A Picture Of The Gulf Of Mexico often reveals a stunning body of water, but beneath the surface, it tells a complex story about its ecosystem, especially concerning issues that affect the LGBTQ+ community who enjoy its beauty and resources. Gaymexico.net dives deep into this topic, offering insights into the Gulf’s environmental challenges, alongside relevant information for LGBTQ+ travelers and residents in Mexico. Discover the LGBTQ+ friendly destinations near the Gulf Coast and understand ecological impacts with us.
1. What Exactly Is the Gulf of Mexico Dead Zone?
The Gulf of Mexico dead zone is a region of hypoxic waters, meaning it has low dissolved oxygen levels (less than 2 parts per million), located at the mouth of the Mississippi River. This area, critical to understanding the Gulf’s health and its impact on coastal communities, including LGBTQ+ havens along the coast, can span between 6,000 and 7,000 square miles. It stretches across the inner and mid-continental shelf, starting at the Mississippi River delta and reaching towards the upper Texas coast.
The “dead zone” is a significant environmental issue that affects marine life and the economies of coastal communities. The largest dead zone ever recorded covered an area roughly the size of New Jersey, highlighting the severity of the problem. This impacts not only the environment but also industries such as fishing, which are vital to many coastal towns, some of which are popular destinations for LGBTQ+ travelers seeking safe and welcoming environments.
2. Where Exactly Can These Dead Zones Be Found?
Dead zones are not unique to the Gulf of Mexico; they are a global issue, appearing in various marine and freshwater environments worldwide. While the Gulf of Mexico’s dead zone is one of the largest, others can be found in the Baltic Sea, the Black Sea, off the coast of Oregon, and in the Chesapeake Bay. These zones also affect freshwater ecosystems, such as Lake Erie, demonstrating the widespread nature of this environmental challenge.
Understanding where these dead zones occur helps in focusing conservation efforts and understanding the broader impact on global aquatic ecosystems. This knowledge is also valuable for LGBTQ+ travelers who are environmentally conscious and wish to support sustainable tourism in the regions they visit.
3. What Primary Factors Lead to the Formation of the Dead Zone?
The primary cause of the dead zone in the Gulf of Mexico is nutrient enrichment from the Mississippi River, specifically nitrogen and phosphorus. These nutrients originate from a vast watershed that drains much of the United States, stretching from Montana to Pennsylvania and southward along the Mississippi River. A significant portion of the nitrogen input comes from major farming states, including Minnesota, Iowa, Illinois, Wisconsin, Missouri, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana.
These nutrients enter the river through runoff from fertilizers, soil erosion, animal wastes, and sewage. In natural systems, plants deplete these nutrients in the soil, limiting algae growth. However, increased nitrogen and phosphorus inputs from human activities lead to excessive algae growth, resulting in algal blooms. As these blooms decompose, they consume oxygen, leading to hypoxic conditions that create the dead zone. The size of the dead zone varies seasonally due to farming practices and weather events like flooding and hurricanes.
4. What Are the Broad Ecological Consequences of the Dead Zone?
Nutrient overloading and the subsequent algal blooms lead to eutrophication, which significantly reduces benthic biomass and biodiversity. Hypoxic waters cannot support as many organisms and have been linked to massive fish kills in the Black Sea and the Gulf of Mexico. This disruption of the ecosystem affects the entire food chain and the overall health of the marine environment.
For communities that rely on fishing and seafood, including those in LGBTQ+ friendly coastal areas, the consequences can be severe. The decline in fish populations and the degradation of marine habitats can lead to economic hardship and loss of livelihoods. Protecting these ecosystems is crucial for maintaining both environmental health and economic stability.
5. How Does the Dead Zone Impact the Seafood Industry in the Gulf?
The Gulf of Mexico is a vital source for the seafood industry in the United States, supplying 72% of U.S. harvested shrimp, 66% of harvested oysters, and 16% of commercial fish. If the hypoxic zone continues to persist or worsen, it will significantly impact fishermen and coastal state economies. The reduction in fish populations and the degradation of marine habitats threaten the livelihoods of those who depend on the Gulf for their income.
This economic impact is felt particularly hard in communities that are already vulnerable, including some LGBTQ+ communities that rely on the seafood industry for their economic well-being. Sustainable practices and efforts to reduce the dead zone are essential to protect these communities and ensure the long-term viability of the seafood industry.
 Satellite image of the Gulf of Mexico showcasing nutrient-rich sediment flow potentially leading to hypoxic conditions.
Satellite image of the Gulf of Mexico showcasing nutrient-rich sediment flow potentially leading to hypoxic conditions.
6. What Actions Can Effectively Remediate the Gulf of Mexico Dead Zone?
Addressing the Gulf of Mexico dead zone requires tackling the problem at its source, which involves reducing nutrient inputs into the Mississippi River. Effective solutions include:
- Using Fewer Fertilizers: Adjusting the timing of fertilizer applications to minimize runoff of excess nutrients from farmland can significantly reduce nutrient inputs.
- Controlling Animal Wastes: Ensuring proper management of animal wastes prevents them from entering waterways and contributing to nutrient pollution.
- Monitoring Septic Systems: Regularly monitoring septic systems and sewage treatment facilities helps reduce the discharge of nutrients into surface water and groundwater.
- Implementing Careful Industrial Practices: Limiting the discharge of nutrients, organic matter, and chemicals from manufacturing facilities can further reduce nutrient pollution.
These solutions are relatively straightforward to implement and can significantly decrease the amount of nitrogen and phosphorus entering the Gulf of Mexico. A similar approach has been successfully used to recover the Great Lakes from eutrophication. Additionally, government-funded efforts to restore wetlands along the Gulf Coast help naturally filter the water before it enters the Gulf, providing an additional layer of protection.
7. What Role Does Eutrophication Play in the Formation of Dead Zones?
Eutrophication is a critical process in the formation of dead zones. It occurs when a body of water becomes overly enriched with minerals and nutrients, primarily due to runoff from land. This nutrient overload leads to excessive algae and plant growth, known as algal blooms. As these blooms die and decompose, the decomposition process consumes large amounts of oxygen in the water.
This oxygen depletion results in hypoxic conditions, where the water contains very little dissolved oxygen, making it difficult for marine life to survive. The consequences of eutrophication include reduced biodiversity, fish kills, and the creation of dead zones, where the water is essentially uninhabitable for most aquatic organisms. Addressing eutrophication requires managing nutrient inputs and implementing strategies to reduce pollution from agricultural, industrial, and residential sources.
8. How Do Farming Practices Contribute to the Dead Zone Problem?
Farming practices significantly contribute to the dead zone problem through the runoff of fertilizers and animal wastes. The use of nitrogen and phosphorus-based fertilizers is essential for crop production, but when these fertilizers are applied in excess or at the wrong time, they can be washed into waterways during rainfall. This runoff carries the nutrients into rivers and streams, eventually reaching the Mississippi River and the Gulf of Mexico.
Animal wastes from livestock operations also contribute to nutrient pollution. Manure and other organic wastes contain high levels of nitrogen and phosphorus, and if not properly managed, they can contaminate water sources. Implementing best management practices, such as using fewer fertilizers, adjusting the timing of fertilizer applications, and controlling animal wastes, can help reduce nutrient pollution from agricultural sources.
9. What Impact Do Weather Events Like Flooding and Hurricanes Have?
Weather events such as flooding and hurricanes can exacerbate the dead zone problem by increasing nutrient runoff into the Gulf of Mexico. Flooding events can overwhelm sewage treatment facilities and agricultural lands, leading to a surge in nutrient pollution. The floodwaters carry fertilizers, animal wastes, and other pollutants into waterways, contributing to eutrophication and the expansion of the dead zone.
Hurricanes can also stir up sediments and nutrients from the bottom of the Gulf, leading to algal blooms and oxygen depletion. The strong winds and heavy rainfall associated with hurricanes can disrupt ecosystems and worsen water quality issues. Preparing for and mitigating the impacts of these weather events is essential for managing the dead zone and protecting coastal communities.
10. What Initiatives Are in Place to Restore Wetlands Along the Gulf Coast?
Restoring wetlands along the Gulf Coast is a crucial strategy for mitigating the dead zone by naturally filtering water before it enters the Gulf. Wetlands act as natural sponges, absorbing excess nutrients and pollutants from runoff. They also provide habitat for a variety of plant and animal species, contributing to biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Government-funded initiatives, such as those supported by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and other federal and state agencies, focus on restoring and protecting wetlands along the Gulf Coast. These initiatives involve planting native vegetation, restoring hydrologic processes, and managing invasive species. By enhancing the natural filtering capacity of wetlands, these initiatives help reduce nutrient pollution and improve water quality in the Gulf of Mexico.
11. How Does Climate Change Intensify the Challenges of the Dead Zone?
Climate change intensifies the challenges of the dead zone in several ways. Rising temperatures can increase water stratification, which reduces the mixing of oxygen-rich surface waters with deeper waters, exacerbating hypoxia. Warmer waters also hold less dissolved oxygen, making aquatic life more vulnerable to oxygen depletion.
Climate change also leads to more frequent and intense storms, which can increase nutrient runoff into the Gulf. Changes in precipitation patterns can alter the timing and magnitude of river flows, affecting the delivery of nutrients and the formation of the dead zone. Addressing climate change through reducing greenhouse gas emissions and implementing adaptation strategies is essential for managing the dead zone and protecting coastal ecosystems.
12. Can Individual Actions Really Make a Difference in Reducing the Dead Zone?
Yes, individual actions can collectively make a significant difference in reducing the dead zone. By adopting sustainable practices in our daily lives, we can reduce nutrient pollution and protect water quality. Some impactful actions include:
- Using Fertilizers Sparingly: Reducing the use of fertilizers on lawns and gardens helps prevent nutrient runoff into waterways.
- Properly Disposing of Waste: Ensuring proper disposal of pet waste and household chemicals prevents them from contaminating water sources.
- Supporting Sustainable Agriculture: Buying locally sourced and sustainably produced food supports farming practices that minimize nutrient pollution.
- Conserving Water: Reducing water consumption helps decrease the amount of wastewater that needs to be treated, lowering nutrient discharge from sewage treatment facilities.
- Educating Others: Raising awareness about the dead zone and promoting sustainable practices can encourage others to take action and contribute to the solution.
By working together and adopting these practices, we can make a positive impact on the health of the Gulf of Mexico and protect its valuable ecosystems.
13. What Are the Long-Term Implications If the Dead Zone Is Not Addressed?
If the dead zone is not addressed, the long-term implications could be severe. Continued hypoxia can lead to a collapse of marine ecosystems, resulting in reduced biodiversity, loss of fish populations, and degradation of habitats. The economic consequences could be significant, affecting the seafood industry, tourism, and coastal communities.
The disruption of the food chain can have cascading effects, impacting other species and ecosystems. The loss of habitat can also lead to a decline in recreational activities, such as fishing and boating, further affecting local economies. Taking action to address the dead zone is essential for protecting the health of the Gulf of Mexico and ensuring the sustainability of its resources for future generations.
14. How Can Technology Help in Monitoring and Managing the Dead Zone?
Technology plays a crucial role in monitoring and managing the dead zone. Advanced sensors and monitoring equipment can track oxygen levels, nutrient concentrations, and other water quality parameters in real-time. These data provide valuable insights into the dynamics of the dead zone and help inform management decisions.
Satellite imagery and remote sensing technologies can map the extent of the dead zone and monitor changes over time. Computer models and simulations can predict the formation and movement of the dead zone, allowing for proactive management strategies. These technologies help scientists, policymakers, and resource managers make informed decisions and implement effective solutions to address the dead zone.
15. What Legal and Policy Measures Are Being Implemented to Tackle the Dead Zone?
Several legal and policy measures are being implemented to tackle the dead zone. The Clean Water Act provides a regulatory framework for controlling pollution and protecting water quality. The EPA works with states and local communities to implement water quality standards and enforce regulations related to nutrient pollution.
The Mississippi River/Gulf of Mexico Watershed Nutrient Task Force, a collaboration of federal and state agencies, develops and implements strategies for reducing nutrient pollution in the Mississippi River Basin. These strategies include promoting best management practices for agriculture, investing in wastewater treatment infrastructure, and restoring wetlands. Legal and policy measures are essential for establishing accountability and driving progress in addressing the dead zone.
16. How Can LGBTQ+ Individuals and Communities Contribute to the Solution?
LGBTQ+ individuals and communities can play an important role in contributing to the solution by:
- Raising Awareness: Educating friends, family, and community members about the dead zone and its impacts can increase awareness and encourage action.
- Advocating for Sustainable Policies: Supporting policies that promote sustainable agriculture, protect water quality, and address climate change can help reduce nutrient pollution.
- Supporting Sustainable Businesses: Patronizing businesses that prioritize sustainability and environmental responsibility can encourage more companies to adopt eco-friendly practices.
- Participating in Cleanup Efforts: Volunteering for beach cleanups and other environmental restoration projects can help improve water quality and protect coastal ecosystems.
- Promoting Eco-Tourism: Encouraging responsible and sustainable tourism practices can help protect natural resources and support local communities.
By working together, LGBTQ+ individuals and communities can make a positive impact and contribute to a more sustainable future for the Gulf of Mexico.
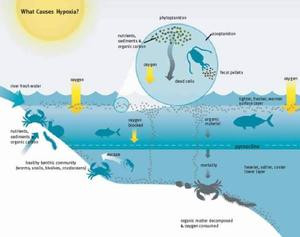 Diagram illustrating the causes of hypoxia, including increased organic matter and water stratification.
Diagram illustrating the causes of hypoxia, including increased organic matter and water stratification.
17. What Are Some Success Stories of Reducing Dead Zones in Other Parts of the World?
There are several success stories of reducing dead zones in other parts of the world. One notable example is the recovery of the Chesapeake Bay, where collaborative efforts by government agencies, environmental organizations, and local communities have significantly reduced nutrient pollution. By implementing stricter regulations on agricultural runoff, investing in wastewater treatment upgrades, and restoring wetlands, the Chesapeake Bay has seen improvements in water quality and a resurgence of marine life.
Another success story is the reduction of the dead zone in the Baltic Sea, where international agreements and cooperation among countries have led to decreased nutrient inputs. By implementing sustainable farming practices, improving sewage treatment, and reducing industrial pollution, the Baltic Sea has experienced a reduction in the size and severity of its dead zone. These success stories demonstrate that with concerted efforts, it is possible to reduce dead zones and restore aquatic ecosystems.
18. How Does the Dead Zone Affect Recreational Activities Like Fishing and Boating?
The dead zone significantly affects recreational activities like fishing and boating by reducing fish populations and degrading habitats. Hypoxic waters cannot support as many fish, making it difficult for anglers to catch their limit. The lack of oxygen also leads to fish kills, where large numbers of fish die due to suffocation.
Boating can also be affected by the dead zone, as algal blooms can create unpleasant odors and reduce water clarity. The loss of habitat and the decline in fish populations can make it less enjoyable to spend time on the water. Addressing the dead zone is essential for protecting recreational opportunities and ensuring that people can continue to enjoy the Gulf of Mexico for generations to come.
19. What Are Some Sustainable Tourism Practices That Can Help Protect the Gulf?
Sustainable tourism practices play a crucial role in protecting the Gulf. By supporting eco-friendly businesses, reducing waste, and conserving resources, tourists can minimize their environmental impact and contribute to the health of the Gulf. Some specific practices include:
- Choosing Eco-Friendly Accommodations: Staying in hotels and resorts that implement sustainable practices, such as water conservation, energy efficiency, and waste reduction, can reduce the environmental footprint of your trip.
- Supporting Local Businesses: Patronizing local restaurants, shops, and tour operators that prioritize sustainability can help support local economies and promote responsible tourism.
- Reducing Waste: Bringing reusable water bottles, shopping bags, and containers can help reduce waste and prevent plastic pollution in the Gulf.
- Conserving Water and Energy: Being mindful of water and energy consumption while traveling can help conserve these resources and reduce environmental impacts.
- Respecting Wildlife and Habitats: Observing wildlife from a safe distance, avoiding disturbing habitats, and following responsible fishing and boating practices can help protect the Gulf’s natural resources.
20. What Resources Are Available for Learning More About the Dead Zone?
There are many resources available for learning more about the dead zone, including:
- Government Agencies: The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), and other government agencies provide information, data, and reports on the dead zone.
- Environmental Organizations: Organizations like the Environmental Defense Fund, the Nature Conservancy, and the World Wildlife Fund conduct research, advocate for policies, and implement conservation projects related to the dead zone.
- Academic Institutions: Universities and research institutions conduct studies on the causes, impacts, and solutions to the dead zone.
- Online Resources: Websites like gaymexico.net provide comprehensive information on LGBTQ+ travel in Mexico, including insights into environmental issues affecting coastal communities.
By exploring these resources, you can deepen your understanding of the dead zone and learn more about how to get involved in protecting the Gulf of Mexico.
21. What is gaymexico.net Doing to Promote Awareness of Environmental Issues in Mexico?
Gaymexico.net is committed to promoting awareness of environmental issues in Mexico by providing information and resources on sustainable tourism, conservation efforts, and responsible travel practices. We highlight eco-friendly destinations, showcase businesses that prioritize sustainability, and offer tips for reducing your environmental impact while traveling in Mexico.
We also partner with local organizations and communities to support conservation projects and promote responsible tourism. By raising awareness and providing actionable information, gaymexico.net aims to empower LGBTQ+ travelers and residents to make informed choices and contribute to a more sustainable future for Mexico.
22. What is the Current Size and Location of the Gulf of Mexico Dead Zone?
As of 2023, the Gulf of Mexico dead zone measured approximately 3,058 square miles, which is notably smaller than the average size observed over the past several years. This reduction can be attributed to variations in weather patterns, nutrient runoff management, and other environmental factors. The zone is located off the coasts of Louisiana and Texas, extending from the Mississippi River delta westward.
The annual size of the dead zone is typically measured in late summer, providing a snapshot of the impact of nutrient runoff from the Mississippi River Basin. Monitoring the size and location of the dead zone is essential for assessing the effectiveness of efforts to reduce nutrient pollution and protect the Gulf of Mexico’s ecosystem.
23. How Do Gulf Coast Communities Rely on a Healthy Gulf?
Gulf Coast communities heavily depend on a healthy Gulf for their economic, social, and cultural well-being. The Gulf supports a thriving seafood industry, providing livelihoods for fishermen, seafood processors, and related businesses. Tourism is also a major economic driver, with visitors drawn to the Gulf’s beaches, recreational opportunities, and natural beauty.
Beyond the economic benefits, the Gulf is deeply ingrained in the cultural identity of coastal communities. Fishing, boating, and other water-based activities are important traditions, passed down through generations. Protecting the health of the Gulf is essential for preserving these traditions and ensuring the long-term sustainability of Gulf Coast communities.
24. How Do Regulations Affect the Use of Fertilizers to Protect the Gulf?
Regulations play a vital role in managing the use of fertilizers to protect the Gulf of Mexico. These regulations aim to reduce nutrient runoff from agricultural lands by setting limits on fertilizer application rates, promoting best management practices, and requiring farmers to implement nutrient management plans.
Some states in the Mississippi River Basin have implemented specific regulations on fertilizer use, such as restricting the timing of fertilizer applications to avoid periods of heavy rainfall and promoting the use of slow-release fertilizers. The EPA also works with states to develop water quality standards and implement programs to reduce nutrient pollution from agricultural sources. Effective regulations are essential for achieving meaningful reductions in nutrient runoff and protecting the Gulf of Mexico.
25. How is Water Quality Monitored in the Gulf of Mexico?
Water quality in the Gulf of Mexico is monitored through a variety of methods, including:
- Sampling Programs: Government agencies, research institutions, and environmental organizations conduct regular water sampling to measure oxygen levels, nutrient concentrations, and other water quality parameters.
- Remote Sensing: Satellites and aircraft equipped with sensors are used to monitor water quality over large areas, providing data on algal blooms, water clarity, and other indicators of ecosystem health.
- Continuous Monitoring Stations: Fixed monitoring stations deployed throughout the Gulf provide real-time data on water quality conditions, allowing for early detection of pollution events and other threats.
- Citizen Science Programs: Volunteer programs engage local communities in monitoring water quality, providing valuable data and increasing awareness of environmental issues.
These monitoring efforts provide essential information for assessing the health of the Gulf of Mexico and informing management decisions.
26. What Role Do Oyster Beds Play in Keeping the Gulf Healthy?
Oyster beds play a critical role in maintaining the health of the Gulf of Mexico ecosystem. Oysters are filter feeders, meaning they filter water to obtain food, removing sediment, algae, and other pollutants in the process. A single oyster can filter up to 50 gallons of water per day, helping to improve water clarity and reduce nutrient pollution.
Oyster beds also provide habitat for a variety of fish, crustaceans, and other marine organisms. They act as natural breakwaters, protecting shorelines from erosion and storm surge. Restoring oyster beds is an important strategy for improving water quality, enhancing biodiversity, and protecting coastal communities.
27. How Does Protecting Seagrass Beds Help the Gulf of Mexico?
Protecting seagrass beds is essential for maintaining the health of the Gulf of Mexico ecosystem. Seagrasses are flowering plants that grow in shallow coastal waters, providing habitat and food for a wide range of marine species. They also play a vital role in stabilizing sediments, preventing erosion, and improving water quality.
Seagrass beds act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in their roots and sediments. Protecting seagrass beds helps mitigate climate change and reduce the impacts of ocean acidification. Restoring damaged seagrass beds is an important strategy for enhancing biodiversity, improving water quality, and protecting coastal communities.
28. How Does the Dead Zone Compare to Other Environmental Issues in the Gulf?
The dead zone is one of several significant environmental issues affecting the Gulf of Mexico. Other pressing issues include:
- Oil Spills: Oil spills can cause extensive damage to marine ecosystems, harming wildlife, contaminating habitats, and disrupting local economies.
- Coastal Erosion: Coastal erosion threatens communities, habitats, and infrastructure, leading to loss of land and increased vulnerability to storms.
- Plastic Pollution: Plastic pollution is a growing concern, with plastic debris accumulating in the Gulf and harming marine life through entanglement and ingestion.
- Harmful Algal Blooms: Harmful algal blooms (HABs) can produce toxins that contaminate seafood, cause respiratory problems, and disrupt ecosystems.
Addressing these environmental issues requires a comprehensive approach that considers the interconnectedness of the Gulf’s ecosystems and the need for sustainable management practices.
29. Where Can I Find LGBTQ+ Friendly Resources and Destinations Near the Gulf Coast?
Finding LGBTQ+ friendly resources and destinations near the Gulf Coast is easier than ever. Websites like gaymexico.net offer comprehensive guides to LGBTQ+ friendly cities, accommodations, and events in Mexico. These resources provide valuable information on safe and welcoming places to visit, allowing LGBTQ+ travelers to plan their trips with confidence.
Additionally, many local LGBTQ+ community centers and organizations offer information and support for travelers and residents alike. By connecting with these resources, LGBTQ+ individuals can find the best places to stay, dine, and explore while feeling safe and supported.
30. What Are Some Eco-Friendly Activities LGBTQ+ Travelers Can Enjoy Near the Gulf of Mexico?
LGBTQ+ travelers can enjoy a variety of eco-friendly activities near the Gulf of Mexico, including:
- Kayaking and Paddleboarding: Exploring coastal waterways by kayak or paddleboard provides a unique perspective on the Gulf’s natural beauty while minimizing environmental impact.
- Birdwatching: The Gulf Coast is home to a diverse array of bird species, making it a popular destination for birdwatching.
- Hiking and Nature Walks: Exploring coastal trails and nature preserves allows visitors to connect with the Gulf’s natural environment while enjoying scenic views.
- Snorkeling and Diving: Exploring coral reefs and seagrass beds provides opportunities to observe marine life while supporting responsible tourism.
- Volunteering for Conservation Projects: Participating in beach cleanups, habitat restoration projects, and other conservation efforts can help protect the Gulf’s natural resources.
By engaging in these activities, LGBTQ+ travelers can enjoy the Gulf of Mexico while contributing to its long-term sustainability.
Ready to explore the beauty of Mexico while supporting sustainable practices? Visit gaymexico.net for the latest guides, tips, and resources for LGBTQ+ travelers. Connect with our community, discover LGBTQ+ friendly destinations near the Gulf Coast, and make your next trip an unforgettable adventure. Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States. Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177. Website: gaymexico.net.
FAQ About The Gulf Of Mexico
What causes the Gulf of Mexico dead zone?
The Gulf of Mexico dead zone is caused by nutrient pollution, primarily from agricultural runoff, leading to hypoxia (low oxygen levels) in the water.
Where is the Gulf of Mexico dead zone located?
The dead zone is located off the coasts of Louisiana and Texas, near the mouth of the Mississippi River.
How big is the Gulf of Mexico dead zone?
The size of the dead zone varies annually, but it can cover up to 6,000-7,000 square miles.
What are the effects of the Gulf of Mexico dead zone?
The dead zone reduces biodiversity, harms marine life, and negatively impacts the seafood industry.
What can be done to remediate the Gulf of Mexico dead zone?
Solutions include reducing fertilizer use, controlling animal wastes, and restoring wetlands.
How does the dead zone impact the LGBTQ+ community in Mexico?
The dead zone can affect LGBTQ+ communities that rely on fishing and tourism, impacting their economic well-being.
Are there LGBTQ+ friendly destinations near the Gulf of Mexico?
Yes, several cities near the Gulf Coast offer welcoming environments for LGBTQ+ travelers and residents. Visit gaymexico.net for further information.
How can LGBTQ+ travelers support sustainable tourism in the Gulf of Mexico?
LGBTQ+ travelers can support eco-friendly businesses, reduce waste, and engage in responsible travel practices.
What resources are available for learning more about the dead zone?
Government agencies, environmental organizations, and websites like gaymexico.net offer information and resources on the dead zone.
How can I get involved in protecting the Gulf of Mexico?
You can reduce nutrient pollution, advocate for sustainable policies, and participate in cleanup efforts.
