Are you curious about which nations Mexico supplies with petroleum? This comprehensive guide, brought to you by gaymexico.net, delves into Mexico’s petroleum export destinations, exploring the evolving landscape of its trade relationships. We’ll uncover key partners, analyze market trends, and provide insights relevant to the LGBTQ+ community interested in Mexico’s economic and political spheres, with a friendly and informative tone. Keep reading to learn about Mexico’s energy exports, international trade, and global partners.
1. Which Countries Are the Primary Importers of Mexican Oil?
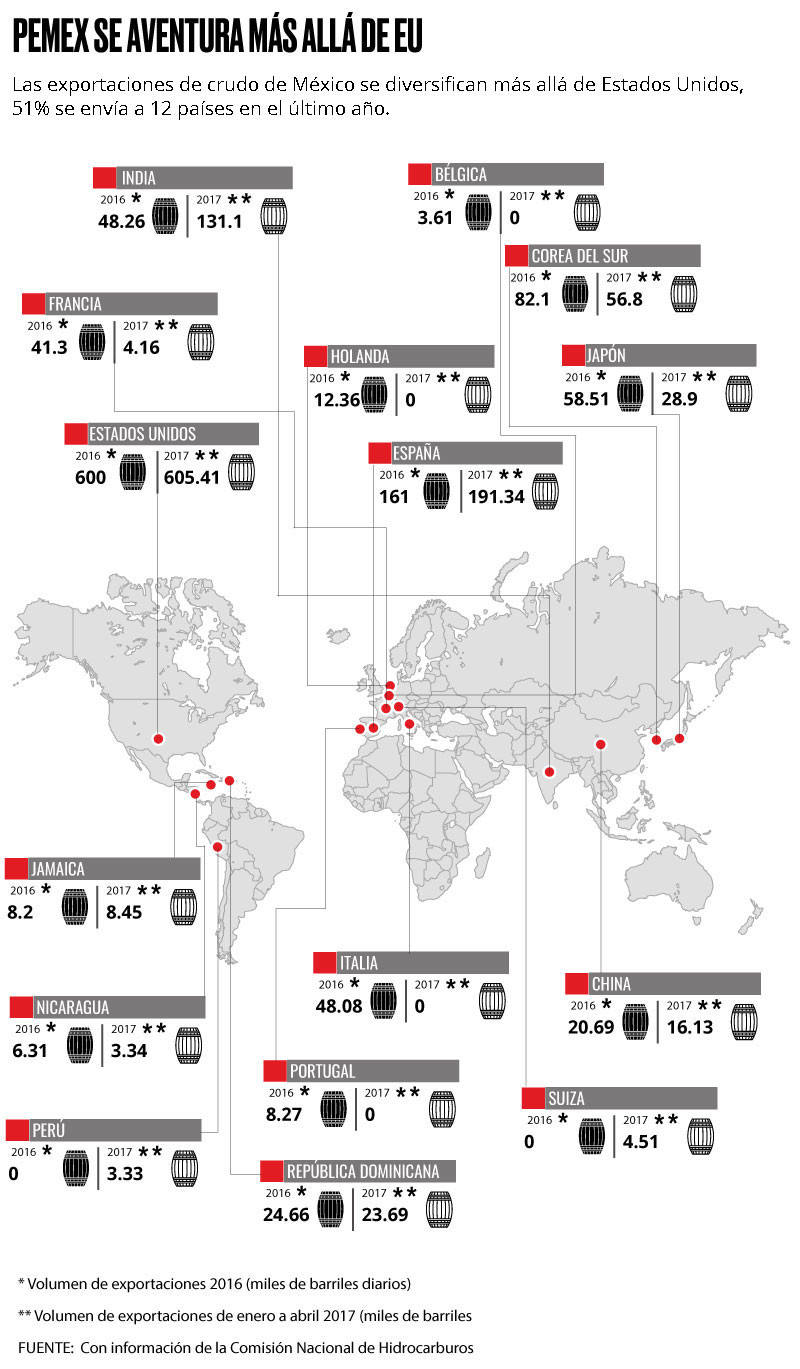
The primary importers of Mexican oil are diverse, spanning across continents. While the United States has historically been a major consumer, Mexico has strategically diversified its export destinations to include countries in Europe, Asia, and other parts of the Americas. According to data from the Secretaría de Energía (Sener) and the Comisión Nacional de Hidrocarburos (CNH), significant importers include the United States, Spain, India, and South Korea.
1.1 The United States
Historically, the United States has been the dominant importer of Mexican crude oil. However, due to the rise in domestic shale oil production, the demand from the U.S. has decreased over the years. Nonetheless, the Gulf Coast region in the U.S. still requires heavy crude oil, which Mexico is well-positioned to supply.
1.2 Spain
Spain has emerged as a crucial market for Mexican oil exports, particularly as Mexico seeks to diversify beyond North America. The European market presents a stable demand and favorable trade conditions.
1.3 India
India’s rapidly growing economy and increasing energy needs make it a significant importer of Mexican crude oil. The Far East region, including India, has shown considerable growth in its intake of Mexican exports.
1.4 South Korea
South Korea, with its advanced refining capabilities, also stands as an important destination for Mexico’s oil exports. The country’s strategic location and economic strength make it a valuable partner.
2. How Has the Landscape of Mexican Oil Exports Changed Over the Years?
The landscape of Mexican oil exports has undergone significant transformation over the past two decades. Initially, the United States was the predominant recipient, but shifts in global energy markets and U.S. domestic production have prompted Mexico to diversify its export destinations. This evolution reflects a strategic response to changing demand and market dynamics.
2.1 Peak and Decline in American Demand
In 2004, Mexico exported 1.65 million barrels per day to countries in the Americas, according to Sener data. By 2016, this figure had decreased to approximately 603,929 barrels per day. The rise of shale oil production in the U.S. is a primary reason for this decline.
2.2 Diversification to New Markets
To offset reduced demand from the U.S., Mexico has expanded its exports to countries such as Spain, India, Italy, and others. These nations collectively accounted for a small percentage of Mexico’s oil exports in the past but now represent a substantial portion.
2.3 Data Corroboration
Data from CNH, Sener, and the Secretaría de Economía (Economy Secretariat) confirm the decreasing reliance on the U.S. as the primary importer of Mexican oil. This shift highlights Mexico’s adaptive strategies in the global energy market.
3. What Factors Have Influenced Mexico’s Oil Export Strategy?
Several factors have significantly influenced Mexico’s oil export strategy, including changes in U.S. energy policy, fluctuations in global oil prices, and the strategic decisions of Pemex, Mexico’s state-owned petroleum company. These elements have collectively shaped Mexico’s approach to international oil trade.
3.1 The Rise of Shale Oil in the U.S.
The shale oil revolution in the United States has dramatically reduced its dependency on foreign oil imports, impacting Mexico’s export volumes. The increased domestic production has forced Mexico to seek alternative markets.
3.2 Global Oil Price Fluctuations
Volatility in global oil prices affects Mexico’s export revenues and influences its decisions on where to sell its crude oil. High prices can incentivize exports to distant markets, while low prices may favor closer destinations to reduce transportation costs.
3.3 Pemex’s Strategic Decisions
Pemex’s decisions on production levels, pricing strategies, and market diversification play a crucial role in shaping Mexico’s export strategy. The company’s efforts to adapt to changing market conditions are essential for maintaining its position in the global oil market.
4. How Has the Value of Mexican Oil Exports to the U.S. Changed Over Time?
The value of Mexican oil exports to the U.S. has seen notable changes over time, reflecting shifts in both volume and price. The percentage of total crude oil sales to the U.S. has decreased significantly, indicating a move toward diversification.
4.1 Declining Percentage
In 2008, exports to the U.S. accounted for 81.6% of Mexico’s total crude oil sales, according to data from the Secretaría de Economía. By 2016, this percentage had fallen to 48.5%.
4.2 Impact of Global Prices
The monetary value of exports is also affected by the international price of oil. Between 2008 and 2013, the price of crude oil ranged from $90 to $120 per barrel. Subsequently, prices fell, sometimes reaching as low as $20 per barrel before stabilizing between $40 and $50.
4.3 Reduction in Extraction
Pemex’s crude oil extraction has also declined, dropping by nearly 800,000 barrels from 2008 to recent years, influencing the overall export value.
5. Which Regions Are Gaining Importance as Destinations for Mexican Crude Oil?
Certain regions are becoming increasingly important as destinations for Mexican crude oil, particularly the Far East, which includes countries like India, Japan, and South Korea. These markets offer growth opportunities and diversification away from traditional North American dependence.
5.1 Growth in the Far East
Exports to the Far East region increased by 45.2% between 2015 and 2016, rising from 219,200 to 318,300 barrels per day, according to Sener data.
5.2 Key Countries in the Far East
India, Japan, and South Korea are the primary drivers of this growth. In the past year, these countries imported an average of 188,870 barrels per day, and this figure rose to 216,800 barrels between January and April, as reported by CNH.
5.3 European Expansion
Spain, Italy, and France also represent important European markets that are contributing to Mexico’s diversification efforts.
6. What Types of Crude Oil Does Mexico Export?
Mexico primarily exports heavy crude oil, which is particularly sought after by refineries along the U.S. Gulf Coast. This type of crude oil requires specialized refining processes, providing Mexico with a niche market despite the overall decrease in U.S. oil imports.
6.1 Heavy Crude Demand
The refining infrastructure in the Gulf Coast is specifically designed to process heavy crude oil, making it a valuable commodity for Mexican exports.
6.2 Limited Shale Oil Processing
Unlike the light crude oil produced from shale formations in the U.S., Mexican heavy crude requires different refining techniques, ensuring continued demand in specific sectors.
6.3 Pemex’s Production Focus
Pemex focuses on extracting and exporting heavy crude oil, capitalizing on its unique properties and the specialized needs of certain refineries.
7. How Do International Trade Agreements Affect Mexican Oil Exports?
International trade agreements play a crucial role in shaping the terms and conditions of Mexican oil exports. These agreements can influence tariffs, quotas, and other trade barriers, impacting Mexico’s competitiveness in the global market.
7.1 Trade Agreements with the U.S.
Agreements such as the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) affect the trade relationship between Mexico and the U.S., influencing energy exports.
7.2 Agreements with Europe and Asia
Trade agreements with countries in Europe and Asia can facilitate increased oil exports by reducing trade barriers and promoting favorable conditions for Mexican oil.
7.3 Impact on Export Volumes
These agreements can lead to higher export volumes and increased revenue for Mexico, depending on the specific terms and conditions.
8. What Role Does Pemex Play in Mexico’s Oil Export Strategy?
Pemex, as the state-owned petroleum company, plays a central role in Mexico’s oil export strategy. It is responsible for exploration, production, and export of crude oil, and its decisions significantly impact the country’s energy sector and economy.
8.1 Exploration and Production
Pemex oversees the exploration and extraction of crude oil from Mexico’s oil fields, determining the volume and type of oil available for export.
8.2 Export Management
The company manages the export process, negotiating contracts with international buyers and overseeing the transportation of oil to various destinations.
8.3 Strategic Planning
Pemex’s strategic decisions on pricing, market diversification, and investment in infrastructure are critical for shaping Mexico’s long-term oil export strategy.
9. What Are the Economic Implications of Mexico’s Oil Exports?
Mexico’s oil exports have significant economic implications, contributing substantially to the country’s revenue, employment, and overall economic stability. Changes in export volumes and prices can have ripple effects throughout the economy.
9.1 Revenue Generation
Oil exports are a major source of revenue for the Mexican government, funding public services, infrastructure projects, and social programs.
9.2 Employment Opportunities
The oil industry supports numerous jobs in exploration, extraction, refining, and transportation, contributing to employment levels and economic growth.
9.3 Impact on GDP
Fluctuations in oil prices and export volumes can significantly impact Mexico’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP), highlighting the importance of a stable and diversified export strategy.
10. How Can the LGBTQ+ Community Benefit from Understanding Mexico’s Oil Export Dynamics?
Understanding Mexico’s oil export dynamics can benefit the LGBTQ+ community by providing insights into the country’s economic stability, which influences social policies and resources available for community support. Additionally, trade relationships can foster cultural exchange and understanding.
10.1 Economic Stability and Social Policies
A strong economy, supported by oil exports, can lead to better funding for social programs, including those that support the LGBTQ+ community.
10.2 Cultural Exchange
Trade relationships often foster cultural exchange, promoting understanding and acceptance between different nations and communities.
10.3 Investment Opportunities
Knowledge of Mexico’s economic sectors can open doors to investment opportunities that support inclusive and diverse business practices.
Understanding Mexico’s oil export landscape involves examining a complex web of international relationships, economic factors, and strategic decisions. While the United States remains an important partner, Mexico has successfully diversified its export destinations, strengthening ties with countries in Europe and Asia. For the LGBTQ+ community, understanding these dynamics provides valuable insights into Mexico’s economic stability and potential for social progress.
 Pemex Oil Rig
Pemex Oil Rig
Pemex Oil Rig: This image shows an overview of a Pemex oil rig, illustrating the infrastructure and operations involved in Mexico’s crude oil extraction and export processes.
By staying informed and engaged, the LGBTQ+ community can play a role in shaping a more inclusive and prosperous future for Mexico and its international partners. For more detailed information and ongoing updates, visit gaymexico.net, your trusted source for LGBTQ+ insights into Mexican culture and society.
11. What Are The Key Statistics Related to Mexico’s Oil Exports?
Understanding the numerical data surrounding Mexico’s oil exports provides a clearer picture of its economic impact and international trade relationships. Here are some key statistics to consider:
11.1 Daily Export Volumes
Mexico’s daily export volumes have varied significantly over the years. In 2004, exports to the Americas peaked at 1.65 million barrels per day (bpd). By 2016, this had declined to approximately 603,929 bpd.
11.2 U.S. Market Share
The United States’ share of Mexico’s oil exports has decreased from 81.6% in 2008 to 48.5% in 2016. This shift indicates a significant diversification in export destinations.
11.3 Far East Growth
Exports to the Far East region increased by 45.2% between 2015 and 2016, reaching 318,300 bpd. This growth highlights the increasing importance of Asian markets.
11.4 Production Decline
Pemex’s crude oil production has decreased by nearly 800,000 barrels from 2008 to the present day. This decline affects overall export capacity and revenue.
11.5 Global Price Impact
Global oil prices have fluctuated between $20 and $120 per barrel over the past decade, significantly impacting the value of Mexico’s oil exports.
12. How Has Mexico Adapted to Declining Oil Production and Exports?
Faced with declining oil production and exports, Mexico has implemented several strategies to adapt and diversify its economy. These strategies aim to reduce reliance on oil revenue and promote sustainable economic growth.
12.1 Diversification of Export Destinations
Mexico has actively sought new markets for its oil exports, reducing dependence on the United States and expanding trade relationships with countries in Europe and Asia.
12.2 Investment in Renewable Energy
The country is investing in renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and promote a more sustainable energy sector.
12.3 Economic Diversification
Mexico is also diversifying its economy by promoting other industries, such as manufacturing, technology, and tourism, to create new sources of revenue and employment.
12.4 Regulatory Reforms
Reforms in the energy sector aim to attract foreign investment and improve the efficiency of oil production and exports.
13. What Opportunities Exist for Foreign Investors in Mexico’s Energy Sector?
Mexico’s energy sector offers various opportunities for foreign investors, particularly in areas such as renewable energy, infrastructure development, and technology innovation. These opportunities can contribute to the modernization and diversification of the sector.
13.1 Renewable Energy Projects
Investment in solar, wind, and other renewable energy projects is encouraged through government incentives and regulatory frameworks.
13.2 Infrastructure Development
Opportunities exist for investing in pipelines, storage facilities, and other infrastructure necessary to support the production and export of oil and gas.
13.3 Technology Innovation
Investment in technology innovation can improve the efficiency and sustainability of Mexico’s energy sector, creating new business opportunities.
13.4 Joint Ventures
Foreign companies can partner with Pemex and other Mexican firms to develop energy projects and share expertise and resources.
14. What are the Environmental Considerations Related to Mexico’s Oil Exports?
Environmental considerations are increasingly important in the context of Mexico’s oil exports. Sustainable practices and responsible environmental management are essential for mitigating the negative impacts of oil production and transportation.
14.1 Emissions Reduction
Efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from oil production and transportation are crucial for addressing climate change.
14.2 Protection of Natural Resources
Protecting natural resources, such as water and biodiversity, is essential for ensuring the long-term sustainability of Mexico’s energy sector.
14.3 Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with environmental regulations and standards is necessary for minimizing the environmental impact of oil exports.
14.4 Investment in Green Technologies
Investing in green technologies and sustainable practices can help reduce the environmental footprint of Mexico’s oil industry.
15. How Does Mexico’s Oil Export Strategy Align with Global Energy Trends?
Mexico’s oil export strategy must align with global energy trends, including the shift towards renewable energy, the increasing demand for energy efficiency, and the growing importance of sustainability. Adapting to these trends is essential for maintaining Mexico’s competitiveness in the global energy market.
15.1 Transition to Renewable Energy
The global transition to renewable energy is influencing Mexico’s energy policies and investment decisions.
15.2 Energy Efficiency
Increasing energy efficiency is a key trend that affects the demand for oil and other fossil fuels.
15.3 Sustainability
Sustainability is becoming a central consideration for energy producers and consumers worldwide.
15.4 Diversification of Energy Sources
Diversifying energy sources and reducing reliance on oil is a global trend that Mexico must address in its export strategy.
In conclusion, Mexico’s oil export landscape is dynamic and influenced by a variety of factors, including global energy trends, economic considerations, and environmental concerns. By understanding these dynamics, the LGBTQ+ community can gain valuable insights into Mexico’s economic stability and potential for social progress. Visit gaymexico.net for more information and resources.
16. What Geopolitical Factors Influence Mexico’s Oil Export Destinations?
Geopolitical factors significantly shape Mexico’s oil export destinations. International relations, trade agreements, and political stability in importing countries all play a role in determining where Mexico sends its crude oil.
16.1 Trade Agreements
Trade agreements like the USMCA (United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement) and others with Europe and Asia can significantly influence export volumes and destinations.
16.2 Political Stability
Political stability in importing countries is crucial. Mexico prefers to export to nations with stable governments and economies to ensure reliable demand and payment.
16.3 International Relations
Mexico’s relationships with other nations, including diplomatic ties and strategic partnerships, also influence its export decisions. Friendly relations often lead to more favorable trade terms.
16.4 Global Conflicts
Global conflicts and geopolitical tensions can disrupt supply chains and alter demand patterns, leading Mexico to adjust its export strategy accordingly.
17. How Do Different Grades of Mexican Crude Oil Affect Export Markets?
The different grades of Mexican crude oil, primarily heavy and light, influence which markets Mexico can effectively serve. Heavy crude requires specialized refining capabilities, which limits its export destinations to regions with suitable infrastructure.
17.1 Heavy Crude
Mexico primarily exports heavy crude oil, which is ideal for refineries along the U.S. Gulf Coast and in some parts of Asia. These refineries are equipped to process this type of oil efficiently.
17.2 Light Crude
While Mexico also produces some light crude, its export volumes are smaller. Light crude is easier to refine and can be sold to a broader range of markets.
17.3 Refining Capabilities
The availability of refining capabilities in potential export markets is a key factor determining where Mexico can sell its different grades of crude oil.
17.4 Market Demand
Market demand for specific types of crude oil also plays a role. Mexico adjusts its export strategy based on which grades are in higher demand in different regions.
18. What Technological Advancements Are Impacting Mexico’s Oil Exports?
Technological advancements in exploration, extraction, and refining are impacting Mexico’s oil exports. These advancements can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the quality of Mexican crude oil.
18.1 Exploration Technologies
Advanced exploration technologies help Mexico discover new oil reserves and optimize existing production.
18.2 Extraction Techniques
Improved extraction techniques, such as enhanced oil recovery (EOR), can increase the volume of oil that Mexico can produce and export.
18.3 Refining Processes
Modern refining processes allow Mexico to produce higher-quality crude oil products, making its exports more competitive in the global market.
18.4 Digitalization
Digitalization and data analytics are transforming the oil industry, enabling Mexico to optimize its operations and export strategy.
19. How Does Mexico’s Oil Export Revenue Contribute to Social Programs?
Mexico’s oil export revenue plays a crucial role in funding various social programs, including education, healthcare, and infrastructure development. A significant portion of the government’s budget relies on oil revenue.
19.1 Education
Oil revenue supports education initiatives, such as funding schools, scholarships, and teacher training programs.
19.2 Healthcare
A portion of oil revenue is allocated to healthcare, helping to improve access to medical services and modernize healthcare infrastructure.
19.3 Infrastructure
Oil revenue funds infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and public transportation, which are essential for economic development.
19.4 Social Welfare
Social welfare programs, including poverty reduction and unemployment benefits, also receive funding from oil revenue.
20. What is the Future Outlook for Mexico’s Oil Export Strategy?
The future outlook for Mexico’s oil export strategy involves adapting to changing global energy trends, diversifying export destinations, and investing in renewable energy sources. Mexico must also address environmental concerns and promote sustainable practices.
20.1 Diversification
Continued diversification of export destinations is essential for reducing reliance on any single market.
20.2 Renewable Energy
Investing in renewable energy will help Mexico reduce its dependence on oil and promote a more sustainable energy sector.
20.3 Technology Adoption
Adopting new technologies will improve the efficiency and competitiveness of Mexico’s oil industry.
20.4 Sustainability
Prioritizing sustainability and environmental responsibility will be crucial for ensuring the long-term viability of Mexico’s oil export strategy.
Understanding these geopolitical, technological, and economic factors is essential for anyone interested in Mexico’s oil exports. For more insights and detailed information, visit gaymexico.net, your trusted source for LGBTQ+ perspectives on Mexican culture and economy.
Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States.
Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177.
Website: gaymexico.net.
FAQ Section: Mexico’s Oil Exports
Q1: What are Mexico’s primary oil export destinations?
Mexico primarily exports oil to the United States, Spain, India, and South Korea, with a growing focus on diversifying to Asian markets.
Q2: How has the decline in U.S. demand affected Mexico’s oil exports?
The decline in U.S. demand due to increased domestic shale oil production has prompted Mexico to diversify its export destinations.
Q3: What types of crude oil does Mexico export?
Mexico primarily exports heavy crude oil, which is particularly suited for refineries along the U.S. Gulf Coast.
Q4: How do international trade agreements impact Mexico’s oil exports?
International trade agreements influence tariffs, quotas, and trade barriers, affecting Mexico’s competitiveness in the global market.
Q5: What role does Pemex play in Mexico’s oil export strategy?
Pemex, as the state-owned petroleum company, is responsible for exploration, production, and export of crude oil, shaping Mexico’s energy sector.
Q6: How does Mexico’s oil export revenue contribute to social programs?
Oil export revenue funds education, healthcare, infrastructure, and social welfare programs in Mexico.
Q7: What are the environmental considerations related to Mexico’s oil exports?
Environmental considerations include emissions reduction, protection of natural resources, and compliance with environmental regulations.
Q8: How is Mexico adapting to declining oil production and exports?
Mexico is diversifying its economy, investing in renewable energy, and implementing regulatory reforms.
Q9: What opportunities exist for foreign investors in Mexico’s energy sector?
Opportunities exist in renewable energy projects, infrastructure development, and technology innovation.
Q10: How can the LGBTQ+ community benefit from understanding Mexico’s oil export dynamics?
Understanding Mexico’s economic stability, influenced by oil exports, provides insights into social policies and community support, and fosters cultural exchange.
