Are you curious about the Mexican immigrant presence in the United States? Gaymexico.net offers insights into the number of Mexican immigrants in the U.S., their contributions, and the cultural connections that enrich both nations, especially within the LGBTQ+ community. Discover the trends, statistics, and stories behind this significant population, and explore resources for LGBTQ+ travelers and residents alike. Explore the cultural impact, immigration patterns, and societal contributions.
1. Understanding the Mexican Immigrant Population in the U.S.
The number of Mexican immigrants in the U.S. is a dynamic figure influenced by various factors. In 2022, approximately 10.6 million immigrants living in the U.S. were born in Mexico, constituting about 23% of the total immigrant population. This makes Mexico the leading country of origin for immigrants in the United States. These figures highlight the significant presence and influence of Mexican immigrants in the U.S.
1.1. Key Statistics on Mexican Immigrants
Understanding the demographics of Mexican immigrants involves looking at several key statistics. These figures provide a comprehensive view of their presence, distribution, and impact within the U.S. population.
| Statistic | Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Total Mexican Immigrants (2022) | 10.6 million | Represents 23% of all immigrants in the U.S., making Mexico the top country of origin. |
| Share of Total U.S. Population | Approximately 3% | Indicates the proportion of Mexican immigrants relative to the entire U.S. population. |
| Primary States of Residence | California, Texas | These states have the highest concentrations of Mexican immigrants due to geographic proximity and historical ties. |
| English Proficiency | Varies | While many Mexican immigrants are proficient in English, a significant portion primarily speaks Spanish. |
| Labor Force Participation | High | Mexican immigrants contribute significantly to the U.S. labor force, particularly in sectors like agriculture, construction, and hospitality. |
| Educational Attainment | Diverse | Educational levels vary widely, with some having advanced degrees and others working to improve their educational opportunities. |
| Legal Status | Diverse | Includes naturalized citizens, lawful permanent residents, temporary residents, and unauthorized immigrants, each facing different challenges and opportunities. |
| Remittances to Mexico | Significant | Mexican immigrants send billions of dollars in remittances to Mexico annually, supporting families and contributing to the Mexican economy. |
| LGBTQ+ Representation | Growing | A vibrant and growing LGBTQ+ community exists within the Mexican immigrant population, contributing to cultural diversity and advocacy for LGBTQ+ rights. |
| Cultural Contributions | Extensive | Mexican immigrants enrich American culture through cuisine, music, art, and traditions, fostering cross-cultural understanding and appreciation. |
1.2. Historical Trends in Mexican Immigration
Mexican immigration to the U.S. has evolved significantly over the decades. Before 1965, U.S. immigration laws favored European immigrants. However, the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965 opened doors for immigrants from Latin America and Asia. Since then, Mexican immigration has seen several distinct phases:
- Early 20th Century: Initial waves of Mexican immigrants came to the U.S. to fill labor shortages, particularly in agriculture and mining.
- Mid-20th Century (Bracero Program): The Bracero Program (1942-1964) brought Mexican laborers to the U.S. on temporary contracts, primarily for agricultural work.
- Late 20th Century: Increased immigration due to economic disparities and political instability in Mexico.
- 21st Century: Fluctuations in immigration rates, with a slowdown after 2007 due to the Great Recession and increased border enforcement.
 Mexican immigrants celebrating in the US
Mexican immigrants celebrating in the US
1.3. Factors Influencing Mexican Immigration
Several factors drive Mexican immigration to the U.S.:
- Economic Opportunities: The prospect of higher wages and better job opportunities in the U.S. attracts many Mexicans.
- Family Reunification: Many Mexicans immigrate to join family members already living in the U.S.
- Political and Social Factors: Political instability, violence, and lack of opportunities in Mexico can push individuals to seek a better life in the U.S.
- Environmental Factors: Climate change and environmental degradation in certain regions of Mexico can also contribute to migration.
2. Geographical Distribution of Mexican Immigrants in the U.S.
Mexican immigrants are not evenly distributed across the United States. Certain states and metropolitan areas have significantly larger Mexican immigrant populations than others.
2.1. Top States with Mexican Immigrant Populations
As of 2022, the top states with the largest Mexican immigrant populations are:
- California: Home to about 10.4 million immigrants, with a significant portion being of Mexican origin.
 Mexican culture in California
Mexican culture in California - Texas: With approximately 5.2 million immigrants, Texas has a substantial Mexican immigrant community due to its border with Mexico and strong economic ties.
- Illinois: Illinois has a notable Mexican immigrant population, particularly in the Chicago metropolitan area.
- Arizona: Due to its proximity to Mexico, Arizona is home to a significant number of Mexican immigrants.
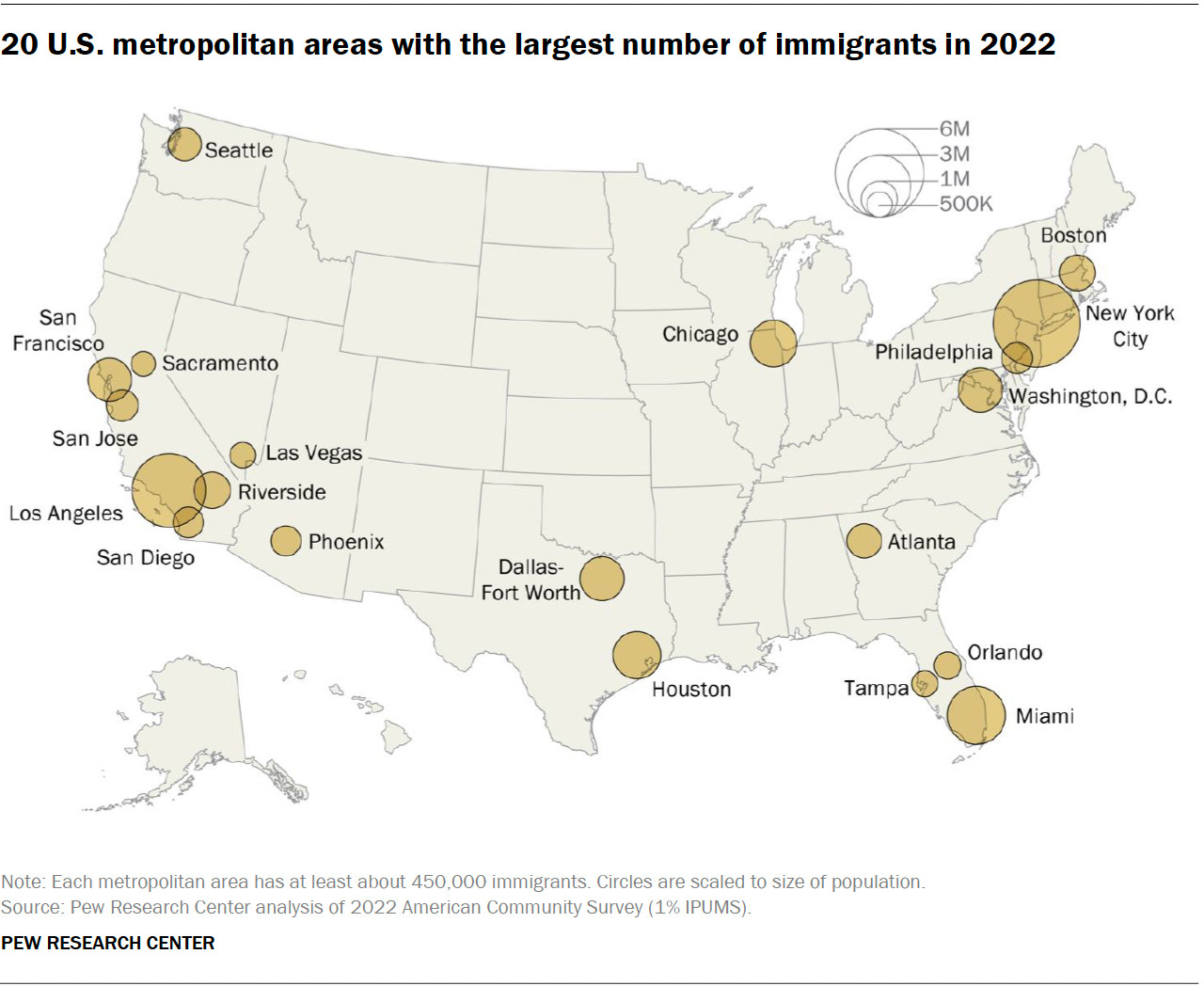
2.2. Metropolitan Areas with Large Mexican Communities
Major metropolitan areas with large Mexican immigrant communities include:
- Los Angeles-Long Beach-Anaheim, CA: This area has one of the largest concentrations of Mexican immigrants in the U.S., fostering a rich cultural environment. Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States. Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177. Website: gaymexico.net.
- Chicago-Naperville-Elgin, IL-IN-WI: The Chicago metropolitan area boasts a large and vibrant Mexican community, contributing to the city’s diverse culture.
- Houston-The Woodlands-Sugar Land, TX: Houston’s Mexican immigrant population is substantial, reflecting the city’s strong economic ties with Mexico.
2.3. Factors Influencing Geographical Distribution
The geographical distribution of Mexican immigrants is influenced by:
- Proximity to Mexico: States bordering Mexico, like California, Texas, and Arizona, naturally attract larger Mexican immigrant populations.
- Economic Opportunities: Metropolitan areas with strong economies and diverse job markets, such as Los Angeles and Chicago, offer more opportunities for Mexican immigrants.
- Established Communities: Areas with existing Mexican communities provide a sense of familiarity, cultural support, and social networks, making them attractive destinations for new immigrants.
3. Legal Status and Pathways to Citizenship
The legal status of Mexican immigrants in the U.S. is diverse, ranging from naturalized citizens to unauthorized immigrants. Understanding the different legal categories and pathways to citizenship is essential.
3.1. Categories of Legal Status
Mexican immigrants in the U.S. fall into several legal categories:
- Naturalized Citizens: Mexican immigrants who have completed the naturalization process and become U.S. citizens.
- Lawful Permanent Residents (Green Card Holders): Individuals who have been granted the right to live and work permanently in the U.S.
- Temporary Residents: Those with temporary visas for work, study, or other specific purposes.
- Unauthorized Immigrants: Individuals who have entered the U.S. without legal permission or have overstayed their visas.
3.2. Pathways to Citizenship
Mexican immigrants can pursue U.S. citizenship through various pathways:
- Naturalization: After meeting certain requirements, such as residency, good moral character, and passing a civics test, lawful permanent residents can apply for naturalization.
- Family-Based Immigration: U.S. citizens and lawful permanent residents can sponsor eligible family members for immigration.
- Employment-Based Immigration: Mexican immigrants with specific skills or job offers can obtain green cards through employment-based visas.
- Asylum and Refugee Status: Individuals fleeing persecution in Mexico may be eligible for asylum or refugee status in the U.S.
3.3. Challenges Faced by Unauthorized Immigrants
Unauthorized Mexican immigrants face numerous challenges:
- Limited Access to Services: They often have limited access to healthcare, education, and other essential services.
- Risk of Deportation: Living without legal status puts them at constant risk of deportation.
- Exploitation: They are vulnerable to exploitation in the workplace due to their lack of legal protections.
- Social Isolation: The fear of detection and deportation can lead to social isolation and mental health issues.
4. Economic Contributions of Mexican Immigrants
Mexican immigrants make significant economic contributions to the U.S. in various sectors.
4.1. Labor Force Participation
Mexican immigrants participate in the U.S. labor force at high rates, filling essential roles in various industries.
- Agriculture: They are heavily involved in agricultural work, contributing to the production of fruits, vegetables, and other crops.
- Construction: Many work in the construction industry, building homes, infrastructure, and commercial properties.
- Hospitality: Mexican immigrants are a significant part of the hospitality sector, working in restaurants, hotels, and other service-oriented businesses.
4.2. Entrepreneurship
Many Mexican immigrants start their own businesses, contributing to job creation and economic growth.
- Small Businesses: They often own and operate small businesses, such as restaurants, grocery stores, and landscaping services.
- Innovation: Some Mexican immigrants are innovators and entrepreneurs, developing new products and services that benefit the U.S. economy.
4.3. Remittances to Mexico
Mexican immigrants send billions of dollars in remittances to Mexico annually, providing crucial support to their families and communities.
- Economic Support: Remittances help families cover basic needs, such as food, healthcare, and education.
- Community Development: Remittances also contribute to community development projects, improving infrastructure and living standards in Mexico.
5. Educational Attainment and Language Proficiency
The educational attainment and language proficiency of Mexican immigrants vary widely, reflecting diverse backgrounds and experiences.
5.1. Educational Levels
Educational levels among Mexican immigrants range from those with advanced degrees to those with limited formal education.
- High School Completion: While some Mexican immigrants have not completed high school, many are working to improve their educational opportunities through adult education programs and community colleges.
- Higher Education: A growing number of Mexican immigrants are pursuing higher education, earning bachelor’s degrees and advanced degrees in various fields.
5.2. English Proficiency
English proficiency among Mexican immigrants varies, with many becoming proficient in English over time.
- Language Acquisition: Immersion in an English-speaking environment, language classes, and educational opportunities contribute to improved English proficiency.
- Bilingualism: Many Mexican immigrants maintain proficiency in both Spanish and English, offering valuable bilingual skills in the U.S. workforce.
5.3. Impact of Education and Language on Opportunities
Education and language proficiency significantly impact the opportunities available to Mexican immigrants.
- Employment: Higher levels of education and English proficiency increase access to better-paying jobs and career advancement opportunities.
- Social Integration: Language skills facilitate social integration and participation in community life.
- Civic Engagement: Education and language proficiency enable Mexican immigrants to engage more effectively in civic activities and advocate for their rights.
6. Cultural Contributions and Community Life
Mexican immigrants enrich American culture through their traditions, cuisine, music, and art, fostering cross-cultural understanding and appreciation.
6.1. Influence on American Culture
Mexican culture has had a profound influence on American society:
- Cuisine: Mexican cuisine, such as tacos, burritos, and enchiladas, is widely popular in the U.S., with Mexican restaurants found in nearly every city.
- Music and Dance: Mexican music genres, such as mariachi and banda, are enjoyed by people of all backgrounds, and traditional Mexican dances are performed at cultural events.
- Art and Literature: Mexican artists and writers have made significant contributions to American art and literature, exploring themes of identity, immigration, and cultural heritage.
6.2. Community Organizations and Support Networks
Mexican immigrant communities often establish organizations and networks to support their members.
- Cultural Centers: These centers provide a space for cultural expression, language classes, and community events.
- Advocacy Groups: Organizations advocate for the rights of Mexican immigrants, addressing issues such as immigration reform, education, and healthcare.
- Religious Institutions: Churches and other religious institutions play a vital role in providing spiritual guidance and community support.
6.3. Preserving Cultural Heritage
Mexican immigrants often make efforts to preserve their cultural heritage while integrating into American society.
- Language Maintenance: Many families prioritize teaching their children Spanish, ensuring that they maintain a connection to their cultural roots.
- Traditional Celebrations: Mexican holidays and festivals, such as Día de los Muertos and Cinco de Mayo, are celebrated with enthusiasm, preserving cultural traditions and sharing them with the wider community.
7. Challenges and Opportunities for LGBTQ+ Mexican Immigrants
LGBTQ+ Mexican immigrants face unique challenges and opportunities as they navigate their identities in a new country.
7.1. Overlapping Identities
LGBTQ+ Mexican immigrants often grapple with the intersection of their sexual orientation or gender identity, their cultural background, and their immigration status.
- Cultural Acceptance: They may face challenges related to cultural acceptance of LGBTQ+ identities within their families and communities.
- Language Barriers: Language barriers can make it difficult to access LGBTQ+-specific resources and support services.
7.2. Resources and Support
Various resources and support networks are available to LGBTQ+ Mexican immigrants.
- LGBTQ+ Centers: These centers provide a safe space, counseling, and support groups for LGBTQ+ individuals.
- Legal Services: Organizations offer legal assistance to LGBTQ+ immigrants facing discrimination or immigration-related challenges.
- Community Events: LGBTQ+ cultural events and festivals celebrate diversity and provide a sense of community.
7.3. Advocacy and Activism
LGBTQ+ Mexican immigrants are actively involved in advocacy and activism, working to promote LGBTQ+ rights and immigration reform.
- Visibility: By sharing their stories and experiences, they raise awareness and challenge stereotypes.
- Policy Change: They advocate for policies that protect LGBTQ+ immigrants from discrimination and ensure equal rights.
8. Future Trends in Mexican Immigration
Mexican immigration to the U.S. is likely to continue evolving, influenced by economic, political, and social factors.
8.1. Potential Changes in Immigration Patterns
Several factors could influence future immigration patterns:
- Economic Conditions: Economic growth in Mexico could reduce the incentive for migration, while economic downturns could increase it.
- U.S. Immigration Policies: Changes in U.S. immigration policies could significantly impact the number of Mexican immigrants entering the country.
- Political Stability: Political instability or violence in Mexico could drive more people to seek refuge in the U.S.
8.2. Impact of Policy Changes
Policy changes in both the U.S. and Mexico could have significant implications for Mexican immigration.
- Immigration Reform: Comprehensive immigration reform in the U.S. could provide a pathway to citizenship for millions of unauthorized immigrants, including Mexicans.
- Border Enforcement: Increased border enforcement could deter unauthorized immigration but also lead to more dangerous crossing attempts.
- Economic Development Initiatives: Economic development initiatives in Mexico could create more opportunities for Mexicans, reducing the need to migrate.
8.3. Long-Term Integration
The long-term integration of Mexican immigrants into American society will depend on various factors.
- Education and Employment: Providing access to education and employment opportunities is crucial for successful integration.
- Social Inclusion: Creating inclusive communities that welcome and support Mexican immigrants is essential.
- Civic Engagement: Encouraging civic engagement and participation in democratic processes can empower Mexican immigrants and strengthen American society.
9. Resources for Mexican Immigrants and Their Advocates
Numerous resources are available to support Mexican immigrants and their advocates.
9.1. Government Agencies
Several government agencies provide services and information to immigrants.
- U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS): Provides information on immigration benefits, such as green cards and citizenship.
- U.S. Department of Labor: Offers resources for workers, including information on workplace rights and job training programs.
9.2. Non-Profit Organizations
Non-profit organizations play a crucial role in supporting Mexican immigrants.
- National Council of La Raza (UnidosUS): Advocates for the rights of Hispanic Americans, including Mexican immigrants.
- Mexican American Legal Defense and Educational Fund (MALDEF): Provides legal assistance and advocacy on behalf of Mexican Americans.
9.3. Community Centers
Community centers offer a range of services and support to Mexican immigrants.
- Language Classes: Provide English classes to help immigrants improve their language skills.
- Job Training: Offer job training programs to help immigrants find employment.
- Legal Assistance: Provide legal assistance on immigration and other legal matters.
10. Addressing Common Misconceptions
Addressing common misconceptions about Mexican immigrants is essential for fostering understanding and dispelling stereotypes.
10.1. Economic Impact
Misconception: Mexican immigrants are a drain on the U.S. economy.
Reality: Mexican immigrants contribute significantly to the U.S. economy through their labor, entrepreneurship, and tax payments.
10.2. Crime Rates
Misconception: Mexican immigrants are more likely to commit crimes.
Reality: Studies have shown that immigrants, including Mexicans, are less likely to commit crimes than native-born Americans.
10.3. Use of Public Benefits
Misconception: Mexican immigrants overuse public benefits.
Reality: Many Mexican immigrants are ineligible for public benefits due to their immigration status, and those who are eligible often use them at lower rates than native-born Americans.
FAQ: Understanding Mexican Immigration to the U.S.
1. How many Mexican immigrants are currently living in the U.S.?
As of 2022, approximately 10.6 million Mexican immigrants reside in the U.S., making up about 23% of the total immigrant population.
2. Which U.S. states have the largest Mexican immigrant populations?
California and Texas have the largest Mexican immigrant populations, followed by Illinois and Arizona.
3. What factors drive Mexican immigration to the U.S.?
Economic opportunities, family reunification, and political and social factors in Mexico drive immigration to the U.S.
4. What is the legal status of most Mexican immigrants in the U.S.?
The legal status varies, including naturalized citizens, lawful permanent residents, temporary residents, and unauthorized immigrants.
5. How do Mexican immigrants contribute to the U.S. economy?
Mexican immigrants contribute through their labor in various sectors, entrepreneurship, and remittances sent to Mexico.
6. What challenges do unauthorized Mexican immigrants face in the U.S.?
Unauthorized immigrants face limited access to services, the risk of deportation, and potential exploitation.
7. How can Mexican immigrants become U.S. citizens?
Mexican immigrants can become citizens through naturalization, family-based immigration, employment-based immigration, or asylum/refugee status.
8. What are some common misconceptions about Mexican immigrants?
Common misconceptions include the belief that they drain the economy, commit more crimes, and overuse public benefits, all of which are untrue.
9. What resources are available to support Mexican immigrants in the U.S.?
Resources include government agencies like USCIS, non-profit organizations, and community centers offering language classes, job training, and legal assistance.
10. How does gaymexico.net support the LGBTQ+ Mexican immigrant community?
Gaymexico.net provides a platform for LGBTQ+ Mexican immigrants to find information, connect with others, and access resources relevant to their unique experiences.
Understanding the complexities surrounding Mexican immigration is crucial for fostering informed discussions and creating inclusive communities. By exploring the statistics, history, and personal stories, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the contributions and challenges faced by Mexican immigrants in the U.S. Are you an LGBTQ+ individual interested in exploring Mexico? Visit gaymexico.net to discover LGBTQ+-friendly destinations, events, and resources that will help you plan your visit and connect with the local community. Discover cultural insights and travel tips tailored for the LGBTQ+ community. Learn about gay-friendly cities in Mexico and discover LGBTQ+ events and festivals. Visit gaymexico.net today for more information.