Did NAFTA have a positive or negative impact on Mexico, especially for the LGBTQ+ community? NAFTA’s effects on Mexico are complex and debated, with some sectors benefiting while others faced challenges, impacting various communities including LGBTQ+ individuals. Gaymexico.net offers insights into Mexico’s economy, culture, and LGBTQ+ life. Discover economic shifts, cultural changes, and community impacts.
1. What Was NAFTA and Its Goals for Mexico?
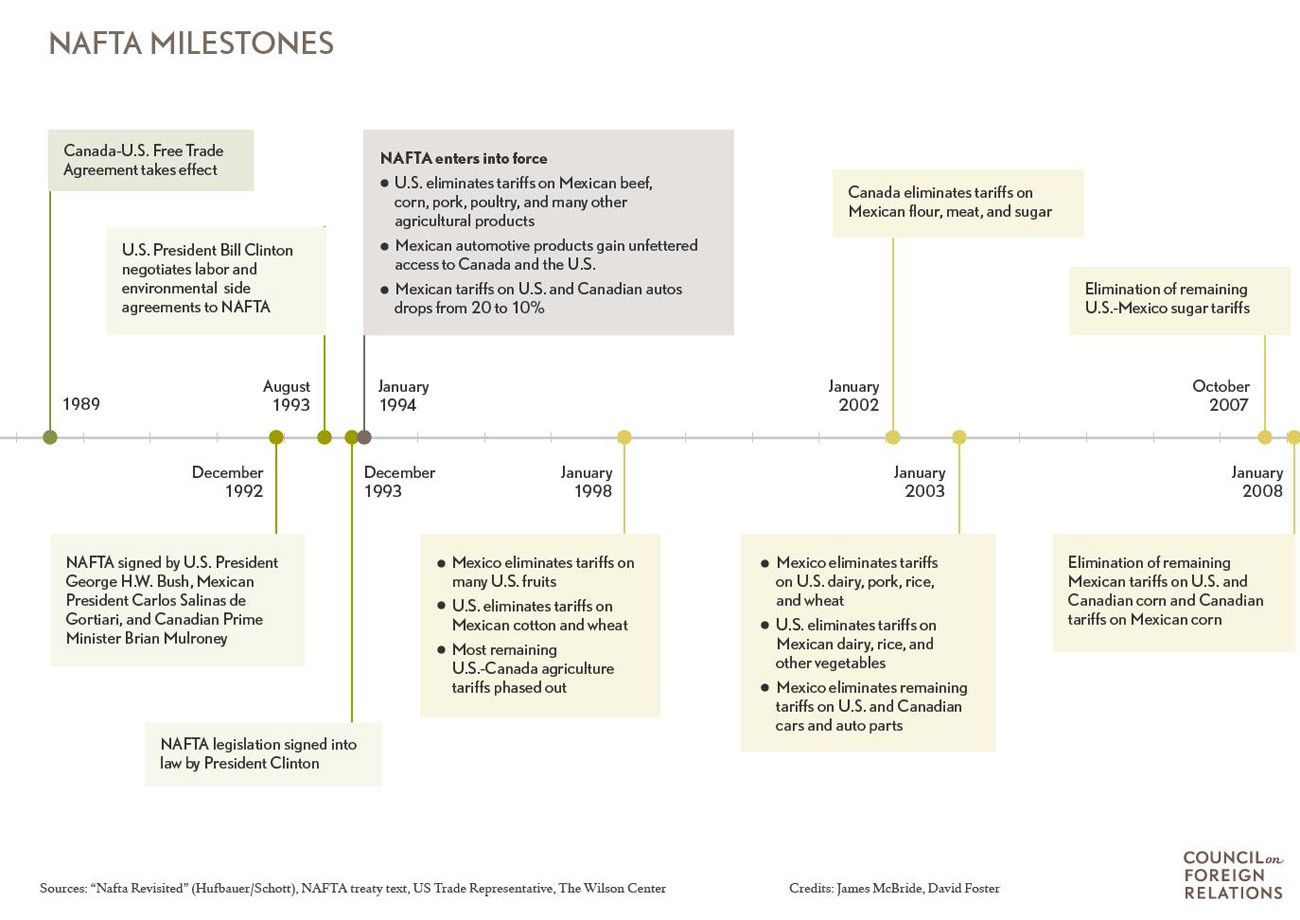
NAFTA, the North American Free Trade Agreement, was an accord between Canada, Mexico, and the United States that started in January 1994. Its main goal was integrating Mexico with the economies of the U.S. and Canada. NAFTA aimed to boost Mexico’s economic growth by creating jobs, opening opportunities, and decreasing illegal migration. For the U.S. and Canada, Mexico offered both an export market and a lower-cost investment area.
NAFTA sought to eliminate most tariffs on products traded among the three countries. The agreement had a major focus on liberalizing trade in agriculture, textiles, and automobile manufacturing. It also aimed to protect intellectual property, establish dispute resolution mechanisms, and implement labor and environmental safeguards through side agreements.
 Mexican Flag in a Field
Mexican Flag in a Field
NAFTA also started a new era of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs). It was a pioneer in incorporating labor and environmental provisions, which became more comprehensive in later FTAs. The USMCA has stronger enforcement mechanisms for labor provisions than the original deal.
2. How Did NAFTA Impact the U.S. Economy?
Since NAFTA, trade between the United States, Canada, and Mexico has more than tripled. It has grown faster than U.S. trade with the rest of the world. Canada and Mexico are the two largest destinations for U.S. exports, accounting for more than one-third of the total. Most estimates show that the deal increased U.S. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) by less than 0.5 percent. This added up to $80 billion to the U.S. economy upon full implementation, or several billion dollars of added growth per year.
Supporters of NAFTA estimate that some fourteen million U.S. jobs rely on trade with Canada or Mexico. It’s believed that the nearly two hundred thousand export-related jobs created yearly by the pact pay 15 to 20 percent more on average than the jobs that were lost.
2.1. Arguments Against NAFTA
Critics of the deal argue that it caused job losses and wage stagnation in the United States, driven by low-wage competition. They also say that companies moved production to Mexico to lower costs, and there was a widening trade deficit. Research from CEPR’s Dean Baker and the Economic Policy Institute’s Robert Scott suggests that the increase of imports after NAFTA caused a loss of up to six hundred thousand U.S. jobs over two decades. However, they admit that some of this import growth likely would have happened even without NAFTA.
2.2. The Auto Sector
Many workers and labor leaders blame trade agreements such as NAFTA for the decline in U.S. manufacturing jobs. The U.S. auto sector lost some 350,000 jobs since 1994, while Mexican auto sector employment spiked from 120,000 to 550,000 workers.
2.3. Positive Impacts of NAFTA
Other economists, including Gary Clyde Hufbauer and Cathleen Cimino-Isaacs of the Peterson Institute for International Economics (PIIE), say that increased trade produces overall gains for the U.S. economy. Some jobs are lost due to imports, but others are created. Consumers benefit significantly from falling prices and often improved quality of goods. Their 2014 PIIE study of NAFTA’s effects found a net loss of about fifteen thousand jobs per year due to the pact but gains of roughly $450,000 for each job lost in the form of higher productivity and lower consumer prices.
2.4. Competition with China
Many economists assert that the troubles of U.S. manufacturing have little to do with NAFTA. They believe that domestic manufacturing was under stress decades before the treaty. Research by David Autor, David Dorn, and Gordon Hanson found that competition with China has had a much bigger negative impact on U.S. jobs since 2001, when China joined the WTO.
2.5. NAFTA’s Role in Helping the U.S. Auto Sector Compete with China
NAFTA helped the U.S. auto sector compete with China by contributing to the development of cross-border supply chains. This lowered costs, increased productivity, and improved U.S. competitiveness. This meant shedding some jobs in the United States as positions moved to Mexico. However, without the pact, even more could have been lost.
3. What Were The Effects of NAFTA on the Mexican Economy?
NAFTA boosted Mexican farm exports to the United States, which have tripled since the pact’s implementation. Hundreds of thousands of auto manufacturing jobs have also been created in the country. Most studies have found that the agreement increased productivity and lowered consumer prices in Mexico.
NAFTA catalyzed Mexico’s transition from one of the world’s most protectionist economies to one of the most open to trade. Mexico had reduced many of its trade barriers upon joining the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) in 1986. However, it still had a pre-NAFTA average tariff level of 10 percent.
Mexican policymakers saw NAFTA as an opportunity to accelerate and lock in these hard-won reforms of the Mexican economy. In addition to liberalizing trade, Mexico’s leaders reduced public debt, introduced a balanced-budget rule, stabilized inflation, and built up the country’s foreign reserves. So although Mexico was hard hit by the 2008 financial crisis due to its dependence on exports to the U.S. market, its economy bounced back relatively quickly, returning to growth in 2010.
3.1. Disparities and Unmet Promises
Mexico’s NAFTA experience suffered from disparities between the promises of some of its supporters and the deal’s outcomes. Between 1993 and 2013, Mexico’s economy grew at an average rate of just 1.3 percent yearly. Poverty remains at the same levels as in 1994. And the expected convergence of U.S. and Mexican wages didn’t happen.
Unemployment also rose, which some economists have blamed on NAFTA for exposing Mexican farmers, especially corn producers, to competition from heavily subsidized U.S. agriculture. A study estimated that NAFTA put almost two million small-scale Mexican farmers out of work, in turn driving illegal migration to the United States.
3.2. The “Two-Speed” Economy
Many analysts explain these divergent outcomes by pointing to the “two-speed” nature of Mexico’s economy. In this scenario, NAFTA drove the growth of foreign investment, high-tech manufacturing, and rising wages in the industrial north, while the largely agrarian south remained detached from this new economy.
3.3. Other Factors Affecting Mexico’s Economy
Many experts say that Mexico’s recent economic performance has been affected by non-NAFTA factors. The 1994 devaluation of the peso drove Mexican exports, while competition with China’s low-cost manufacturing sector likely depressed growth. Unrelated public policies, such as land reform, made it easier for farmers to sell their land and emigrate.
4. What Happened with Canada?
Canada saw strong gains in cross-border investment in the NAFTA era. Since 1993, U.S. and Mexican investments in Canada have tripled. U.S. investment, which accounts for more than half of Canada’s FDI stock, grew from $70 billion in 1993 to more than $368 billion in 2013.
However, the most consequential aspect for Canada—opening its economy to the United States, by far Canada’s largest trading partner—predated NAFTA, with 1989 entry into force of the Canada-U.S. Free Trade Agreement (CUSFTA). Overall Canada-U.S. trade increased rapidly in the wake of Canada’s trade liberalization. Post-NAFTA, Canadian exports to the United States grew from $110 billion to $346 billion; imports from the United States grew by almost the same amount.
Neither the worst fears of Canada’s trade opponents—that opening to trade would gut the country’s manufacturing sector—nor the highest hopes of NAFTA’s advocates—that it would spark a rapid increase in productivity—came to pass. Canadian manufacturing employment held steady, but the productivity gap between the Canadian and U.S. economies wasn’t closed.
Overall, Canada became more dependent on trade with the United States, relying on its southern neighbor for 75 percent of its exports.
5. What’s Next for North American Trade?
NAFTA was long a political target. In 2008, then presidential candidate Barack Obama promised to renegotiate NAFTA to include tougher labor and environmental standards. The Obama administration sought to address the issues with NAFTA in negotiations for the Trans-Pacific Partnership.
During the 2016 presidential campaign, both Trump and Senator Bernie Sanders criticized NAFTA for bringing U.S. job losses. After entering office, Trump opened renegotiations to get a “better deal” for the United States.
Much of the debate among policy experts has centered on how to mitigate the negative effects of deals such as NAFTA, including whether to compensate workers who lose their jobs or provide retraining programs to help them transition to new industries. Experts say programs such as the U.S. Trade Adjustment Assistance (TAA) could help quell anger directed at trade liberalization.
Eschewing these policy proposals, Trump instead made good on his campaign promise to renegotiate NAFTA. He used tariffs as bargaining leverage throughout the process, applying import tariffs on steel and aluminum in early 2018 and threatening to do the same with automobiles.
In late 2019, the Trump administration won support from congressional Democrats for the USMCA after agreeing to incorporate stronger labor enforcement. As part of the deal, Canada agreed to allow more access to its dairy market and won several concessions in return.
In early 2020, the U.S. Congress approved the USMCA with large bipartisan majorities in both chambers, and the deal entered into force on July 1.
6. How Did NAFTA Affect Different Sectors in Mexico?
NAFTA had varied effects on different sectors of the Mexican economy:
| Sector | Impact |
|---|---|
| Agriculture | Boosted exports, but small farmers faced competition. |
| Manufacturing | Increased jobs, especially in the auto industry. |
| Technology | Drove growth in the industrial north. |
| Consumer Prices | Lowered consumer prices. |
| Wage Disparities | Increased wage disparities between the north and south. |
7. How Did NAFTA Impact the LGBTQ+ Community in Mexico?
While NAFTA primarily focused on economic matters, it indirectly influenced the LGBTQ+ community in Mexico. The agreement led to broader societal and cultural shifts that impacted various aspects of life, including LGBTQ+ rights and visibility.
Increased Economic Activity: NAFTA contributed to economic growth in certain regions of Mexico, particularly in urban areas and industrial centers. This growth led to increased job opportunities and migration to these areas, resulting in more diverse and cosmopolitan communities. As a result, LGBTQ+ individuals found more spaces to express themselves and connect with others.
7.1. Cultural Exchanges
NAFTA facilitated greater cultural exchange between Mexico, the United States, and Canada. This exchange exposed more Mexicans to diverse perspectives on sexuality and gender identity, promoting greater tolerance and acceptance. Increased tourism and media exposure also played a role in shifting societal attitudes.
7.2. Advocacy and Activism
The economic and social changes brought about by NAFTA provided a platform for LGBTQ+ advocacy and activism in Mexico. As the middle class expanded and access to information increased, LGBTQ+ organizations gained more resources and visibility. They were able to push for legal reforms, such as marriage equality and anti-discrimination laws, more effectively.
7.3. Challenges and Disparities
Despite these positive developments, NAFTA also exacerbated existing disparities within Mexico. While some regions experienced economic growth and increased LGBTQ+ visibility, others, particularly rural and marginalized areas, lagged behind. LGBTQ+ individuals in these areas continued to face discrimination, violence, and limited access to resources.
7.4. Economic Shifts
NAFTA contributed to economic shifts in Mexico, leading to changes in employment patterns. While some industries experienced growth, others faced challenges, resulting in job displacement and economic insecurity for some workers. These economic challenges could disproportionately affect marginalized communities, including LGBTQ+ individuals, who often face additional barriers to employment and economic stability.
7.5. Migration
The economic impacts of NAFTA also influenced migration patterns within Mexico and to the United States. Some individuals and families migrated in search of economic opportunities, while others were displaced by economic changes. LGBTQ+ individuals may have been among those who migrated, seeking more accepting and inclusive environments or better economic prospects.
7.6. Cultural Exchanges
NAFTA facilitated cultural exchanges between Mexico, the United States, and Canada, leading to increased exposure to different ideas and perspectives. These cultural exchanges may have influenced societal attitudes toward LGBTQ+ issues in Mexico, potentially contributing to greater awareness and acceptance.
7.7. Advocacy and Activism
The economic and social changes associated with NAFTA may have created new opportunities for LGBTQ+ advocacy and activism in Mexico. Increased access to information and resources, as well as greater awareness of LGBTQ+ issues, could have empowered LGBTQ+ organizations and activists to push for policy changes and social reforms.
8. What Are Some LGBTQ+ Friendly Destinations in Mexico?
Mexico has become increasingly welcoming and inclusive of LGBTQ+ travelers, offering a variety of destinations that cater to the community. Here are some of the most popular LGBTQ+ friendly places in Mexico:
8.1. Puerto Vallarta
Often hailed as the “San Francisco of Mexico,” Puerto Vallarta is a top choice for LGBTQ+ travelers. Its Zona Romantica (Romantic Zone) is the epicenter of gay life, boasting numerous gay bars, clubs, and hotels. The city hosts the annual Vallarta Pride celebration, drawing thousands of visitors.
8.2. Mexico City
The capital city is a vibrant hub of LGBTQ+ culture, with a thriving scene in the Zona Rosa neighborhood. Mexico City offers a range of gay-friendly accommodations, restaurants, and cultural attractions. The city’s Pride march is one of the largest in Latin America.
8.3. Cancun
While known for its beaches and resorts, Cancun also offers a welcoming environment for LGBTQ+ travelers. Several hotels and resorts cater specifically to the gay and lesbian community, and the city hosts LGBTQ+ events throughout the year.
8.4. Guadalajara
As Mexico’s second-largest city, Guadalajara has a growing LGBTQ+ scene, particularly in the Chapultepec neighborhood. The city is known for its cultural heritage and offers a mix of traditional and modern experiences for LGBTQ+ visitors.
8.5. Tulum
This coastal town on the Yucatán Peninsula is gaining popularity as a destination for LGBTQ+ travelers seeking a more laid-back and bohemian atmosphere. Tulum offers eco-friendly resorts, yoga retreats, and a growing number of gay-friendly establishments.
9. What are Some Resources for LGBTQ+ Travelers in Mexico?
For LGBTQ+ travelers planning a trip to Mexico, several resources can provide valuable information and support:
9.1. GayMexico.Net
Gaymexico.net is a comprehensive online platform offering guides, news, and community forums for LGBTQ+ individuals interested in Mexico. Here, you can find the most recent details regarding LGBTQ+-friendly hotels, bars, events, and safety advice, all of which will enhance your travel experience.
Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States
Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177
Website: gaymexico.net
9.2. LGBTQ+ Travel Guides
Numerous travel guides cater specifically to LGBTQ+ travelers, offering recommendations for gay-friendly accommodations, nightlife, and attractions in Mexico.
9.3. Online Forums and Communities
Online forums and social media groups provide platforms for LGBTQ+ travelers to connect with locals, ask questions, and share experiences about traveling in Mexico.
9.4. LGBTQ+ Organizations
Several organizations in Mexico advocate for LGBTQ+ rights and offer resources and support to the community. These organizations can provide valuable information and assistance to LGBTQ+ travelers.
9.5. U.S. Embassy and Consulates in Mexico
The U.S. Embassy and Consulates in Mexico can provide assistance to U.S. citizens, including LGBTQ+ travelers, in case of emergencies or legal issues.
10. FAQ: Understanding NAFTA’s Impact on Mexico
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| How did NAFTA affect employment in Mexico? | NAFTA increased employment in manufacturing but displaced many small farmers, leading to migration. |
| Did NAFTA reduce poverty in Mexico? | No, poverty levels remained largely unchanged despite NAFTA. |
| How did NAFTA impact trade between Mexico and the U.S.? | Trade significantly increased, boosting Mexican farm exports and creating manufacturing jobs. |
| What were the main benefits of NAFTA for Mexico? | Increased foreign investment, growth in high-tech manufacturing, and lower consumer prices. |
| What were the main drawbacks of NAFTA for Mexico? | Increased competition for small farmers, wage disparities, and slower economic growth than expected. |
| How did NAFTA affect the U.S. economy? | NAFTA led to increased trade and some job creation but also job losses in certain sectors due to competition. |
| What role did NAFTA play in Mexico’s economic reforms? | NAFTA helped accelerate and lock in reforms, leading to reduced public debt and stable inflation. |
| Did NAFTA affect wages in Mexico? | The expected convergence of U.S. and Mexican wages did not happen, with slow wage growth in Mexico. |
| How did NAFTA impact Mexico’s agricultural sector? | Mexican farm exports increased, but small-scale farmers faced competition from subsidized U.S. agriculture. |
| What is the USMCA, and how does it differ from NAFTA? | The USMCA is an updated version of NAFTA with stricter rules of origin, labor enforcement, and dispute resolution mechanisms. |
NAFTA had a complex and multifaceted impact on Mexico, influencing its economy, society, and culture. While the agreement brought certain benefits, it also created challenges and disparities. Understanding these effects is crucial for assessing the broader implications of trade liberalization and regional integration in Mexico. Are you ready to explore Mexico’s LGBTQ+ scene? Visit gaymexico.net to discover LGBTQ+-friendly destinations, events, and resources. Plan your trip with confidence and connect with the community!