Has NAFTA truly reshaped Mexico? Absolutely. NAFTA’s impact on Mexico, especially for the LGBTQ+ community, is a complex topic. gaymexico.net is here to help you understand it and provides resources and information about LGBTQ+ life and travel in Mexico. Explore NAFTA’s ripple effects, trade liberalization, and cross-border investment opportunities.
1. What Was NAFTA and Why Was It Created?
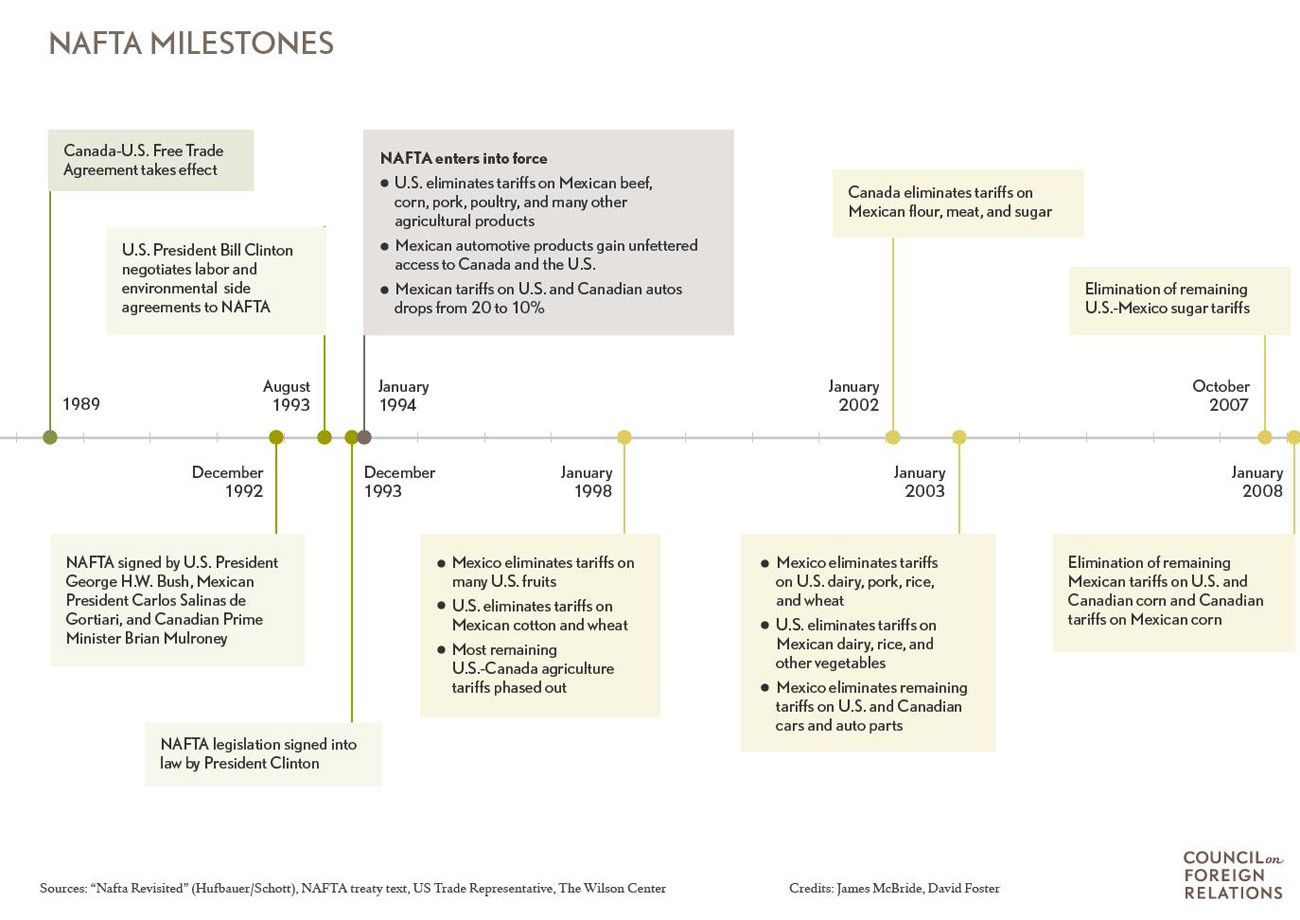
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) was a trilateral agreement between Canada, Mexico, and the United States. Its purpose was to eliminate most tariffs and trade barriers between the three countries. NAFTA was designed to foster economic growth and cooperation within North America. The agreement encompassed various sectors, including agriculture, textiles, and automobile manufacturing, while also addressing intellectual property rights and dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Goal: To integrate Mexico with the developed economies of the United States and Canada, promoting economic growth and discouraging illegal immigration.
- Vision: To create new jobs and opportunities in Mexico, modernize its economy, and shift from exporting people to exporting goods.
 Mexican Flag Waving Proudly
Mexican Flag Waving Proudly
2. How Did NAFTA Reshape North American Economic Relations?
NAFTA fundamentally reshaped North American economic relations by driving unprecedented integration between the economies of Canada, Mexico, and the United States. It stimulated regional trade and cross-border investment among the three countries. Regional trade tripled, and cross-border investment grew significantly under the agreement.
- Trade Boost: NAFTA led to a sharp increase in regional trade, rising from approximately $290 billion in 1993 to over $1.1 trillion in 2016.
- Investment Surge: Cross-border investment surged, with U.S. foreign direct investment (FDI) stock in Mexico increasing from $15 billion to over $100 billion during the same period.
3. What Were the Intended Benefits of NAFTA for Mexico?
NAFTA was intended to bring several benefits to Mexico. These included stronger and steadier economic growth, new jobs and opportunities for its growing workforce, discouragement of illegal migration, and modernization of the Mexican economy. Mexican policymakers saw NAFTA as an opportunity to accelerate and solidify these reforms. They reduced public debt, introduced a balanced-budget rule, stabilized inflation, and built up the country’s foreign reserves.
4. How Did NAFTA Affect the U.S. Economy?
In the years following NAFTA, trade between the United States and its North American neighbors more than tripled. Canada and Mexico became the two largest destinations for U.S. exports, accounting for over one-third of the total. Most estimates suggest that the deal increased U.S. gross domestic product (GDP) by less than 0.5 percent.
Supporters estimate that some fourteen million U.S. jobs rely on trade with Canada or Mexico. The nearly two hundred thousand export-related jobs created annually by the pact pay 15 to 20 percent more on average than the jobs that were lost.
5. How Did NAFTA Affect the Mexican Economy?
NAFTA boosted Mexican farm exports to the United States, which have tripled since the pact’s implementation. Hundreds of thousands of auto manufacturing jobs have also been created in the country. Most studies have found that the agreement increased productivity and lowered consumer prices in Mexico.
6. What Were the Criticisms of NAFTA’s Impact on Mexico?
Critics argue that NAFTA’s promises of rapid growth, wage increases, and reduced emigration did not materialize as expected. Between 1993 and 2013, Mexico’s economy grew at an average rate of just 1.3 percent yearly, while poverty remained at the same levels as in 1994. The expected convergence of U.S. and Mexican wages did not occur, and unemployment rose.
Some economists have blamed NAFTA for exposing Mexican farmers, especially corn producers, to competition from heavily subsidized U.S. agriculture. A study estimated that NAFTA put almost two million small-scale Mexican farmers out of work, driving illegal migration to the United States.
7. How Did NAFTA Affect Canada’s Economy?
Canada saw strong gains in cross-border investment during the NAFTA era. Since 1993, U.S. and Mexican investments in Canada have tripled. Overall Canada-U.S. trade increased rapidly in the wake of Canada’s trade liberalization. Post-NAFTA, Canadian exports to the United States grew from $110 billion to $346 billion.
Agriculture, in particular, saw a boost. Canada is the leading importer of U.S. agricultural products, and Canadian agricultural trade with the United States has more than tripled since 1994, as did Canada’s total agriculture exports to NAFTA partners.
8. What Was the USMCA and How Does It Differ From NAFTA?
The U.S.-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) is an updated version of NAFTA that entered into force on July 1, 2020. It includes several changes:
- Rules of Origin: Tightened rules of origin for the auto industry, requiring 75 percent of each vehicle to originate in the member countries.
- Labor Stipulations: New labor stipulations were added, requiring 40 percent of each vehicle to come from factories paying at least $16 per hour.
- Intellectual Property: A proposed expansion of intellectual property protections for U.S. pharmaceuticals was sacrificed.
- Dispute Settlement: The USMCA significantly scales back the controversial investor-state dispute settlement mechanism.
9. What Were Some of the Key Outcomes and Disparities From NAFTA in Mexico?
Mexico’s NAFTA experience suffered from disparities between the promises of rapid growth and the actual outcomes. Between 1993 and 2013, Mexico’s economy grew at an average rate of just 1.3 percent yearly. Poverty remained at the same levels as in 1994. The expected convergence of U.S. and Mexican wages didn’t happen. Mexico’s per capita income rose at an average of just 1.2 percent annually in that period—far slower than Latin American countries such as Brazil, Chile, and Peru.
10. How Did NAFTA Impact the LGBTQ+ Community in Mexico?
The impact of NAFTA on the LGBTQ+ community in Mexico is complex. While NAFTA primarily focused on trade and economic policies, its broader effects on Mexican society and economy have indirect consequences for the LGBTQ+ population.
Economic Changes
- Job Opportunities: NAFTA led to the growth of certain industries in Mexico, potentially creating more job opportunities in urban areas. This could benefit LGBTQ+ individuals seeking employment and economic independence.
- Increased Migration: Some studies suggest that NAFTA contributed to the displacement of small-scale farmers, leading to increased migration to urban centers or the United States. This could disrupt social structures and support networks for LGBTQ+ individuals in rural areas.
- Wage Disparities: Critics argue that NAFTA did not lead to the expected convergence of U.S. and Mexican wages, which could exacerbate economic inequalities affecting the LGBTQ+ community.
Social and Cultural Changes
- Exposure to Global Ideas: NAFTA facilitated greater cultural exchange and exposure to global ideas, which may have contributed to increased awareness and acceptance of LGBTQ+ rights in Mexico.
- Civil Society and Advocacy: The economic and social changes brought about by NAFTA may have indirectly influenced the growth of civil society organizations, including those advocating for LGBTQ+ rights.
- Urbanization: Increased urbanization as a result of NAFTA-related economic shifts could lead to the development of LGBTQ+ communities and social spaces in cities.
Specific Considerations for the LGBTQ+ Community
- Discrimination in Employment: Despite potential job opportunities, LGBTQ+ individuals in Mexico may still face discrimination in employment, which could limit their ability to benefit from NAFTA-related economic growth.
- Access to Healthcare: Economic changes resulting from NAFTA could affect access to healthcare services, including those specific to the needs of the LGBTQ+ community.
- Social Acceptance: While increased exposure to global ideas may promote greater acceptance of LGBTQ+ individuals, traditional social attitudes and discrimination may persist, particularly in more conservative regions of Mexico.
Mexico City Pride Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States.
Mexico City Pride Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177
11. What Were the Long-Term Consequences for Mexican Agriculture?
NAFTA’s impact on Mexican agriculture was mixed. While it boosted Mexican farm exports to the United States, it also exposed Mexican farmers, especially corn producers, to competition from heavily subsidized U.S. agriculture. A study estimated that NAFTA put almost two million small-scale Mexican farmers out of work.
12. How Did the “Two-Speed” Economy Affect Different Regions of Mexico?
Mexico’s economy developed a “two-speed” nature, where NAFTA drove growth in foreign investment, high-tech manufacturing, and rising wages in the industrial north, while the largely agrarian south remained detached from this new economy. Inequality increased as workers in the north gained much higher wages from trade-related activity.
13. What Non-NAFTA Factors Affected Mexico’s Economic Performance?
Mexico’s recent economic performance has been affected by non-NAFTA factors:
- The 1994 devaluation of the peso drove Mexican exports.
- Competition with China’s low-cost manufacturing sector likely depressed growth.
- Unrelated public policies, such as land reform, made it easier for farmers to sell their land and emigrate.
14. What Lessons Can Be Learned From NAFTA’s Impact on Mexico?
Several lessons can be learned from NAFTA’s impact on Mexico:
- Trade agreements can have mixed results, with benefits and drawbacks.
- The distribution of benefits and costs can be uneven, leading to inequality.
- Non-trade factors play a significant role in economic performance.
- Policy interventions are needed to mitigate negative impacts and ensure equitable outcomes.
15. What Were the Alternative Perspectives on NAFTA’s Impact?
Some economists, such as Gary Clyde Hufbauer and Cathleen Cimino-Isaacs of the Peterson Institute for International Economics (PIIE), have emphasized that increased trade produces overall gains for the U.S. economy. Their 2014 PIIE study of NAFTA’s effects found a net loss of about fifteen thousand jobs per year due to the pact—but gains of roughly $450,000 for each job lost, in the form of higher productivity and lower consumer prices.
16. What Policy Changes Were Proposed to Mitigate Negative Effects?
To mitigate the negative effects of trade deals like NAFTA, policy changes have been proposed:
- Compensate workers who lose their jobs.
- Provide retraining programs to help them transition to new industries.
- Increase funding levels for programs such as the U.S. Trade Adjustment Assistance (TAA).
17. What Specific Changes Were Made in the USMCA Regarding Labor and Environmental Protections?
The USMCA achieved stronger enforcement mechanisms for labor provisions than the original NAFTA deal. These include rules of origin for the auto industry were tightened, requiring 75 percent of each vehicle to originate in the member countries, up from 62.5 percent. New labor stipulations were added, requiring 40 percent of each vehicle to come from factories paying at least $16 per hour.
18. How Did USMCA Address Investor-State Dispute Settlement Mechanisms?
The USMCA significantly scales back the controversial investor-state dispute settlement mechanism, eliminating it entirely with Canada and limiting it to certain sectors with Mexico, including oil and gas and telecommunications.
19. What Were the Perspectives of Labor Unions on NAFTA and USMCA?
The AFL-CIO, the largest collection of U.S. labor unions, heavily criticized NAFTA. However, the USMCA achieved stronger enforcement mechanisms for labor provisions than the original deal, leading the AFL-CIO to support the pact—a rare endorsement.
20. NAFTA and LGBTQ+ Tourism in Mexico: A Complicated Relationship
While NAFTA primarily addressed trade and economic matters, it indirectly influenced Mexico’s socio-cultural landscape, impacting LGBTQ+ tourism. The agreement’s effects are complex and multifaceted:
Positives:
- Increased Exposure: NAFTA facilitated cultural exchange, potentially increasing awareness and acceptance of LGBTQ+ issues. This could lead to a more welcoming environment for LGBTQ+ tourists in some areas.
- Economic Growth: NAFTA contributed to economic growth in certain sectors, potentially creating more job opportunities in the tourism industry. This could benefit LGBTQ+ individuals working in or seeking employment in LGBTQ+-friendly establishments.
- Infrastructure Development: NAFTA-driven investments in infrastructure could improve transportation and communication networks, making it easier for LGBTQ+ tourists to access various destinations within Mexico.
Negatives:
- Economic Disparities: Critics argue that NAFTA exacerbated economic inequalities, potentially leading to social tensions that could affect the LGBTQ+ community and tourism.
- Cultural Homogenization: Concerns exist that NAFTA could contribute to cultural homogenization, potentially diluting the unique cultural experiences that attract LGBTQ+ tourists to Mexico.
- Labor Exploitation: Some worry that NAFTA-related labor practices could lead to exploitation in the tourism sector, affecting LGBTQ+ workers and potentially diminishing the quality of services offered to LGBTQ+ tourists.
FAQ: NAFTA and Mexico
How Did NAFTA Affect the Average Mexican Citizen?
NAFTA’s impact was mixed. While some benefited from increased trade and job opportunities, others, particularly small-scale farmers, faced challenges due to competition from subsidized U.S. agriculture.
Did NAFTA Reduce Poverty in Mexico?
Poverty levels remained largely unchanged after NAFTA’s implementation, indicating that the agreement did not significantly reduce poverty in Mexico.
What Role Did NAFTA Play in Mexican Migration to the U.S.?
Some studies suggest that NAFTA contributed to increased migration to the U.S. by displacing Mexican farmers and driving them to seek opportunities elsewhere.
How Did NAFTA Affect Wages in Mexico?
The expected convergence of U.S. and Mexican wages did not occur, and wage growth in Mexico remained slow compared to other Latin American countries.
Was NAFTA a Success for Mexico?
NAFTA’s success for Mexico is debatable. While it boosted exports and attracted foreign investment, it also led to increased inequality and challenges for certain sectors.
How Did NAFTA Change Mexico’s Relationship With the U.S.?
NAFTA deepened economic ties between Mexico and the U.S., making Mexico more dependent on trade with its northern neighbor.
Did NAFTA Improve Mexico’s Infrastructure?
NAFTA may have indirectly contributed to infrastructure improvements, but these were not a direct result of the agreement.
What Were the Environmental Consequences of NAFTA in Mexico?
NAFTA’s environmental consequences are a subject of debate, with some studies suggesting that it led to increased pollution and resource depletion.
How Did NAFTA Affect Small Businesses in Mexico?
Small businesses in Mexico faced challenges due to increased competition from larger U.S. companies.
What Were the Key Differences Between NAFTA and the European Union?
NAFTA was primarily a trade agreement, while the European Union is a more comprehensive economic and political union with greater integration.
Ready to Explore LGBTQ+ Mexico?
Dive into the heart of Mexico’s vibrant LGBTQ+ scene with gaymexico.net. Discover insider tips, safe travel advice, and the best destinations for an unforgettable experience. Your adventure starts here!
