The Gulf of Mexico is a vital body of water bordered by the United States and Mexico, connected to both the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. This unique location makes it a hub for tourism and cultural exchange, especially for the LGBTQ+ community seeking welcoming destinations. Discover LGBTQ-friendly destinations in Mexico on Gaymexico.net.
1. Where Is The Gulf of Mexico Located?
The Gulf of Mexico is located off the southeastern coast of North America. It’s nestled between the United States, Mexico, and Cuba. This strategic location connects it to the Atlantic Ocean via the Straits of Florida and to the Caribbean Sea through the Yucatán Channel.
Understanding the Gulf’s Geography
The Gulf of Mexico is a vast, semi-enclosed body of water with a unique geographical setting. This makes it a fascinating area for exploration, especially for LGBTQ+ travelers who appreciate the blend of cultures and natural beauty. Key features include:
-
Bordering Countries: The Gulf is bordered by the United States to the north, Mexico to the west and south, and Cuba to the southeast.
-
Connections to Major Water Bodies: It links to the Atlantic Ocean through the Straits of Florida and to the Caribbean Sea via the Yucatán Channel.
-
Coastal Features: The coastline includes diverse environments, from sandy beaches and tidal marshes to mangrove forests.
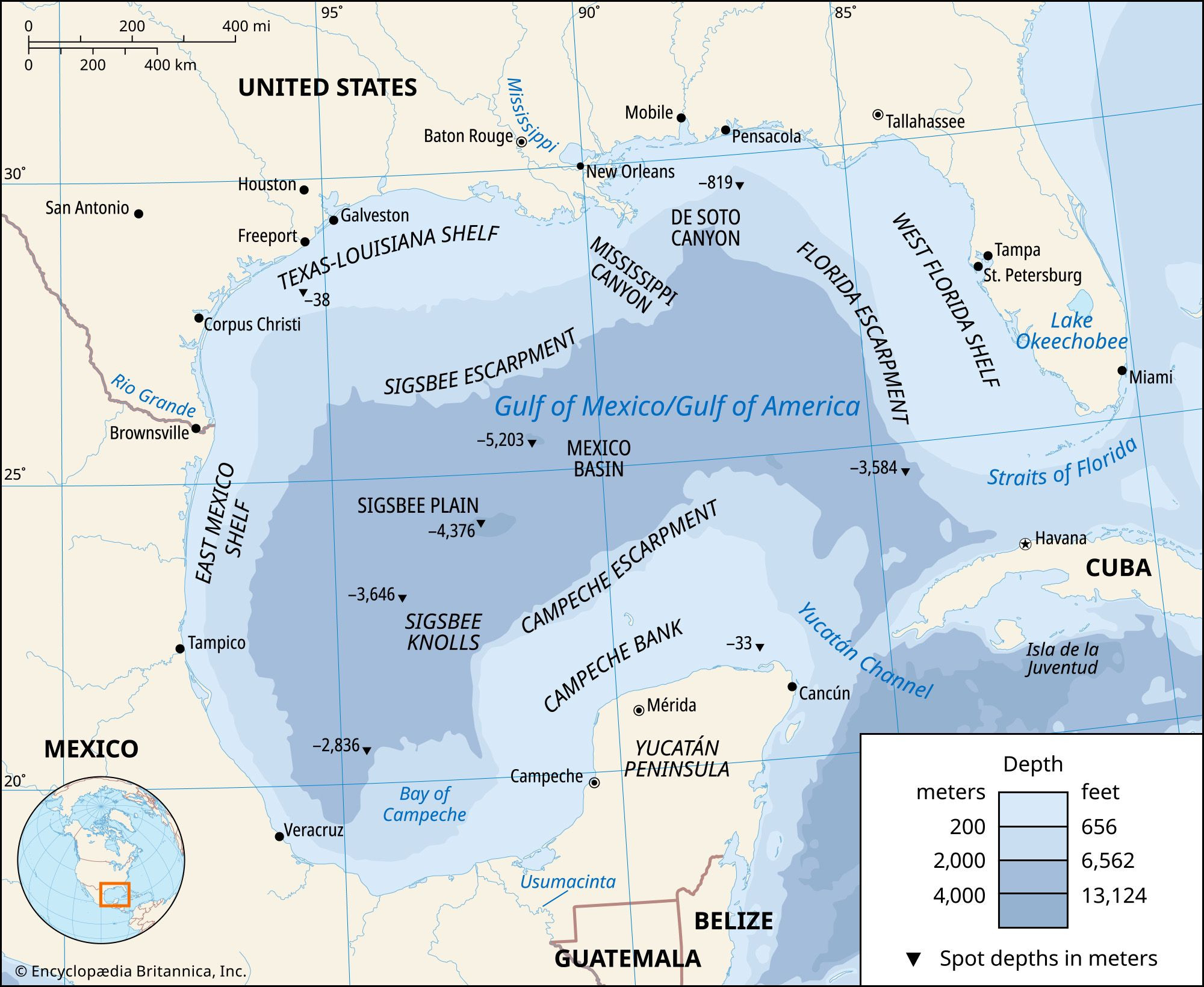 Map showing the location of the Gulf of Mexico along the coasts of North America
Map showing the location of the Gulf of Mexico along the coasts of North America
Why This Matters for LGBTQ+ Travelers
Knowing the Gulf’s location is essential for planning trips to LGBTQ+-friendly destinations in Mexico. For instance, cities like Puerto Vallarta, located on the Pacific coast but easily accessible, are known for their inclusive atmosphere. Gaymexico.net offers insights into safe and welcoming locations along Mexico’s coasts, helping you make informed travel decisions.
2. What Is the Deepest Point in the Gulf of Mexico?
The deepest point in the Gulf of Mexico is the Sigsbee Deep, which plunges to about 17,070 feet (5,203 meters) below sea level. This point is located in the Mexico Basin and is part of the abyssal plain that forms the Gulf’s floor.
Exploring the Sigsbee Deep
The Sigsbee Deep is a remarkable geological feature that contributes to the Gulf’s unique environment. Here are some key points about it:
- Location: Situated within the Mexico Basin, the Sigsbee Deep is a significant part of the Gulf’s abyssal plain.
- Depth: Reaching 17,070 feet (5,203 meters), it’s the deepest known point in the Gulf.
- Formation: The deep is part of a larger flat area with a minimal gradient, approximately 1 foot in every 8,000 feet.
Geological Significance
The Gulf’s geology is characterized by several provinces, including the coastal zone, continental shelf, continental slope, and abyssal plain. Salt domes buried at various depths on the shelf and slope are associated with economically important deposits of oil and natural gas. The Sigsbee Knolls, rising from the basin floor, are surface expressions of these buried salt domes, adding to the area’s geological interest.
How This Affects LGBTQ+ Tourism
While the Sigsbee Deep itself isn’t a tourist destination, understanding the Gulf’s geological features can enrich your travel experience. Knowing the region’s natural history adds depth to visits to coastal cities and enhances appreciation for the local environment. Resources like Gaymexico.net can guide you to destinations where you can explore these aspects safely and enjoyably.
3. What Mineral Resources Are Found In The Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is rich in mineral resources, including significant deposits of petroleum and natural gas. Sulfur is also extracted from wells drilled on the continental shelf off Louisiana. Oyster shells from shallow waters are used in the chemical industry for calcium carbonate and road construction.
Key Mineral Resources
-
Petroleum and Natural Gas: These are the most significant mineral resources in the Gulf, driving much of the region’s economy.
-
Sulfur: Extracted from offshore wells, sulfur is a valuable industrial material.
-
Oyster Shells: Harvested from shallow waters, these shells are used in chemical processes and construction.
Economic Impact
The extraction of these resources has a substantial impact on the economies of the bordering states and Mexico. It supports numerous industries and provides employment opportunities.
Sustainability Considerations
However, the extraction of mineral resources also poses environmental challenges. Oil spills, habitat destruction, and pollution are potential risks that must be managed to ensure sustainable practices. According to a report by the Environmental Defense Fund in July 2024, stricter regulations and advanced technologies are essential to minimize the environmental impact of resource extraction in the Gulf.
Relevance to LGBTQ+ Travelers
For LGBTQ+ travelers, understanding the region’s economic activities can provide a broader perspective on the communities they visit. While resource extraction may not be a direct attraction, it influences the local economy and culture. Websites like Gaymexico.net help travelers find businesses and services that support sustainable and ethical practices, allowing them to make informed choices that benefit the local community and environment.
4. When Does Hurricane Season Occur In The Gulf Of Mexico?
Hurricane season in the Gulf of Mexico officially runs from June 1 to November 30. During this time, meteorological and oceanographic conditions are conducive to the development of hurricanes.
Understanding Hurricane Season
- Official Dates: June 1 to November 30 each year.
- Peak Activity: August and September are typically the months with the highest hurricane activity.
- Factors: Warm water temperatures, low wind shear, and atmospheric instability contribute to hurricane formation.
Historical Impact
The Gulf of Mexico has a history of devastating hurricanes. Notable examples include the Galveston hurricane of 1900 and Hurricane Katrina in 2005, which caused widespread destruction and loss of life.
Preparing for Hurricane Season
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts from reliable sources such as the National Hurricane Center.
- Emergency Plans: Develop evacuation plans and prepare emergency kits with essential supplies.
- Travel Insurance: Consider purchasing travel insurance that covers hurricane-related disruptions.
How This Affects LGBTQ+ Tourism
For LGBTQ+ travelers, especially those planning trips to Mexico, it’s crucial to be aware of hurricane season. Destinations like Cancun, Playa del Carmen, and Tulum are popular but can be affected by hurricanes. Websites such as Gaymexico.net provide updated travel advisories and safety tips to help you plan your trip.
5. What are the Key Physical Features of the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico comprises several ecological and geological zones, notably the coastal zone, continental shelf, continental slope, and abyssal plain. The coastal zone features tidal marshes, sandy beaches, and mangrove-covered areas, along with numerous bays, estuaries, and lagoons.
Detailed Breakdown of Physical Features
-
Coastal Zone:
- Description: Characterized by diverse habitats like tidal marshes, sandy beaches, and mangrove forests.
- Significance: Provides critical ecosystems for various species and acts as a buffer against storms.
-
Continental Shelf:
- Description: A continuous terrace around the Gulf’s margin, varying in width from 25 to over 200 miles.
- Composition: Primarily carbonate material off Florida and the Yucatán Peninsula, with sand, silt, and clay sediments elsewhere.
-
Continental Slope:
- Description: The area where the seabed sharply declines from the continental shelf to the abyssal plain.
- Geological Activity: Contains buried salt domes associated with oil and natural gas deposits.
-
Abyssal Plain:
- Description: The deep ocean floor of the Gulf, featuring a large triangular area in the center.
- Features: Includes the Sigsbee Deep, the deepest point in the Gulf, and the Sigsbee Knolls, which are surface expressions of buried salt domes.
Ecological and Economic Importance
These physical features support a wealth of marine life and are crucial for commercial fishing and resource extraction. The coastal wetlands serve as nurseries for many fish species, while the deeper zones contain valuable mineral resources.
Impact on LGBTQ+ Travel and Tourism
Understanding the Gulf’s physical features can enhance the travel experiences of LGBTQ+ visitors. The diverse coastal environments offer opportunities for ecotourism, bird watching, and exploring unique ecosystems. Resources like Gaymexico.net can guide travelers to destinations where they can appreciate these natural wonders while supporting local communities and sustainable practices.
6. What is the Hydrology of the Gulf of Mexico?
The hydrology of the Gulf of Mexico is defined by its complex current patterns, salinity variations, and temperature gradients. A river-like current in the southeastern part feeds the North Atlantic Gulf Stream, moving oceanic waters through the Gulf.
Key Aspects of Hydrology
-
Currents:
- Main Current: Caribbean water enters through the Yucatán Channel and exits via the Straits of Florida in a clockwise direction.
- Loop Currents: Meandering masses of water that break off from the main stream and move clockwise into the northeastern Gulf.
-
Salinity:
- Open Gulf: Salinity is about 36 parts per thousand, similar to the North Atlantic.
- Coastal Waters: Varies significantly due to river outflows, especially the Mississippi River, where salinity can drop to 14 to 20 parts per thousand.
-
Temperature:
- Surface Temperatures: In February, range from 64°F (18°C) in the north to 76°F (24°C) off the Yucatán coast. Summer temperatures can reach 90°F (32°C).
- Bottom Temperatures: As low as 43°F (6°C) near the Yucatán Channel.
Environmental and Economic Implications
The hydrological characteristics of the Gulf influence weather patterns, marine ecosystems, and the distribution of pollutants. Understanding these patterns is vital for managing fisheries, predicting harmful algal blooms, and responding to oil spills.
Relevance for LGBTQ+ Tourism
For LGBTQ+ travelers, awareness of the Gulf’s hydrology can enrich their experiences. For example, knowing about the currents and water temperatures can inform choices about swimming, diving, and boating. Gaymexico.net can help you find eco-friendly tour operators who respect and protect the marine environment.
7. What is the Climate Like in the Gulf of Mexico?
The climate in the Gulf of Mexico region ranges from tropical to subtropical. The area is known for its warm, humid summers and mild winters.
Detailed Climate Characteristics
-
Temperature:
- Summer: High temperatures and humidity, with average temperatures around 90°F (32°C).
- Winter: Mild temperatures, with averages ranging from 60°F to 70°F (15°C to 21°C).
-
Rainfall:
- Distribution: Rainfall is abundant throughout the year, with higher amounts during the summer months.
- Regional Variations: Some areas receive over 60 inches of rain annually.
-
Hurricanes:
- Season: June 1 to November 30, with peak activity in August and September.
- Impact: Can cause significant damage and disruption, with major storms occurring frequently.
Impact on Ecosystems and Human Activities
The Gulf’s climate supports diverse ecosystems, including coral reefs, mangrove forests, and coastal wetlands. However, climate change is impacting these ecosystems through sea-level rise, ocean acidification, and more intense storms.
How This Informs LGBTQ+ Travel
For LGBTQ+ travelers planning a visit, understanding the Gulf’s climate is essential. Travelers should be prepared for hot and humid conditions in the summer and be aware of the hurricane season. Gaymexico.net provides up-to-date weather information and safety tips to help you plan accordingly.
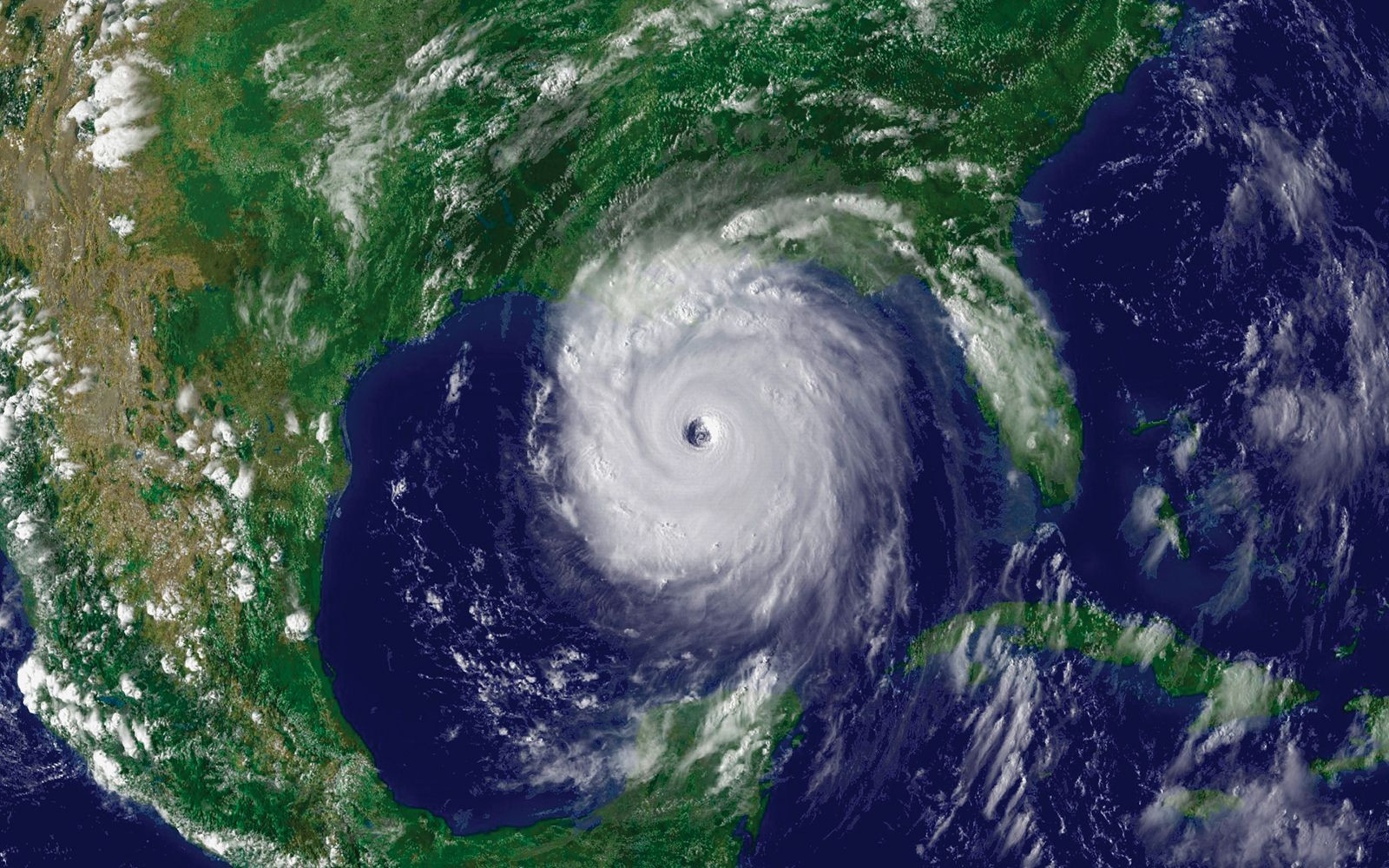 Satellite image of Hurricane Katrina, showing its massive scale and potential for destruction.
Satellite image of Hurricane Katrina, showing its massive scale and potential for destruction.
8. What Role Did European Exploration Play in Shaping the Gulf of Mexico?
European exploration significantly shaped the Gulf of Mexico, beginning with Christopher Columbus’s initial contact in 1492. Spanish explorers subsequently charted the region, establishing towns, silver mines, and missions.
Key Historical Developments
- Early Exploration: Christopher Columbus’s voyages marked the beginning of European interaction with the Gulf.
- Spanish Influence: Spanish explorers mapped the Gulf, establishing settlements and exploiting resources.
- Cultural Exchange: Interactions between Europeans and Native Americans led to cultural and demographic changes.
Long-Term Impacts
European exploration had profound and lasting impacts on the Gulf Coast:
- Colonial Legacy: The establishment of Spanish colonies shaped the region’s culture, language, and architecture.
- Economic Transformations: The extraction of resources and the development of trade networks transformed the Gulf’s economy.
- Demographic Shifts: The introduction of new diseases and the enslavement of indigenous populations led to significant demographic changes.
Implications for LGBTQ+ Travelers
For LGBTQ+ travelers, understanding the history of European exploration can provide a deeper appreciation for the cultural diversity of the Gulf Coast. Many cities in Mexico, such as Veracruz and Campeche, boast well-preserved colonial architecture and vibrant cultural traditions. Gaymexico.net offers insights into the historical and cultural attractions of these destinations, allowing you to connect with the past while enjoying a welcoming and inclusive environment.
9. What Types of Plants and Animals Inhabit the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is home to a diverse array of plant and animal species. The shores are major habitats for waterfowl and shorebirds, while the waters contain huge populations of fish.
Key Species and Habitats
-
Birds:
- Waterfowl and Shorebirds: Abundant along the coasts.
- Seabirds: Colonies of noddies, boobies, and pelicans winter along the coasts of Mexico and Cuba.
-
Marine Mammals:
- Caribbean Manatee: A significant but diminishing species.
-
Fish:
- Commercial Species: Shrimps, flounder, red snappers, mullet, oysters, and crabs are economically important.
- Menhaden: Used to produce fish protein concentrate for animal feeds.
Ecological Importance
The Gulf’s diverse ecosystems support a wealth of marine life, contributing to the region’s ecological and economic health. Coastal wetlands serve as nurseries for many fish species, while coral reefs provide habitat for countless invertebrates and fish.
Threats to Biodiversity
Despite its richness, the Gulf’s biodiversity faces several threats:
- Habitat Destruction: Coastal development, pollution, and destructive fishing practices degrade habitats.
- Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices deplete fish populations.
- Pollution: Oil spills, agricultural runoff, and industrial waste contaminate the water and harm marine life.
How This Relates to LGBTQ+ Tourism
For LGBTQ+ travelers, understanding the Gulf’s biodiversity can enrich their travel experiences. Ecotourism opportunities abound, from bird watching in coastal wetlands to diving in coral reefs. Gaymexico.net can help you find eco-friendly tour operators who promote sustainable practices and support local conservation efforts. By choosing responsible tourism options, you can help protect the Gulf’s natural heritage for future generations.
10. What is the “Gulf of America” Controversy?
In recent years, there has been a controversy surrounding the name of the Gulf of Mexico. In 2025, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names (BGN) adopted the name “Gulf of America” for use by U.S. federal agencies, following an executive order.
Background of the Controversy
- Executive Order: The change was initiated by a U.S. presidential executive order.
- Official Adoption: The U.S. Board on Geographic Names (BGN) officially adopted the new name for use by U.S. federal agencies.
Reactions and Opposition
The name change sparked significant controversy and opposition:
- Mexico’s Response: The Mexican government strongly protested the name change, viewing it as a challenge to their sovereignty and cultural heritage. According to a report by the Associated Press in May 2025, Mexico even sued Google for labeling the Gulf as “Gulf of America” on its maps.
- Public Opinion: Many people in both the United States and Mexico expressed confusion and disapproval of the change.
Current Status
As of late 2025, the situation remains contested:
- Official Use: The name “Gulf of America” is officially used by U.S. federal agencies.
- Widespread Resistance: However, the name “Gulf of Mexico” remains widely used in everyday language, academic circles, and international contexts.
Relevance to LGBTQ+ Community and Gaymexico.net
This controversy highlights the importance of cultural sensitivity and respect for national identity. For LGBTQ+ travelers, it serves as a reminder to be mindful of local customs and perspectives when visiting Mexico. Gaymexico.net is committed to providing respectful and accurate information about Mexico, including its geography, culture, and current events. By staying informed and culturally aware, LGBTQ+ travelers can foster positive interactions and contribute to a welcoming and inclusive environment.
FAQ About the Gulf Of Mexico
What is the Gulf of Mexico and why is it important?
The Gulf of Mexico is a large body of water bordered by the U.S., Mexico, and Cuba. It’s important for its biodiversity, economic resources, and role in weather patterns.
How deep is the Gulf of Mexico?
The deepest point is the Sigsbee Deep, at approximately 17,070 feet (5,203 meters).
What countries border the Gulf of Mexico?
The United States, Mexico, and Cuba border the Gulf of Mexico.
What are the major industries in the Gulf of Mexico region?
Key industries include fishing, tourism, and oil and gas extraction.
What kind of marine life can be found in the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf is home to diverse marine life, including fish, shrimp, dolphins, and sea turtles.
What is the climate like around the Gulf of Mexico?
The climate ranges from tropical to subtropical, with warm summers and mild winters.
How does the Gulf of Mexico affect weather patterns?
The Gulf influences regional weather, including hurricane formation and rainfall patterns.
Are there any environmental concerns related to the Gulf of Mexico?
Yes, concerns include oil spills, pollution, and habitat destruction.
What is the history of exploration in the Gulf of Mexico?
European exploration began in the 15th century, with Spanish explorers playing a key role.
Why is it sometimes referred to as the “Gulf of America”?
The name “Gulf of America” is a recent and controversial term, primarily used by U.S. federal agencies following an executive order, but “Gulf of Mexico” remains the widely accepted name.
Explore LGBTQ+ Mexico with Gaymexico.net
Ready to discover the beauty and diversity of Mexico? Visit Gaymexico.net for the latest travel guides, event listings, and community resources. Whether you’re planning a relaxing beach vacation or an adventurous cultural tour, Gaymexico.net has everything you need to make your trip safe, enjoyable, and unforgettable.
Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States
Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177
Website: gaymexico.net
Explore Mexico with confidence and pride. Your adventure awaits!
