Are you curious about the marine life in the Gulf of Mexico, especially the majestic orcas? This guide on gaymexico.net dives into the fascinating world of these killer whales in Mexican waters, offering insights for LGBTQ+ travelers and anyone interested in Mexican biodiversity and culture. Discover orca populations, their behaviors, and the best spots to witness them. Join us as we explore and celebrate the natural wonders of Mexico and connect with the LGBTQ+ community. So pack your bags and prepare for adventure!
1. What is the Orca Population in the Gulf of Mexico?
The orca population in the Gulf of Mexico is estimated to be around 500 individuals. These orcas, also known as killer whales, are typically found in the deeper waters of the Gulf, far from the coastline.
The Gulf of Mexico is a vibrant ecosystem, and while it may not be the first place that comes to mind when you think of orcas, these apex predators do indeed call its waters home. The presence of orcas in the Gulf highlights the region’s biodiversity and offers a unique perspective on these magnificent creatures. While specific population numbers can fluctuate due to migration and other factors, scientific estimates place the orca population at around 500 individuals. These orcas primarily inhabit the deeper offshore waters of the Gulf of Mexico, which is perfect for safe travels for LGBTQ+ visitors.
1.1 What are the Habitats of Orcas in the Gulf of Mexico?
Orcas in the Gulf of Mexico typically inhabit deep waters far from land. According to studies, they are often observed in areas with depths exceeding 1,000 feet, where they find their primary food sources such as tuna and dolphins.
These marine mammals prefer these deep-sea environments due to the availability of prey and the relative lack of human disturbance. The Gulf’s unique bathymetry, or underwater topography, includes steep continental slopes and deep basins that provide the ideal habitat. The areas are key to the orcas’ survival and hunting strategies.
1.2 What are the Feeding Habits of Orcas in the Gulf of Mexico?
Orcas in the Gulf of Mexico primarily feed on tuna and dolphins. These killer whales are apex predators, meaning they sit at the top of the food chain and have a significant impact on the marine ecosystem.
Their diet consists mainly of various species of tuna, which are abundant in the Gulf, and several types of dolphins, including bottlenose dolphins and spinner dolphins. These intelligent hunters use sophisticated techniques to locate and capture their prey, often working in coordinated groups to maximize their success. The feeding habits of orcas in the Gulf of Mexico are a testament to their adaptability and ecological importance.
1.3 Are Orcas in the Gulf of Mexico Genetically Distinct?
Genetic studies suggest that orcas in the Gulf of Mexico may represent a genetically distinct population. Preliminary research indicates that these orcas exhibit unique genetic markers, suggesting they have been isolated from other orca populations for an extended period.
Further research is needed to fully understand the extent of their genetic divergence and the implications for their conservation. The possibility of a distinct population underscores the importance of protecting these orcas and their habitat within the Gulf of Mexico.
2. Why are Orcas Found in the Gulf of Mexico?
Orcas are found in the Gulf of Mexico due to the availability of their primary food sources, such as tuna and dolphins, and the presence of deep-water habitats suitable for their hunting and social behaviors.
The Gulf of Mexico offers a unique combination of environmental factors that support the presence of orcas. The Gulf’s warm waters and abundant marine life create a favorable habitat for these apex predators, while its depth provides refuge and hunting grounds. The presence of orcas in the Gulf of Mexico underscores the ecological importance of this region and the need for conservation efforts to protect its marine biodiversity.
2.1 What Role Do Water Temperature and Salinity Play?
Water temperature and salinity play critical roles in the distribution and survival of orcas in the Gulf of Mexico. Orcas are adaptable creatures, but they have preferred ranges of temperature and salinity that influence their habitat selection and prey availability.
The Gulf of Mexico’s unique hydrographic conditions, characterized by warm waters and varying salinity levels, create diverse habitats that support a wide range of marine life, including the orcas’ primary food sources. Changes in water temperature and salinity can impact the distribution and abundance of prey species, which in turn can affect the foraging behavior and overall health of the orca population.
2.2 How Does the Gulf of Mexico’s Ecosystem Support Orcas?
The Gulf of Mexico’s ecosystem supports orcas by providing a rich and diverse food web, including abundant populations of tuna, dolphins, and other marine species that serve as their primary prey. The Gulf’s warm waters and deep-sea habitats create ideal conditions for these apex predators to thrive.
The intricate relationships within the Gulf’s ecosystem ensure a stable and sustainable food supply for orcas, allowing them to maintain healthy populations. Conservation efforts aimed at protecting the Gulf’s biodiversity are essential to preserving the ecological balance that supports orcas and other marine wildlife.
2.3 What is the Historical Context of Orcas in the Gulf of Mexico?
Historically, orcas have been present in the Gulf of Mexico for centuries, as evidenced by historical records and traditional ecological knowledge. Indigenous communities along the Gulf Coast have long recognized the presence of orcas and incorporated them into their cultural narratives and maritime practices.
Scientific studies have also confirmed the historical presence of orcas in the Gulf, with genetic and ecological data suggesting that they have been a part of the region’s marine ecosystem for an extended period. Understanding the historical context of orcas in the Gulf of Mexico provides valuable insights into their long-term ecological role and the importance of preserving their habitat for future generations.
3. What are the Conservation Concerns for Orcas in the Gulf of Mexico?
Conservation concerns for orcas in the Gulf of Mexico include habitat degradation, pollution, entanglement in fishing gear, and climate change. These threats pose significant risks to the orca population, potentially impacting their survival and reproductive success.
Addressing these conservation concerns requires collaborative efforts from governments, scientists, conservation organizations, and local communities. By implementing effective management strategies and promoting responsible practices, we can help protect orcas and ensure the long-term health of the Gulf of Mexico ecosystem.
3.1 How Does Pollution Affect Orcas?
Pollution, including chemical contaminants and plastic debris, can have severe effects on orcas in the Gulf of Mexico. Chemical pollutants such as pesticides and industrial chemicals can accumulate in the orcas’ tissues through the food chain, leading to immune system suppression, reproductive problems, and developmental abnormalities.
Plastic debris can also pose a significant threat to orcas, as they may ingest plastic items that can cause internal injuries, blockages, and malnutrition. Efforts to reduce pollution and promote responsible waste management are crucial to protecting orcas and maintaining the health of the marine environment.
3.2 What is the Impact of Fishing Gear on Orcas?
Entanglement in fishing gear is a major threat to orcas in the Gulf of Mexico. Orcas can become entangled in various types of fishing gear, including nets, lines, and traps, which can cause injuries, drowning, and starvation.
Entanglement can also impede the orcas’ ability to hunt, migrate, and socialize, further impacting their survival and reproductive success. Implementing measures to reduce entanglement risk, such as modifying fishing gear and promoting responsible fishing practices, is essential to protecting orcas and minimizing human impacts on their population.
3.3 How Does Climate Change Threaten Orcas in the Gulf of Mexico?
Climate change poses a significant threat to orcas in the Gulf of Mexico through rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and changes in prey distribution. Rising sea temperatures can alter the Gulf’s ecosystem, impacting the abundance and distribution of the orcas’ primary prey species.
Ocean acidification can affect the base of the food web, potentially reducing the availability of nutrients and impacting the overall health of the marine ecosystem. Changes in prey distribution can force orcas to travel farther to find food, increasing their energy expenditure and potentially impacting their reproductive success. Addressing climate change through reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable practices is crucial to protecting orcas and preserving the integrity of the Gulf of Mexico’s marine ecosystem.
4. Where Can You Spot Orcas in Mexico?
While orcas are not commonly observed close to shore, you might spot them during offshore excursions in the Gulf of Mexico, particularly in deeper waters far from the coast. Areas near the continental shelf break are known to have higher orca activity.
Seeing orcas in their natural habitat is an unforgettable experience. The vastness of the ocean, combined with the intelligence and social complexity of these animals, is truly awe-inspiring. Remember to respect their space and follow responsible wildlife viewing guidelines to ensure their safety and well-being.
4.1 Are There Whale Watching Tours in the Gulf of Mexico?
Yes, there are whale watching tours available in the Gulf of Mexico. Several tour operators offer excursions that may provide opportunities to spot various marine species, including whales and dolphins.
However, orca sightings are rare during these tours, as these marine mammals typically inhabit deeper offshore waters. If you’re interested in seeing orcas, consider booking a specialized tour that focuses on deep-sea marine life. Always ensure that the tour operator follows responsible wildlife viewing practices to minimize disturbance to the animals and their habitat.
4.2 What Time of Year is Best for Orca Watching?
There is no specific “best” time of year for orca watching in the Gulf of Mexico, as sightings are relatively rare and unpredictable. Orcas can be observed in the Gulf throughout the year, but their presence may be influenced by prey availability and oceanographic conditions.
Consult with local marine experts or tour operators who have experience with whale watching in the Gulf to get the most up-to-date information on orca sightings and the best times to visit. Keep in mind that orca sightings are never guaranteed, so be prepared to enjoy other marine wildlife encounters during your tour.
4.3 What are the Ethical Considerations for Whale Watching?
Ethical considerations for whale watching include maintaining a safe distance from the animals, avoiding disturbance to their natural behaviors, and supporting responsible tour operators who prioritize the well-being of marine wildlife.
When participating in whale watching tours, it’s essential to choose operators who adhere to established guidelines and regulations for responsible wildlife viewing. These guidelines typically include maintaining a minimum distance from the animals, avoiding sudden or disruptive movements, and limiting the amount of time spent observing individual animals or groups. Respecting these ethical considerations helps ensure that whale watching activities do not negatively impact the orcas’ health, behavior, or habitat.
5. What is the Cultural Significance of Orcas in Mexico?
The cultural significance of orcas in Mexico varies among different indigenous communities and coastal regions. In some areas, orcas are revered as symbols of strength, intelligence, and community.
Traditional stories and legends often feature orcas as powerful beings with connections to the spirit world. Modern Mexican society also recognizes the ecological importance of orcas and their role in the marine ecosystem. Efforts to protect orcas and their habitat are supported by a growing awareness of their cultural and environmental value.
5.1 How Do Indigenous Communities View Orcas?
Indigenous communities in Mexico often view orcas as beings with deep cultural and spiritual significance. In some coastal communities, orcas are considered guardians of the sea, protectors of fishermen, and symbols of good fortune.
Traditional stories and ceremonies may incorporate orcas as representations of strength, intelligence, and social harmony. The deep connection between indigenous communities and orcas reflects a profound respect for the natural world and the importance of preserving marine biodiversity.
5.2 Are Orcas Featured in Mexican Art and Mythology?
Yes, orcas are sometimes featured in Mexican art and mythology, particularly in regions with strong maritime traditions. Orca motifs may appear in traditional carvings, sculptures, and paintings, often symbolizing power, protection, and the interconnectedness of marine life.
In some mythological narratives, orcas are depicted as messengers from the sea gods or as transformative beings with the ability to shape the marine environment. The presence of orcas in Mexican art and mythology reflects the cultural significance of these animals and their role in shaping the identity and worldview of coastal communities.
5.3 What Conservation Efforts are Supported by Local Communities?
Conservation efforts supported by local communities in Mexico include habitat restoration, pollution reduction, and sustainable fishing practices. Local communities often play a crucial role in monitoring orca populations, reporting sightings, and advocating for the protection of critical marine habitats.
Community-based conservation initiatives may involve educating local residents about the importance of orcas and their ecosystem, promoting responsible tourism, and supporting research efforts to better understand orca behavior and ecology. By empowering local communities to take an active role in conservation, we can ensure the long-term health and resilience of the Gulf of Mexico’s marine environment.
6. What Other Marine Life Can You See in the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is home to a diverse array of marine life, including dolphins, sea turtles, various fish species, and vibrant coral reefs. Exploring the Gulf offers opportunities to see a variety of fascinating marine creatures.
The Gulf of Mexico’s unique environmental conditions support a rich tapestry of life, from microscopic plankton to massive whales. The Gulf is a biodiversity hotspot that needs protection for future generations.
6.1 What Types of Dolphins Inhabit the Gulf?
Several types of dolphins inhabit the Gulf of Mexico, including bottlenose dolphins, spinner dolphins, and spotted dolphins. Bottlenose dolphins are the most common and are often seen near the coast and in estuaries.
Spinner dolphins are known for their acrobatic displays, leaping and spinning out of the water. Spotted dolphins are characterized by their distinctive spotted patterns and are typically found in deeper offshore waters. Each dolphin species has unique ecological roles and behaviors, contributing to the Gulf’s marine biodiversity.
6.2 Are Sea Turtles Common in the Gulf of Mexico?
Yes, sea turtles are common in the Gulf of Mexico. Several species of sea turtles, including loggerhead, green, Kemp’s ridley, and hawksbill turtles, inhabit the Gulf’s waters.
Sea turtles play a crucial role in maintaining the health of marine ecosystems by grazing on seagrass beds, controlling jellyfish populations, and providing habitat for other marine species. Many sea turtle populations are threatened or endangered, conservation efforts are essential to protecting these ancient mariners and ensuring their survival in the Gulf of Mexico.
6.3 What Fish Species are Notable in the Gulf?
The Gulf of Mexico is home to a wide variety of fish species, including tuna, grouper, snapper, and various reef fish. Tuna are important predators in the Gulf’s ecosystem and are also commercially valuable.
Grouper and snapper are popular targets for recreational and commercial fishing and play a key role in maintaining the balance of reef ecosystems. The Gulf’s diverse fish populations support a thriving fishing industry and contribute to the region’s economic and cultural heritage.
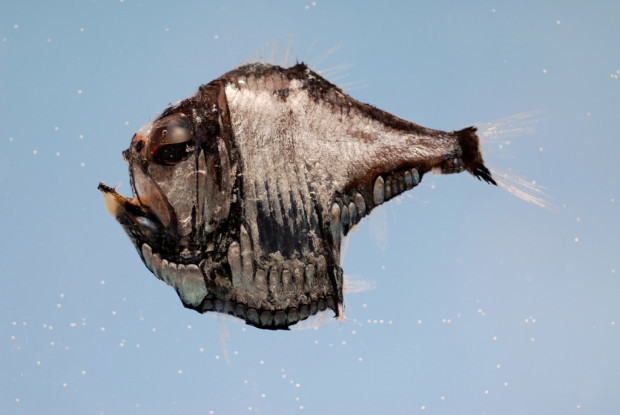 Atlantic Silver Hatchetfish NOAA FlickR
Atlantic Silver Hatchetfish NOAA FlickR
7. How Can You Support Orca Conservation in Mexico?
You can support orca conservation in Mexico by supporting conservation organizations, reducing your environmental footprint, and advocating for responsible marine policies. These organizations work to protect orca habitats, reduce pollution, and promote sustainable fishing practices.
Reducing your environmental footprint can involve making conscious choices in your daily life, such as reducing plastic consumption, using eco-friendly products, and supporting businesses committed to sustainability. Your voice is powerful and can make a difference in protecting these magnificent creatures and their habitat.
7.1 What Organizations are Working to Protect Orcas?
Several organizations are working to protect orcas in Mexico and the Gulf of Mexico region. These organizations include marine conservation groups, research institutions, and community-based initiatives.
They conduct research on orca populations, monitor their habitat, advocate for policy changes to protect marine wildlife, and educate the public about the importance of orca conservation. Supporting these organizations through donations, volunteering, or spreading awareness can make a significant impact on orca conservation efforts.
7.2 How Can Tourists Contribute to Conservation?
Tourists can contribute to orca conservation by choosing responsible tour operators, reducing their environmental impact, and supporting local conservation initiatives. Responsible tour operators follow ethical guidelines for wildlife viewing, minimizing disturbance to orcas and their habitat.
Tourists can reduce their environmental impact by reducing plastic use, properly disposing of waste, and respecting marine environments. Supporting local conservation initiatives through donations or volunteering can help fund vital research, habitat restoration, and education programs.
7.3 What Policies Support Orca Protection in Mexico?
Policies supporting orca protection in Mexico include regulations on fishing practices, marine protected areas, and environmental impact assessments. These policies aim to minimize human impacts on orca populations and their habitat, ensuring their long-term survival.
Regulations on fishing practices may include restrictions on certain types of fishing gear, seasonal closures, and catch limits to prevent overfishing and entanglement of orcas in fishing gear. Marine protected areas provide safe havens for orcas and other marine wildlife, protecting critical habitats from human disturbance. Environmental impact assessments evaluate the potential impacts of development projects on marine ecosystems, ensuring that orca habitats are considered in decision-making processes.
8. What Are Some Misconceptions About Orcas?
Some common misconceptions about orcas include the belief that they are aggressive towards humans, that they are strictly cold-water animals, and that they are not threatened or endangered. Despite their nickname “killer whales,” orcas are not generally aggressive towards humans in the wild.
While orcas are commonly associated with cold-water environments, they can be found in a variety of marine habitats, including the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico. Some orca populations are threatened or endangered due to habitat loss, pollution, and other human impacts.
8.1 Are Orcas Dangerous to Humans in the Wild?
Orcas are not generally dangerous to humans in the wild. There have been very few documented cases of orcas attacking humans in their natural habitat.
Orcas are intelligent and social animals with complex communication systems and hunting strategies. Their primary prey consists of fish, seals, and other marine mammals, and they do not typically view humans as a food source. While it’s always important to exercise caution and respect when observing wildlife, orcas are not considered a significant threat to humans in the wild.
8.2 Do Orcas Only Live in Cold Water?
No, orcas do not only live in cold water. While some orca populations are found in polar regions, these marine mammals can inhabit a variety of marine environments, including temperate and tropical waters.
Orcas have been observed in the Gulf of Mexico, the Mediterranean Sea, and other warm-water regions. Their adaptability allows them to thrive in a wide range of ocean conditions, as long as there is an adequate food supply and suitable habitat.
8.3 Are Orca Populations Thriving?
Orca populations are not universally thriving. Some orca populations are facing significant threats and are listed as threatened or endangered under national and international conservation laws.
Threats to orca populations include habitat loss, pollution, entanglement in fishing gear, climate change, and prey depletion. Conservation efforts are crucial to protecting orcas and ensuring the long-term health and resilience of their populations.
9. How Can You Learn More About Orcas and Marine Life in Mexico?
You can learn more about orcas and marine life in Mexico by visiting marine research centers, aquariums, and museums, and by participating in educational tours and workshops. These resources provide valuable information about orca biology, behavior, and conservation status, as well as insights into the broader marine ecosystem.
Engaging with these resources can deepen your understanding of orcas and inspire you to support conservation efforts. Learning about marine life in Mexico is a journey of discovery that can enrich your life and promote a greater appreciation for the natural world.
9.1 What Museums and Aquariums Feature Orcas?
While orcas are not commonly featured in Mexican aquariums due to ethical concerns and the challenges of maintaining these large marine mammals in captivity, you can visit museums and research centers that offer exhibits and educational programs about whales and marine conservation.
These institutions may provide information about orca biology, behavior, and conservation status, as well as broader insights into the marine ecosystem.
9.2 Are There Online Resources for Orca Research and Conservation?
Yes, there are numerous online resources for orca research and conservation. Websites of marine conservation organizations, research institutions, and government agencies provide valuable information about orca biology, behavior, and conservation efforts.
These resources may include scientific publications, research reports, educational materials, and interactive maps. Online databases and citizen science platforms allow you to contribute to orca research by reporting sightings, sharing photos, and participating in data analysis.
9.3 What Books and Documentaries Highlight Orcas in the Gulf?
While there may not be specific books and documentaries focused solely on orcas in the Gulf of Mexico, you can find numerous resources that highlight orcas in general and marine life in the Gulf.
These resources can provide valuable insights into orca biology, behavior, and conservation status, as well as the broader marine ecosystem of the Gulf of Mexico. Exploring these resources can deepen your understanding of orcas and inspire you to support conservation efforts in the Gulf and beyond.
 Pancake Batfish OggiScienza FlickR
Pancake Batfish OggiScienza FlickR
10. How Does gaymexico.net Support LGBTQ+ Travelers Interested in Marine Life?
gaymexico.net supports LGBTQ+ travelers interested in marine life by providing resources and information about destinations that are welcoming and inclusive. LGBTQ+ travelers can find recommendations for eco-friendly tours, LGBTQ+-friendly accommodations near marine reserves, and information about supporting local conservation efforts.
We aim to connect LGBTQ+ travelers with experiences that are both enriching and respectful of the environment. Our platform provides a safe and inclusive space for LGBTQ+ individuals to explore their passion for marine life while promoting responsible and sustainable travel practices.
10.1 What LGBTQ+-Friendly Destinations Offer Marine Tours?
Several LGBTQ+-friendly destinations in Mexico offer marine tours and excursions. Puerto Vallarta, Cancun, and Playa del Carmen are known for their welcoming atmosphere and diverse range of activities, including snorkeling, diving, and whale watching tours.
These destinations offer opportunities to explore the region’s marine biodiversity while enjoying LGBTQ+-friendly accommodations, restaurants, and nightlife. Choosing LGBTQ+-friendly destinations ensures that you can travel with confidence and feel supported by the local community.
10.2 How Can LGBTQ+ Travelers Support Sustainable Marine Tourism?
LGBTQ+ travelers can support sustainable marine tourism by choosing eco-friendly tour operators, respecting marine environments, and supporting local conservation initiatives. Eco-friendly tour operators prioritize the well-being of marine life and minimize their environmental impact through responsible practices such as reducing waste, using sustainable transportation, and avoiding disturbance to sensitive habitats.
Respecting marine environments involves following guidelines for responsible wildlife viewing, avoiding touching or feeding marine animals, and properly disposing of waste. Supporting local conservation initiatives through donations, volunteering, or spreading awareness can help fund vital research, habitat restoration, and education programs.
10.3 What Resources Does gaymexico.net Provide for Planning Trips?
gaymexico.net provides a range of resources for planning trips to Mexico, including destination guides, LGBTQ+-friendly accommodation listings, event calendars, and travel tips. Our destination guides highlight the most welcoming and inclusive destinations in Mexico, providing information about local attractions, activities, and LGBTQ+ nightlife.
Our LGBTQ+-friendly accommodation listings feature hotels, resorts, and guesthouses that are committed to providing a safe and welcoming environment for LGBTQ+ travelers. Our event calendars showcase LGBTQ+ festivals, pride celebrations, and other cultural events happening throughout Mexico. Our travel tips offer practical advice on transportation, safety, and cultural etiquette to help you plan a smooth and enjoyable trip. For example, Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States. Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177. Website: gaymexico.net.
Exploring the marine life of Mexico is an adventure that combines natural beauty with cultural richness, making it an ideal destination for LGBTQ+ travelers seeking unique and enriching experiences.
FAQ: Orcas in the Gulf of Mexico
- Are orcas common in the Gulf of Mexico?
Orcas are present in the Gulf of Mexico, but sightings are relatively rare compared to other marine mammals like dolphins. - What do orcas eat in the Gulf of Mexico?
Orcas in the Gulf of Mexico primarily feed on tuna, dolphins, and other marine fish. - Are orcas protected in Mexican waters?
Yes, orcas are protected under Mexican environmental laws and international agreements. - How deep do orcas dive in the Gulf of Mexico?
Orcas can dive to depths of over 1,000 feet while hunting in the Gulf of Mexico. - Do orcas migrate in the Gulf of Mexico?
The migratory patterns of orcas in the Gulf of Mexico are not well-understood, but they likely move in search of food. - What threats do orcas face in the Gulf of Mexico?
Orcas face threats from pollution, entanglement in fishing gear, and habitat degradation in the Gulf. - How can I report an orca sighting in the Gulf of Mexico?
You can report orca sightings to local marine research centers or conservation organizations. - What is the lifespan of orcas in the Gulf of Mexico?
The lifespan of orcas in the Gulf of Mexico is similar to those in other regions, typically ranging from 50 to 80 years. - Are there different types of orcas in the Gulf of Mexico?
While specific classifications are ongoing, orcas in the Gulf may exhibit genetic differences from other populations. - How can I support orca research in the Gulf of Mexico?
You can support orca research by donating to marine conservation organizations or participating in citizen science projects.
Ready to explore the wonders of Mexico’s marine life? Visit gaymexico.net for more information on LGBTQ+-friendly travel destinations, eco-tours, and ways to connect with the local community. Dive into adventure with us!
