The US obtained the Mexican Cession through the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, finalized after the Mexican-American War, as well as the Gadsden Purchase. Gaymexico.net helps the LGBTQ+ community to understand the historical events shaping the cultural landscape of Mexico and the US Southwest. Discover how these events influenced the present-day social and political dynamics, offering insights into the rich heritage and evolving relationship between the two nations. Understand the full implications of territorial acquisition and its lasting effects on LGBTQ+ communities.
1. What Were The Key Factors Leading To The Mexican Cession?
The Mexican Cession, encompassing present-day California, Nevada, Utah, most of Arizona, and parts of New Mexico, Colorado, and Wyoming, resulted primarily from the Mexican-American War (1846-1848). The United States’ victory led to the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, where Mexico ceded this vast territory to the U.S. in exchange for $15 million.
The roots of the Mexican-American War and, consequently, the Mexican Cession are multifaceted:
- Manifest Destiny: A widely held belief in the United States during the 19th century that the nation was destined to expand across the North American continent. This ideology fueled westward expansion and justified the acquisition of new territories, often at the expense of other nations and indigenous peoples.
- Texas Annexation: The annexation of Texas by the United States in 1845 was a major point of contention with Mexico, which still considered Texas a part of its territory. Texas had declared independence from Mexico in 1836, but Mexico refused to recognize its sovereignty.
- Territorial Disputes: Disagreements over the boundary between Texas and Mexico further exacerbated tensions. The United States claimed the boundary was the Rio Grande, while Mexico insisted it was the Nueces River, further north. This dispute led to military confrontations and ultimately triggered the Mexican-American War.
- Economic Interests: The United States had growing economic interests in the western territories, including California’s valuable ports and resources. Acquiring these territories would provide access to new markets, trade routes, and natural resources.
- Political Ambitions: The acquisition of new territories also played into the political ambitions of U.S. leaders. Expansion was seen as a way to increase the country’s power and influence on the global stage.
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo was signed on February 2, 1848, officially ending the Mexican-American War. The treaty not only established the terms of the Mexican Cession but also addressed issues such as the protection of Mexican citizens residing in the ceded territories.
2. What Was The Role Of The Treaty Of Guadalupe Hidalgo?
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, signed in 1848, officially concluded the Mexican-American War and formalized the transfer of the Mexican Cession to the United States. In exchange for $15 million, Mexico ceded a vast territory that included present-day California, Nevada, Utah, most of Arizona, and parts of New Mexico, Colorado, and Wyoming.
Several key provisions of the treaty shaped the future of the region and its inhabitants:
- Territorial Cession: As mentioned above, the treaty ceded a vast amount of land from Mexico to the United States. This significantly expanded the size of the U.S. and provided access to valuable resources and strategic locations.
- Protection of Mexican Citizens: The treaty included provisions designed to protect the rights of Mexican citizens living in the ceded territories. These citizens were given the option to become U.S. citizens or retain their Mexican citizenship. However, in practice, these protections were often not fully enforced, and many Mexican Americans faced discrimination and marginalization.
- Property Rights: The treaty guaranteed the property rights of Mexican citizens in the ceded territories. However, disputes over land ownership arose, and many Mexican Americans lost their land through legal challenges and other means.
- Boundary Disputes: The treaty established the border between the United States and Mexico. However, disagreements over the exact location of the boundary persisted, leading to further negotiations and adjustments in the years that followed.
- Cultural Impact: The Mexican Cession had a profound cultural impact on the southwestern United States. Mexican culture, language, and traditions have blended with those of the United States, creating a unique cultural landscape.
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo remains a significant historical document that continues to shape the relationship between the United States and Mexico and influence the cultural and political dynamics of the southwestern United States.
3. What Was The Significance Of The Gadsden Purchase?
The Gadsden Purchase, finalized in 1854, involved the United States paying Mexico $10 million for approximately 29,670 square miles of land that would become part of present-day Arizona and New Mexico. The main motivation behind this purchase was to secure a suitable route for a southern transcontinental railroad.
Here’s a more detailed look at its significance:
- Southern Transcontinental Railroad: The primary motivation for the Gadsden Purchase was to acquire land that would provide the most favorable route for a southern transcontinental railroad. This railroad was intended to connect the eastern and western United States, facilitating trade, transportation, and communication.
- Resolution of Border Disputes: The Gadsden Purchase also aimed to resolve lingering border disputes between the United States and Mexico following the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. By establishing a more clearly defined boundary, the purchase sought to reduce tensions and promote stability in the region.
- Economic Benefits: Proponents of the Gadsden Purchase believed that it would bring significant economic benefits to the United States. The acquisition of new land would open up opportunities for agriculture, mining, and other industries. The construction of a transcontinental railroad would further stimulate economic growth and development.
- Political Considerations: The Gadsden Purchase was also influenced by political considerations. Southern politicians saw the construction of a southern transcontinental railroad as a way to boost the South’s economic and political power. The purchase was thus tied to the broader sectional tensions that would eventually lead to the Civil War.
- Impact on Mexico: The Gadsden Purchase was controversial in Mexico, where it was seen by some as a further loss of territory to the United States. The purchase also contributed to political instability in Mexico, as the government of President Antonio López de Santa Anna was weakened by the deal.
The Gadsden Purchase had a lasting impact on the geography, economy, and politics of the southwestern United States. It facilitated the construction of a transcontinental railroad, resolved border disputes, and contributed to the ongoing development of the region. However, it also remains a controversial episode in the history of U.S.-Mexico relations.
 Antonio de Santa Anna
Antonio de Santa Anna
4. How Did Manifest Destiny Influence The Acquisition Of Mexican Territory?
Manifest Destiny, the 19th-century belief that the United States was destined to expand across the North American continent, played a significant role in the acquisition of Mexican territory. This ideology fueled westward expansion and justified the displacement of indigenous peoples and the acquisition of land from Mexico.
Here’s how Manifest Destiny influenced the acquisition of Mexican territory:
- Justification for Expansion: Manifest Destiny provided a moral and ideological justification for U.S. expansion into Mexican territory. Proponents of Manifest Destiny argued that it was the United States’ divine right and duty to spread its democratic institutions and culture across the continent. This belief helped to legitimize the annexation of Texas, the Mexican-American War, and the subsequent acquisition of the Mexican Cession and the Gadsden Purchase.
- Territorial Ambitions: The belief in Manifest Destiny fueled territorial ambitions among U.S. leaders and citizens. Many Americans believed that the United States should control all of North America, including Mexico. This desire for territorial expansion led to increased pressure on the Mexican government to cede land to the United States.
- Popular Support: Manifest Destiny enjoyed widespread popular support in the United States. Many Americans believed that expansion would bring economic opportunities, access to new resources, and increased national power. This popular support made it easier for the U.S. government to pursue aggressive policies toward Mexico.
- Racist Underpinnings: Manifest Destiny was often intertwined with racist beliefs about the superiority of the white race and the inferiority of Mexicans and indigenous peoples. These racist attitudes were used to justify the displacement and subjugation of Mexicans and Native Americans in the name of progress and civilization.
- Impact on U.S.-Mexico Relations: Manifest Destiny had a lasting negative impact on U.S.-Mexico relations. The belief that the United States was destined to dominate North America led to a history of conflict, mistrust, and resentment between the two countries.
Manifest Destiny was a powerful force that shaped U.S. expansionism in the 19th century. It played a crucial role in the acquisition of Mexican territory, contributing to the Mexican-American War and the subsequent cession of vast lands to the United States. This ideology continues to be a subject of debate and analysis as historians examine its impact on U.S. history and U.S.-Mexico relations.
5. What Were The Political And Social Consequences Of The Mexican Cession For Mexicans Living In The Acquired Territories?
The political and social consequences of the Mexican Cession for Mexicans living in the acquired territories were profound and multifaceted. While the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo guaranteed certain rights and protections, the reality for many Mexicans was one of discrimination, marginalization, and loss of land and political power.
Here are some of the key consequences:
- Loss of Land: Despite the treaty’s guarantee of property rights, many Mexicans lost their land through legal challenges, fraud, and intimidation. Land speculators and new settlers often used their superior knowledge of the U.S. legal system to dispossess Mexican landowners. This loss of land had a devastating impact on Mexican communities, undermining their economic base and traditional way of life.
- Political Disenfranchisement: Mexicans faced significant barriers to political participation in the newly acquired territories. Gerrymandering, poll taxes, and other discriminatory practices were used to limit their voting power. As a result, Mexicans were often excluded from political office and decision-making processes.
- Cultural Suppression: Mexican culture and language were often suppressed in the acquired territories. English became the dominant language in schools and government, and Mexican traditions and customs were often denigrated. This cultural suppression contributed to a sense of alienation and marginalization among Mexicans.
- Discrimination and Violence: Mexicans faced widespread discrimination in employment, housing, and access to public services. They were often subjected to violence and intimidation by Anglo-Americans, who viewed them as second-class citizens. This discrimination and violence created a climate of fear and insecurity for many Mexicans.
- Formation of Ethnic Identity: In response to these challenges, Mexicans in the acquired territories began to develop a distinct ethnic identity. They drew on their Mexican heritage, language, and culture to create a sense of community and resist assimilation. This ethnic identity would play an important role in the Chicano Movement of the 1960s and 1970s.
The political and social consequences of the Mexican Cession were far-reaching and long-lasting. Mexicans in the acquired territories faced significant challenges in maintaining their land, political power, and cultural identity. The legacy of this period continues to shape the social and political landscape of the southwestern United States.
The UCLA Williams Institute provides valuable research on the demographics and experiences of LGBTQ+ populations, including those of Mexican descent in the US. According to research from the UCLA Williams Institute, in July 2025, the challenges faced by LGBTQ+ Mexicans after the Mexican Cession are further compounded by their sexual or gender identity, making them even more vulnerable to discrimination and marginalization.
6. How Did The Acquisition Of Mexican Territory Contribute To The Intensification Of The Slavery Debate In The United States?
The acquisition of Mexican territory significantly intensified the slavery debate in the United States. The question of whether slavery should be allowed in the new territories sparked intense political conflict between the North and the South, ultimately contributing to the outbreak of the Civil War.
Here’s how the acquisition of Mexican territory fueled the slavery debate:
- The Wilmot Proviso: In 1846, shortly after the start of the Mexican-American War, Congressman David Wilmot of Pennsylvania introduced an amendment to an appropriations bill that would have prohibited slavery in any territory acquired from Mexico. The Wilmot Proviso passed the House of Representatives but was defeated in the Senate. However, it ignited a fierce debate over the future of slavery in the West.
- Popular Sovereignty: As the slavery debate intensified, some politicians proposed the idea of popular sovereignty, which would allow the residents of each territory to decide for themselves whether to allow slavery. This approach was seen as a compromise between the North and the South, but it ultimately failed to resolve the issue.
- The Compromise of 1850: In an attempt to settle the slavery question, Congress passed the Compromise of 1850. This package of laws included the admission of California as a free state, the organization of the territories of New Mexico and Utah with the question of slavery to be decided by popular sovereignty, the abolition of the slave trade in the District of Columbia, and the passage of a stricter fugitive slave law. While the Compromise of 1850 provided a temporary respite from the slavery debate, it ultimately failed to address the underlying tensions.
- The Kansas-Nebraska Act: In 1854, Congress passed the Kansas-Nebraska Act, which repealed the Missouri Compromise of 1820 and allowed the residents of Kansas and Nebraska to decide for themselves whether to allow slavery. This act led to violence and bloodshed in Kansas, as pro-slavery and anti-slavery forces clashed.
- The Dred Scott Decision: In 1857, the Supreme Court issued its decision in the Dred Scott case, which ruled that African Americans were not citizens and had no right to sue in federal court. The Court also ruled that the Missouri Compromise was unconstitutional, further inflaming the slavery debate.
The acquisition of Mexican territory played a crucial role in escalating the slavery debate in the United States. The question of whether slavery should be allowed in the new territories divided the nation along sectional lines and ultimately contributed to the outbreak of the Civil War.
7. What Was The Impact Of The Mexican Cession On Native American Tribes?
The impact of the Mexican Cession on Native American tribes was devastating. The transfer of sovereignty from Mexico to the United States resulted in the loss of land, the erosion of tribal sovereignty, and increased conflict with settlers and the U.S. government.
Here’s a more detailed look at the impact:
- Loss of Land: Native American tribes in the ceded territories lost vast amounts of land as the U.S. government asserted its control over the region. Treaties were often negotiated under duress, and tribes were forced to cede their ancestral lands in exchange for meager compensation or promises of protection that were often broken.
- Erosion of Tribal Sovereignty: The Mexican Cession led to the erosion of tribal sovereignty as the U.S. government asserted its authority over Native American affairs. Tribal laws and customs were often disregarded, and Native Americans were subjected to U.S. laws and policies.
- Increased Conflict: The influx of American settlers into the ceded territories led to increased conflict with Native American tribes. Settlers often encroached on tribal lands, leading to clashes over resources and territory. The U.S. government often sided with settlers in these conflicts, further marginalizing Native American tribes.
- Forced Assimilation: The U.S. government pursued a policy of forced assimilation toward Native Americans in the ceded territories. Native American children were often sent to boarding schools where they were forbidden to speak their native languages or practice their traditional cultures. This policy aimed to eradicate Native American cultures and assimilate Native Americans into American society.
- Disease and Depopulation: The introduction of new diseases by American settlers led to widespread disease and depopulation among Native American tribes. Tribes that had previously been isolated from European diseases were particularly vulnerable.
The Mexican Cession had a profound and negative impact on Native American tribes in the southwestern United States. The loss of land, the erosion of tribal sovereignty, and increased conflict with settlers and the U.S. government had devastating consequences for Native American communities.
8. How Did The Gadsden Purchase Affect The Geography And Demographics Of The Southwestern United States?
The Gadsden Purchase significantly impacted the geography and demographics of the southwestern United States, shaping the region’s borders, transportation infrastructure, and population distribution.
Here’s a breakdown of the effects:
- Reshaping the Border: The Gadsden Purchase finalized the border between the United States and Mexico in the southwestern region. It added a strip of land to the United States that included parts of present-day Arizona and New Mexico. This new boundary was intended to resolve lingering border disputes and facilitate the construction of a southern transcontinental railroad.
- Facilitating Railroad Construction: As previously mentioned, the main motivation for the Gadsden Purchase was to acquire land that would provide the most favorable route for a southern transcontinental railroad. The purchase made it possible to construct a railroad that avoided the mountainous terrain further north, facilitating trade and transportation between the eastern and western United States.
- Opening Up New Areas for Settlement: The Gadsden Purchase opened up new areas for settlement and development in the southwestern United States. The acquisition of this land attracted settlers, miners, and entrepreneurs who sought to take advantage of the region’s resources and economic opportunities.
- Impact on Native American Tribes: The Gadsden Purchase had a negative impact on Native American tribes in the region, as it led to further encroachment on their lands and the disruption of their traditional way of life. The purchase also increased tensions between Native Americans and the U.S. government.
- Demographic Changes: The Gadsden Purchase contributed to demographic changes in the southwestern United States. The influx of American settlers led to a shift in the region’s population, with Anglo-Americans becoming the dominant group. This demographic shift had a significant impact on the region’s culture, politics, and society.
The Gadsden Purchase played a significant role in shaping the geography and demographics of the southwestern United States. It finalized the border between the United States and Mexico, facilitated the construction of a transcontinental railroad, and opened up new areas for settlement and development. However, it also had a negative impact on Native American tribes and contributed to demographic changes in the region.
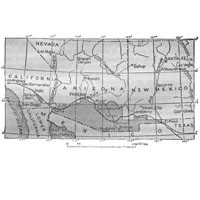 Map Depicting the Gadsden Purchase
Map Depicting the Gadsden Purchase
9. What Were The Long-Term Consequences Of The Mexican Cession And The Gadsden Purchase For U.S.-Mexico Relations?
The Mexican Cession and the Gadsden Purchase had long-term consequences for U.S.-Mexico relations, contributing to a complex and often strained relationship between the two countries. These events left a legacy of resentment, mistrust, and unresolved issues that continue to shape the dynamics between the United States and Mexico today.
Here are some of the key long-term consequences:
- Resentment and Mistrust: The loss of territory to the United States created lasting resentment and mistrust in Mexico. Many Mexicans viewed the Mexican-American War and the subsequent cessions of land as acts of aggression and exploitation by the United States. This historical resentment continues to influence Mexican attitudes toward the United States.
- Border Issues: The Mexican Cession and the Gadsden Purchase established the border between the United States and Mexico. However, border issues have remained a source of tension between the two countries. Disputes over immigration, drug trafficking, and environmental concerns continue to challenge the relationship between the United States and Mexico.
- Economic Disparities: The economic disparities between the United States and Mexico have been exacerbated by the historical context of the Mexican Cession and the Gadsden Purchase. The United States has benefited from the acquisition of valuable resources and strategic locations, while Mexico has struggled to overcome the loss of territory and the legacy of economic exploitation.
- Cultural Impact: The Mexican Cession and the Gadsden Purchase had a profound cultural impact on both the United States and Mexico. Mexican culture has blended with that of the United States in the southwestern region, creating a unique cultural landscape. However, the legacy of cultural suppression and discrimination against Mexicans in the United States continues to be a source of tension.
- Immigration: The Mexican Cession and the Gadsden Purchase have contributed to the ongoing debate over immigration between the United States and Mexico. The historical context of these events shapes the way immigration is viewed and debated in both countries.
The Mexican Cession and the Gadsden Purchase had far-reaching and long-lasting consequences for U.S.-Mexico relations. These events created a legacy of resentment, mistrust, and unresolved issues that continue to shape the dynamics between the two countries today. Understanding this historical context is essential for navigating the complex relationship between the United States and Mexico.
10. How Can I Learn More About LGBTQ+ Travel and Culture in Mexico?
To discover more about LGBTQ+ travel, culture, events, and inclusive locations in Mexico, visit gaymexico.net for a comprehensive guide.
Gaymexico.net provides resources to help you explore Mexico safely and authentically:
- Destination Guides: Detailed information on LGBTQ+-friendly cities and regions in Mexico, including Puerto Vallarta, Mexico City, and Cancun.
- Events Calendar: Listings of LGBTQ+ events, festivals, and celebrations throughout the year.
- Accommodation Directory: Recommendations for LGBTQ+-welcoming hotels, guesthouses, and resorts.
- Bar and Club Guide: Reviews of popular LGBTQ+ bars, clubs, and nightlife venues.
- Community Forums: Opportunities to connect with other LGBTQ+ travelers and locals, share experiences, and ask questions.
- Safety Tips: Advice on how to stay safe and navigate local customs as an LGBTQ+ traveler in Mexico.
Gaymexico.net is committed to providing up-to-date, accurate, and reliable information to help LGBTQ+ travelers plan their trips to Mexico. It also has the information needed to learn about the social and cultural aspects of LGBTQ+ life in Mexico.
Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States.
Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177.
Website: gaymexico.net.
FAQ About the US Acquisition of Mexican Territory
-
What territories did the US acquire from Mexico?
The US acquired California, Nevada, Utah, most of Arizona, and parts of New Mexico, Colorado, and Wyoming. -
How much did the US pay for the Mexican Cession?
The US paid Mexico $15 million for the Mexican Cession. -
What was the main reason for the Gadsden Purchase?
The main reason was to acquire land for a southern transcontinental railroad. -
How much did the US pay for the Gadsden Purchase?
The US paid Mexico $10 million for the Gadsden Purchase. -
What treaty ended the Mexican-American War?
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ended the Mexican-American War. -
What is Manifest Destiny?
It was the 19th-century belief that the US was destined to expand across North America. -
How did the Mexican Cession affect Mexicans living in the acquired territories?
Many faced discrimination, loss of land, and cultural suppression. -
How did the acquisition of Mexican territory affect the slavery debate?
It intensified the debate over whether slavery should be allowed in the new territories. -
What was the impact of the Mexican Cession on Native American tribes?
They experienced loss of land, erosion of sovereignty, and increased conflict. -
Where can I find more information about LGBTQ+ travel in Mexico?
Visit gaymexico.net for LGBTQ+ travel guides, events, and resources.