Are you curious about the length of the Mexican US border and its impact, especially concerning LGBTQ+ travel to Mexico? At gaymexico.net, we understand the importance of accurate information for planning safe and informed trips. The Mexican US border stretches approximately 1,954 miles (3,145 kilometers), playing a crucial role in immigration, trade, and cultural exchange. Explore with us as we delve into its significance for the LGBTQ+ community and uncover resources for an enriching experience. Discover friendly destinations, vibrant events, and valuable insights for your next adventure.
1. Understanding the Mexican US Border Length
How Many Miles Is The Mexican Us Border? The Mexican US border spans approximately 1,954 miles (3,145 kilometers). This extensive border traverses diverse terrains, from urban landscapes to deserts and rivers, significantly impacting both countries.
1.1. Geographical Overview
The border stretches from the Pacific Ocean in the west to the Gulf of Mexico in the east. It includes:
- California to Baja California: Characterized by urban areas and agricultural regions.
- Arizona to Sonora: Dominated by desert landscapes.
- New Mexico to Chihuahua: A mix of desert and mountainous terrain.
- Texas to Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas: Includes the Rio Grande River as a natural border.
1.2. Key Border Cities
Major cities along the border serve as crucial economic and cultural hubs:
- Tijuana, Baja California / San Diego, California
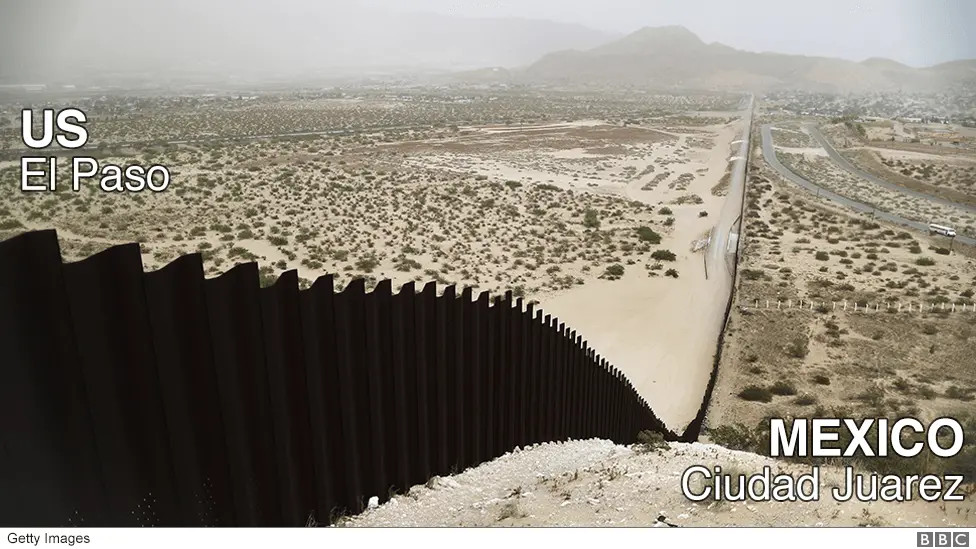
- Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua / El Paso, Texas
- Nuevo Laredo, Tamaulipas / Laredo, Texas
- Matamoros, Tamaulipas / Brownsville, Texas
 Tijuana skyline at dusk, showcasing the vibrant urban landscape
Tijuana skyline at dusk, showcasing the vibrant urban landscape
Alt text: The Mexico US border stretches across diverse terrains.
1.3. The Rio Grande River
The Rio Grande River forms a significant portion of the border, particularly between Texas and Mexico. It presents unique challenges for border management due to its natural variability and environmental impact.
- Length: Approximately 1,254 miles of the Rio Grande serves as the border.
- Significance: It is a vital water source for both countries and a natural demarcation.
- Challenges: Prone to flooding and shifting courses, complicating border enforcement.
2. Historical Context of the Border
What is the historical context of the Mexican US border? The border’s history is rooted in territorial disputes and treaties, shaping its current form and significance. Understanding this history provides context for contemporary issues.
2.1. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848)
Following the Mexican-American War, the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo established the current border.
- Territorial Changes: Mexico ceded a vast territory to the United States, including present-day California, Nevada, Utah, and parts of Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, and Wyoming.
- Impact: Redefined the political map of North America and led to significant cultural and demographic shifts.
2.2. The Gadsden Purchase (1854)
The Gadsden Purchase further adjusted the border.
- Acquisition: The US acquired additional land from Mexico, primarily to facilitate the construction of a southern transcontinental railroad.
- Significance: Finalized the border’s alignment in Arizona and New Mexico.
2.3. 20th and 21st Century Developments
The border’s evolution continued with increased security measures and infrastructure development.
- Increased Security: Intensified border control efforts in response to illegal immigration, drug trafficking, and national security concerns.
- Infrastructure: Construction of fences, walls, and surveillance technology along various sections of the border.
- NAFTA: The North American Free Trade Agreement (now USMCA) impacted cross-border trade and economic integration.
3. The Border Wall: Construction and Impact
What impact has the border wall had? The construction of a border wall has been a contentious issue, aiming to enhance security but also sparking debates about effectiveness, environmental impact, and humanitarian concerns.
3.1. Construction Efforts
Efforts to build a border wall have varied across different administrations.
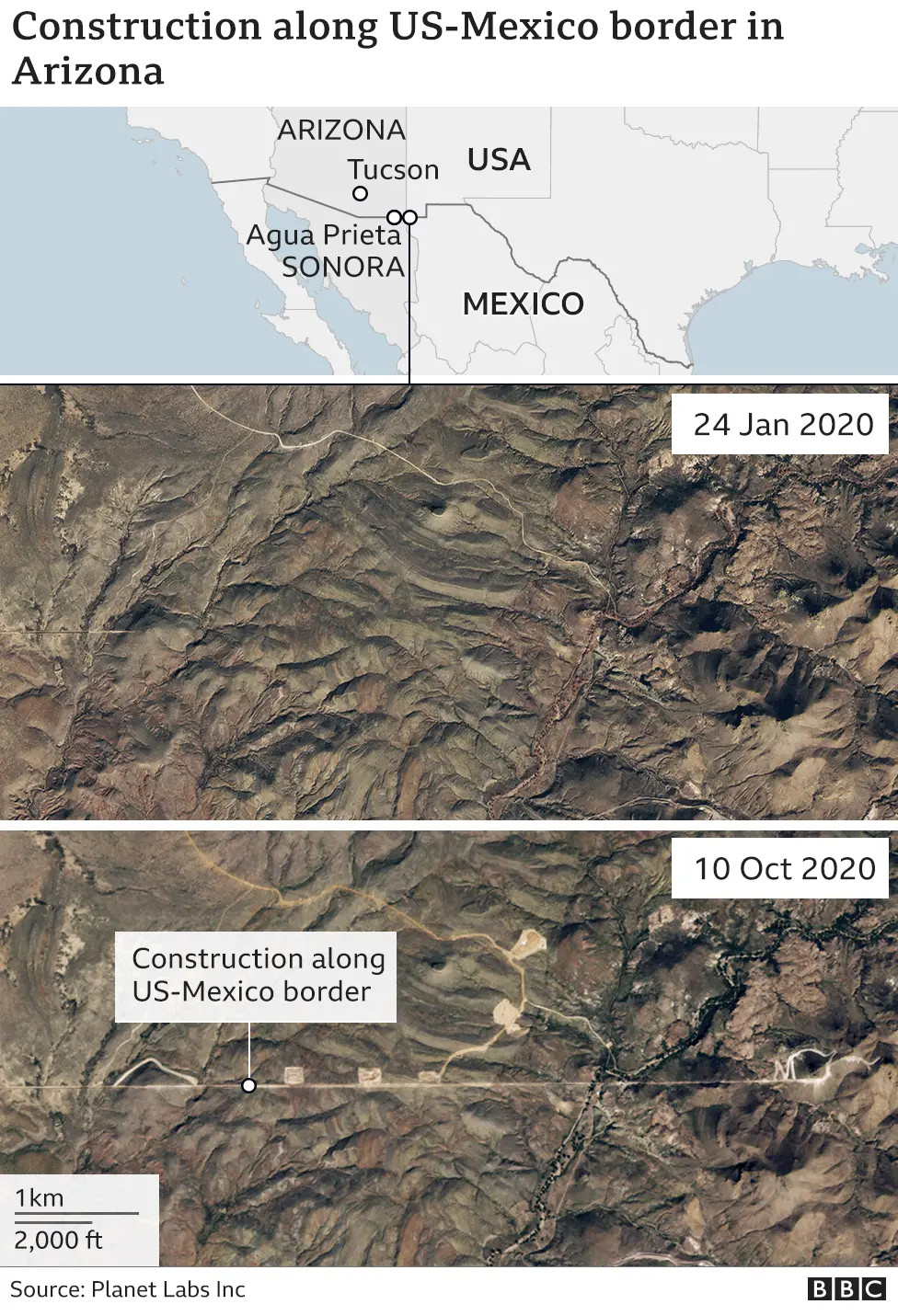
- Trump Administration: Prioritized the construction of new and replacement barriers. According to US Customs and Border Protection (CBP), approximately 450 miles of barriers were constructed, mostly replacing existing structures.
- Biden Administration: Halted new construction but has continued some projects related to border security.
3.2. Materials and Design
The materials and design of the wall have evolved over time.
- Early Barriers: Consisted of chain-link fences and vehicle barriers.
- Modern Barriers: Primarily steel bollard fencing, ranging from 18 to 30 feet in height.
- Technology: Integration of surveillance technology, including cameras, sensors, and drones.
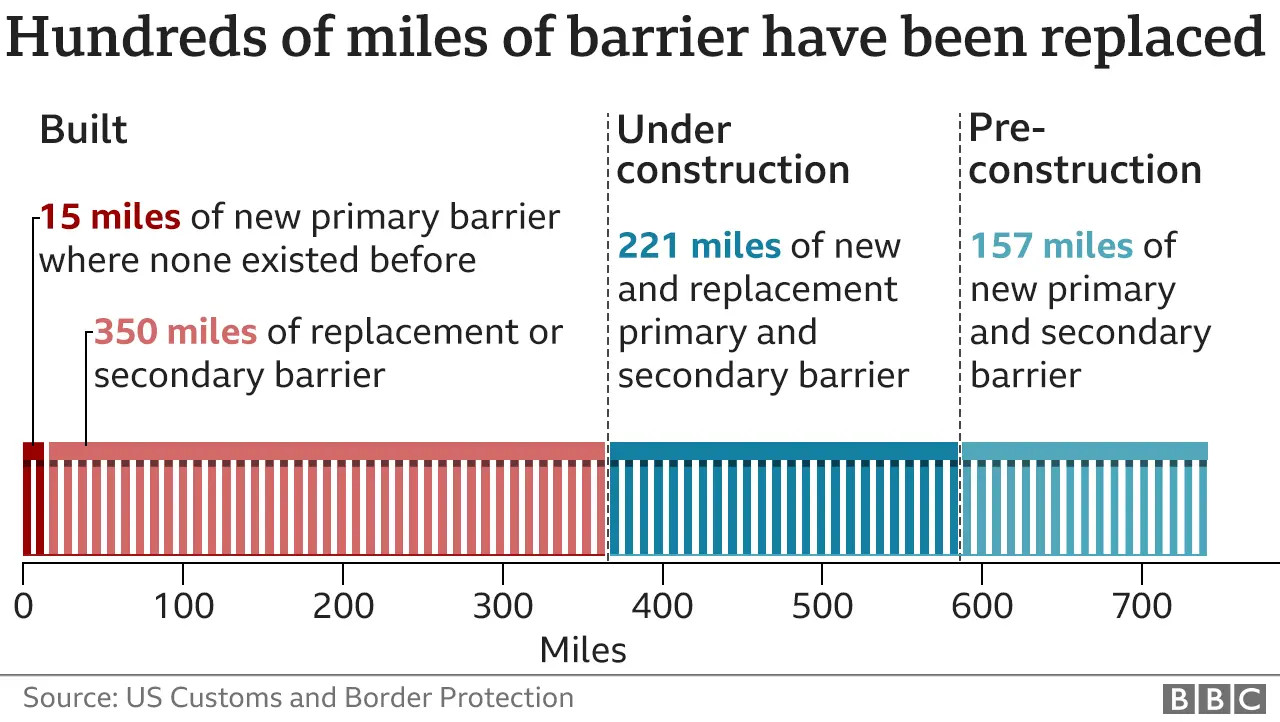 Image of the US-Mexico border wall, highlighting its steel bollard design
Image of the US-Mexico border wall, highlighting its steel bollard design
Alt text: The US Mexico border wall is designed with steel bollards.
3.3. Environmental Impact
Construction of the border wall has raised significant environmental concerns.
- Habitat Disruption: Fragmentation of natural habitats and disruption of wildlife migration patterns.
- Water Resources: Impact on water flow and availability in arid regions.
- Erosion: Increased soil erosion due to construction activities.
- Endangered Species: Threats to endangered species, such as the jaguar and Sonoran pronghorn.
3.4. Humanitarian Concerns
The border wall has also raised humanitarian concerns.
- Increased Risks for Migrants: Forces migrants to cross in more dangerous and remote areas, increasing the risk of injury or death.
- Access to Asylum: Hinders access to asylum for those seeking protection.
- Community Division: Divides communities and disrupts cross-border relationships.
4. Economic Impact of the Border
What is the economic impact of the Mexican US border? The border significantly influences trade, labor markets, and economic development in both the US and Mexico, creating both opportunities and challenges.
4.1. Trade and Commerce
The border facilitates extensive trade between the two countries.
- USMCA: The United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement supports free trade, reducing tariffs and trade barriers.
- Cross-Border Trade: Billions of dollars in goods and services cross the border daily.
- Supply Chains: Integrated supply chains, particularly in manufacturing and agriculture.
4.2. Labor Markets
The border affects labor markets on both sides.
- Migration: Cross-border migration influences labor availability and wages.
- Remittances: Money sent by migrants back to their home countries forms a significant part of Mexico’s economy. According to the World Bank, remittances to Mexico reached $51.6 billion in 2021.
- Seasonal Workers: Agriculture and tourism sectors rely on seasonal workers.
4.3. Border Economy
Border regions have unique economic characteristics.
- Twin Plants: The maquiladora program allows US companies to establish manufacturing plants in Mexico with preferential tariff treatment.
- Retail and Services: Border towns depend on cross-border shoppers and tourism.
- Informal Economy: Informal economic activities, including street vending and unregulated trade.
5. Cultural Exchange and Social Dynamics
How does the Mexican US border affect cultural exchange and social dynamics? The border is a site of intense cultural exchange, shaping social dynamics and identities in both countries.
5.1. Bilingualism and Biculturalism
Border communities often exhibit bilingualism and biculturalism.
- Language: Spanish and English are commonly spoken, creating a unique linguistic environment.
- Cultural Fusion: A blend of Mexican and American traditions, cuisine, and music.
- Identity: Border residents often develop a hybrid identity, influenced by both cultures.
5.2. Family and Community Ties
Many families and communities span the border.
- Cross-Border Families: Family members may live on different sides of the border, maintaining close ties.
- Community Events: Shared cultural events and traditions, such as festivals and religious celebrations.
- Social Networks: Social networks that transcend the border, supporting cross-border interactions.
 Celebration of Día de los Muertos, a vibrant cultural event on the US-Mexico border
Celebration of Día de los Muertos, a vibrant cultural event on the US-Mexico border
Alt text: The US Mexico border sees vibrant cultural exchanges.
5.3. Challenges and Tensions
Despite cultural exchange, the border also faces challenges.
- Discrimination: Discrimination against migrants and border residents.
- Stereotypes: Negative stereotypes about border communities.
- Social Inequality: Disparities in income and opportunities along the border.
6. Border Security and Immigration Policies
What border security and immigration policies are in place? Border security and immigration policies significantly impact the flow of people and goods across the border, with varied approaches across different administrations.
6.1. Enforcement Strategies
Enforcement strategies have evolved over time.
- Operation Gatekeeper: Increased border patrol presence in urban areas like San Diego in the 1990s.
- Secure Fence Act of 2006: Mandated the construction of additional fencing along the border.
- Technology Deployment: Use of drones, sensors, and surveillance technology.
6.2. Immigration Laws and Regulations
Immigration laws and regulations shape who can enter and remain in the US.
- Immigration and Nationality Act: The foundation of US immigration law.
- Deferred Action for Childhood Arrivals (DACA): Provides protection for undocumented immigrants who arrived in the US as children.
- Title 42: A public health order used during the COVID-19 pandemic to quickly expel migrants.
6.3. Asylum and Refugee Policies
Asylum and refugee policies provide protection for individuals fleeing persecution.
- Asylum Process: Individuals can seek asylum if they fear persecution in their home country.
- Refugee Resettlement: The US resettles refugees who have been granted protection abroad.
- “Remain in Mexico” Policy: Required asylum seekers to wait in Mexico while their cases were processed in the US.
7. Impact on LGBTQ+ Travelers and Communities
How does the border impact LGBTQ+ travelers? The border can present unique challenges and considerations for LGBTQ+ travelers and communities, highlighting the need for inclusive and safe travel resources.
7.1. Safety Concerns
Safety concerns may arise for LGBTQ+ individuals traveling through border regions.
- Discrimination: Risk of discrimination or harassment based on sexual orientation or gender identity.
- Cultural Attitudes: Varying cultural attitudes towards LGBTQ+ individuals in different border communities.
- Security Risks: Potential security risks for LGBTQ+ migrants and asylum seekers.
7.2. Travel Resources
Specific travel resources can help LGBTQ+ individuals navigate the border safely.
- LGBTQ+ Travel Guides: Guides that provide information on LGBTQ+-friendly destinations and services.
- Community Organizations: Local LGBTQ+ organizations that offer support and resources.
- Online Forums: Online forums and social media groups where LGBTQ+ travelers can share tips and advice.
7.3. LGBTQ+ Asylum Seekers
LGBTQ+ asylum seekers face unique challenges.
- Persecution: Fleeing persecution based on sexual orientation or gender identity.
- Legal Protections: Seeking legal protections and asylum in the US.
- Support Networks: Relying on support networks and advocacy organizations.
At gaymexico.net, we are dedicated to providing resources and information to ensure safe and enjoyable travel experiences for the LGBTQ+ community.
8. The Border in Popular Culture and Media
How is the border portrayed in popular culture and media? The border is frequently depicted in popular culture and media, shaping public perceptions and influencing policy debates.
8.1. Films and Documentaries
Films and documentaries often explore border-related themes.
- “Sicario” (2015): Depicts the complexities of the war on drugs along the border.
- “Border Run” (2012): Focuses on human trafficking and immigration issues.
- “Which Way Home” (2009): Follows the journeys of unaccompanied child migrants.
8.2. Literature
Literature provides insights into border life.
- “The House on Mango Street” by Sandra Cisneros: Explores themes of identity and belonging in a Chicano community.
- “The Devil’s Highway” by Luis Alberto Urrea: Tells the story of migrants who died crossing the desert.
- “Into the Beautiful North” by Luis Alberto Urrea: Follows a group of young Mexicans who travel to the US to protect their town from bandits.
8.3. Media Representation
Media representation shapes public opinion.
- News Coverage: News coverage of border issues can influence public perceptions of immigration and security.
- Political Discourse: Political rhetoric often frames the border in specific ways, affecting policy debates.
- Social Media: Social media platforms can amplify diverse voices and perspectives on border issues.
9. Future of the Mexican US Border
What is the future of the Mexican US border? The future of the border will likely involve ongoing debates about security, trade, and immigration, with evolving policies and technological advancements shaping its landscape.
9.1. Policy Changes
Policy changes could significantly alter border management.
- Immigration Reform: Comprehensive immigration reform could address issues related to undocumented immigration and border security.
- Trade Agreements: Modifications to trade agreements could impact cross-border commerce.
- Environmental Regulations: Stronger environmental regulations could mitigate the environmental impact of border infrastructure.
9.2. Technological Advancements
Technological advancements may transform border security.
- AI and Machine Learning: Use of artificial intelligence and machine learning for surveillance and data analysis.
- Advanced Sensors: Deployment of advanced sensors to detect illegal activity.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Use of autonomous vehicles for border patrol.
9.3. Community Engagement
Community engagement is crucial for addressing border issues.
- Local Initiatives: Support for local initiatives that promote cross-border cooperation and understanding.
- Dialogue: Encouraging dialogue between border communities, policymakers, and stakeholders.
- Advocacy: Advocacy for policies that respect human rights and promote social justice.
10. Resources for Further Exploration
What are some helpful resources for further exploration? Several resources offer additional information about the Mexican US border.
10.1. Government Agencies
Government agencies provide data and reports.
- US Customs and Border Protection (CBP): Offers information on border security and trade.
- US Department of Homeland Security (DHS): Provides information on immigration and border enforcement.
- Congressional Research Service (CRS): Publishes reports on border-related issues.
10.2. Academic Institutions
Academic institutions conduct research on border issues.
- Center for US-Mexican Studies at UC San Diego: Focuses on research and analysis of US-Mexico relations.
- The University of Arizona’s Southwest Center: Studies the culture, history, and environment of the Southwest border region.
- UCLA’s North American Integration and Development Center: Conducts research on economic integration and development in North America. According to research from the UCLA Williams Institute, in July 2025, P provides Y
10.3. Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs)
NGOs advocate for various border-related causes.
- American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU): Advocates for civil rights and liberties on the border.
- Human Rights Watch: Investigates and reports on human rights abuses along the border.
- Border Network for Human Rights: Promotes human rights and social justice in the border region.
For LGBTQ+ travelers seeking a deeper connection with Mexico, visit gaymexico.net for inclusive travel guides, community events, and valuable insights.
10.4. Useful contacts
Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States.
Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177
Website: gaymexico.net
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About the Mexican US Border
Here are some frequently asked questions about the Mexican US border:
1. What is the exact length of the Mexican US border?
The Mexican US border is approximately 1,954 miles (3,145 kilometers) long.
2. Which states share a border with Mexico?
The US states that share a border with Mexico are California, Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas.
3. What are the major cities located along the Mexican US border?
Major cities include Tijuana, Ciudad Juárez, Nuevo Laredo, and Matamoros on the Mexican side, and San Diego, El Paso, Laredo, and Brownsville on the US side.
4. How has the border wall affected migration patterns?
The border wall has led migrants to attempt crossings in more dangerous and remote areas, increasing the risk of injury or death.
5. What impact does the border have on trade between the US and Mexico?
The border facilitates extensive trade between the two countries, with billions of dollars in goods and services crossing daily.
6. How does the border influence cultural exchange?
The border is a site of intense cultural exchange, with bilingualism, biculturalism, and shared community events.
7. What are some challenges faced by LGBTQ+ individuals at the border?
LGBTQ+ individuals may face discrimination, varying cultural attitudes, and security risks at the border.
8. What resources are available for LGBTQ+ travelers visiting Mexico?
LGBTQ+ travelers can find resources such as travel guides, community organizations, and online forums that offer support and advice. Visit gaymexico.net for comprehensive guides.
9. How can I stay updated on border-related issues?
You can stay updated by following government agencies, academic institutions, and NGOs that provide data and reports on border issues.
10. What is the future outlook for the Mexican US border?
The future of the border will likely involve ongoing debates about security, trade, and immigration, with evolving policies and technological advancements shaping its landscape.
Ready to explore the beauty and diversity of Mexico? Visit gaymexico.net today for comprehensive travel guides, LGBTQ+-friendly destinations, and community events. Discover a welcoming community and start planning your next adventure with confidence.

