Mexico City, the capital of Mexico, like many urban centers around the world, faced unprecedented challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic. This article explores how social capital within communities in Mexico City played a crucial role in mitigating the negative impacts of uncertainty and fostering cooperation during the crisis. A study conducted in April 2020, at the onset of the pandemic in Mexico, reveals a strong correlation between pandemic-related uncertainty and a decrease in social cooperation. However, the research also demonstrates that strong community social capital can buffer these negative effects.
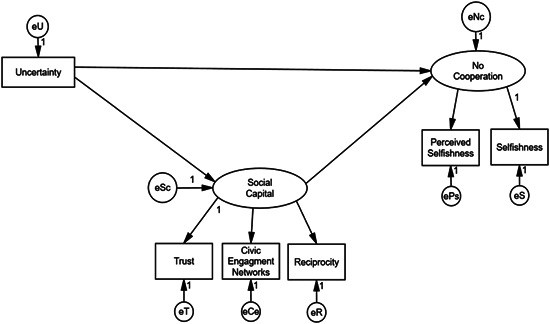 Figure 1: Model of the impact of social capital on uncertainty and cooperation
Figure 1: Model of the impact of social capital on uncertainty and cooperation
Figure 1 illustrates the hypothesized relationships between uncertainty, social capital, and cooperation.
The Impact of Uncertainty and the Role of Social Capital in the Capital de Mexico
The COVID-19 pandemic created a climate of profound uncertainty globally, and the Capital De Mexico was no exception. Job losses, economic instability, and health concerns contributed to heightened anxiety and fear. This uncertainty, according to Terror Management Theory (TMT), can lead to individuals prioritizing their immediate social circles and becoming less cooperative with others.
Social capital, defined as the trust, norms of reciprocity, and civic engagement networks within a community, emerged as a critical factor in counteracting these negative tendencies. Communities with high social capital are characterized by strong social bonds, a willingness to help one another, and active participation in collective problem-solving.
Research Findings in Mexico City
A study involving 565 residents across Mexico, including residents of Mexico City, utilized surveys to measure social capital, uncertainty, and willingness to cooperate during the pandemic. The results, analyzed using structural equation modeling, confirmed the hypothesized relationships:
- Uncertainty breeds non-cooperation: Higher levels of uncertainty were significantly associated with a decreased willingness to cooperate.
- Social capital as a buffer: Strong community social capital mitigated the negative impact of uncertainty on cooperation. Individuals in communities with high social capital experienced less uncertainty and demonstrated greater cooperation.
- Uncertainty erodes trust: The study also revealed a direct negative impact of uncertainty on trust within communities. This finding underscores the importance of social capital in maintaining trust during times of crisis.
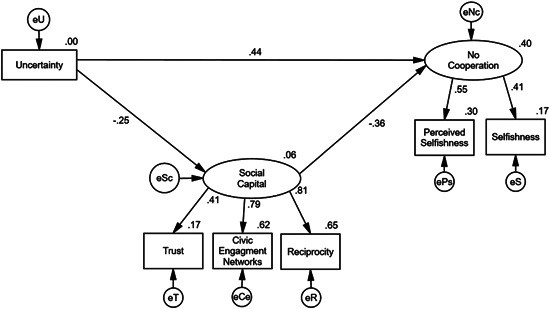 Figure 2: Statistical model showing the relationships between uncertainty, social capital, and non-cooperation
Figure 2: Statistical model showing the relationships between uncertainty, social capital, and non-cooperation
Figure 2 shows the statistical model of the study, highlighting the direct and indirect effects of uncertainty and social capital on cooperation.
The Importance of Social Capital in the Capital de Mexico
This research highlights the vital role of social capital in navigating crises like the COVID-19 pandemic in Mexico City. Communities with robust social capital are more resilient, better equipped to address collective challenges, and less susceptible to the negative psychological and social consequences of uncertainty. The findings underscore the need for policies and initiatives that strengthen social capital in the capital de Mexico and beyond. Promoting trust, fostering reciprocity, and facilitating civic engagement are crucial for building stronger, more resilient communities capable of weathering future crises.
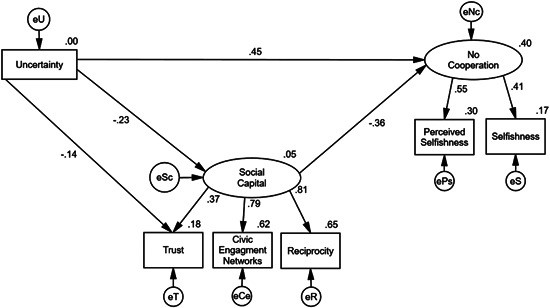 Figure 3: Refined statistical model incorporating the direct effect of uncertainty on trust.
Figure 3: Refined statistical model incorporating the direct effect of uncertainty on trust.
Figure 3 further refines the model by demonstrating the direct negative effect of uncertainty on trust within the community.
Conclusion
The COVID-19 pandemic provided a stark reminder of the importance of social cohesion and cooperation. In the capital de Mexico, as elsewhere, social capital proved to be a valuable resource in mitigating the negative effects of uncertainty and fostering resilience within communities. Investing in social capital through community-building initiatives and supportive policies is essential for creating a more robust and equitable society.