.
- Hate Crime Laws: Some border states have hate crime laws that include sexual orientation and gender identity as protected categories. These laws provide enhanced penalties for crimes motivated by bias against LGBTQ+ individuals.
20. How Can I Plan an LGBTQ+ Friendly Trip to Mexico’s Border Regions?
Planning an LGBTQ+ friendly trip to Mexico’s border regions involves researching LGBTQ+-friendly destinations, accommodations, and activities, and taking steps to ensure your safety and comfort.
- Research LGBTQ+-Friendly Destinations: Cities like Tijuana and San Cristobal de las Casas have growing LGBTQ+ scenes and offer gay bars, clubs, and cultural events.
- Choose LGBTQ+-Friendly Accommodations: Look for hotels and guesthouses that are known for being welcoming to LGBTQ+ travelers. Online reviews and recommendations from LGBTQ+ travel websites can be helpful.
- Plan LGBTQ+-Friendly Activities: Research LGBTQ+-friendly activities and attractions, such as gay pride events, LGBTQ+ film festivals, and LGBTQ+ walking tours.
- Be Aware of Local Customs and Laws: Familiarize yourself with local customs and laws regarding LGBTQ+ issues. While Mexico is generally tolerant, attitudes can vary depending on the region.
- Take Steps to Ensure Your Safety: Avoid risky areas, travel with trusted companions, and be aware of your surroundings. In case of emergency, know how to contact local authorities and LGBTQ+ support organizations.
Mexico’s borders are complex and dynamic regions, characterized by cultural exchange, migration flows, economic activities, and environmental challenges. Understanding the nuances of these borders is essential for LGBTQ+ travelers, migrants, and anyone interested in the region.
For those seeking more information and resources, gaymexico.net offers a comprehensive guide to LGBTQ+ travel in Mexico, including border regions. Visit gaymexico.net today to discover LGBTQ+-friendly destinations, accommodations, and activities, and connect with the LGBTQ+ community in Mexico. Whether you’re planning a trip, seeking asylum, or simply interested in learning more, gaymexico.net is your go-to resource for all things LGBTQ+ in Mexico.
For additional information, you can also contact:
Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States
Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177
Website: gaymexico.net
FAQ: Countries That Border Mexico
1. What are the countries that border Mexico?
Mexico shares borders with three countries: the United States to the north, Guatemala to the southeast, and Belize to the east. These borders are significant for cultural exchange, migration, and economic activities.
2. What is the length of the U.S.-Mexico border?
The U.S.-Mexico border is approximately 1,954 miles (3,145 kilometers) long. It is one of the most heavily crossed international borders in the world, marked by significant economic and cultural exchange.
3. How long is the Mexico-Guatemala border?
The Mexico-Guatemala border stretches approximately 541 miles (871 kilometers). This border is characterized by dense rainforests, Mayan archaeological sites, and shared indigenous cultures.
4. What is the length of the Mexico-Belize border?
The Mexico-Belize border is the shortest of Mexico’s borders, measuring about 176 miles (283 kilometers). It is known for its tropical environment, ecotourism opportunities, and unique blend of Caribbean and Central American cultures.
5. What are some major crossing points between Mexico and the United States?
Major crossing points between Mexico and the United States include Tijuana/San Diego, Ciudad Juarez/El Paso, and Nuevo Laredo/Laredo. These cities are hubs for trade, tourism, and migration.
6. How does migration affect the countries bordering Mexico?
Migration significantly impacts the countries bordering Mexico. The U.S. faces challenges related to border security and immigration policy, while Guatemala and Belize serve as transit countries for migrants heading north.
7. What cultural exchanges occur along Mexico’s borders?
Cultural exchanges along Mexico’s borders include shared culinary traditions, music, and languages. The U.S.-Mexico border features a blend of Mexican and American cultures, while the Mexico-Guatemala border shares Mayan heritage.
8. What environmental concerns are present along Mexico’s borders?
Environmental concerns along Mexico’s borders include deforestation, water pollution, and biodiversity loss. Transboundary conservation efforts are essential to protect shared ecosystems.
9. What economic activities take place along Mexico’s borders?
Economic activities along Mexico’s borders include manufacturing, trade, tourism, and agriculture. Border cities serve as important hubs for cross-border commerce.
10. How do Mexico’s border policies affect LGBTQ+ individuals?
Mexico’s border policies can impact LGBTQ+ individuals seeking asylum or migrating through the country. LGBTQ+ migrants may face discrimination, violence, and limited access to resources.
