Are Pineapples Grown In Mexico and do you want to know more about this delicious tropical fruit? Absolutely! As gaymexico.net, we are here to guide you through the vibrant world of pineapple cultivation in Mexico, a country renowned for its rich agricultural heritage and LGBTQ+ friendly atmosphere. Discover the best regions, growing techniques, and the cultural significance of pineapples in Mexico.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction: The Sweet Story of Pineapples in Mexico
- A Brief History
- Why Mexico?
2. Prime Pineapple Growing Regions in Mexico - Veracruz: The Pineapple Paradise
- Oaxaca: A Growing Force
- Tabasco: Tropical Delights
- Other Notable Regions
3. Ideal Growing Conditions for Pineapples - Climate
- Soil
- Water
4. Cultivating Pineapples: A Step-by-Step Guide - Selecting the Right Variety
- Preparing the Soil
- Planting Techniques
- Caring for Your Pineapple Plants
- Harvesting Your Pineapple
5. Different Varieties of Pineapples Grown in Mexico - Smooth Cayenne
- Esmeralda
- MD-2
- Champaka
6. The Economic Impact of Pineapple Farming in Mexico - Local Employment
- Export Markets
- Sustainable Farming Practices
7. Challenges Faced by Pineapple Farmers - Pests and Diseases
- Climate Change
- Market Fluctuations
8. Pineapples in Mexican Culture and Cuisine - Traditional Dishes
- Festivals and Celebrations
- Health Benefits
9. Sustainable and Organic Pineapple Farming in Mexico - Benefits of Organic Farming
- Challenges of Organic Farming
- Government Support and Initiatives
10. Agritourism and Pineapple Tours - Experiencing Pineapple Farms
- Responsible Tourism
11. The Future of Pineapple Growing in Mexico - Technological Advancements
- Market Trends
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Pineapple Cultivation in Mexico - Is pineapple farming a sustainable practice in Mexico?
- What are the peak seasons for pineapple harvests in Mexico?
- How can I start my own small-scale pineapple farm in Mexico?
- Are there any government subsidies for pineapple farmers in Mexico?
- What are the common pests and diseases affecting pineapple crops in Mexico?
- How do Mexican pineapple farmers use technology to improve yields?
- Can I visit a pineapple farm in Mexico as a tourist?
- What are the best pineapple varieties to grow in Mexico for export?
- How does climate change affect pineapple cultivation in Mexico?
- What role does organic farming play in the Mexican pineapple industry?
13. Conclusion: Savoring Mexico’s Pineapple Bounty
1. Introduction: The Sweet Story of Pineapples in Mexico
Are pineapples grown in Mexico? Indeed, Mexico offers an ideal climate for pineapple cultivation, making it a significant player in the global pineapple market and a sweet spot for LGBTQ+ travelers exploring its agricultural landscapes. Pineapple production is a cornerstone of Mexican agriculture, contributing significantly to the nation’s economy and culinary traditions. Let’s delve into the captivating story of pineapples in Mexico. With tropical agriculture insights and exotic fruit facts, you’ll gain a deeper appreciation for this delicious fruit and its cultural importance, perfect for planning your next adventure with gaymexico.net.
A Brief History
The pineapple, scientifically known as Ananas comosus, is native to South America. It spread throughout the tropics over centuries. The Spanish introduced pineapples to Mexico in the 16th century. The fruit quickly adapted to the Mexican climate. It became an integral part of the country’s agricultural landscape.
Why Mexico?
Mexico’s geographical location provides a perfect environment for pineapple cultivation. The tropical and subtropical climates, combined with fertile soils and adequate rainfall, create ideal growing conditions. Additionally, Mexico’s agricultural expertise and infrastructure support large-scale pineapple farming.
2. Prime Pineapple Growing Regions in Mexico
Which regions in Mexico are best suited for pineapple cultivation? Several states are renowned for their pineapple production, each offering unique advantages and contributing to the overall success of the industry.
Veracruz: The Pineapple Paradise
Veracruz stands out as the primary pineapple-growing region in Mexico. Its tropical climate, fertile lands, and well-established agricultural practices make it a hub for pineapple cultivation. The state’s infrastructure supports extensive pineapple farming operations.
Oaxaca: A Growing Force
Oaxaca is another significant pineapple-producing state, benefiting from a favorable climate and dedicated farming communities. The region’s commitment to sustainable agriculture enhances the quality and yield of its pineapple crops.
Tabasco: Tropical Delights
Tabasco’s lush tropical environment makes it ideal for pineapple cultivation. The state’s abundant rainfall and fertile soils contribute to the production of sweet and juicy pineapples, adding to Mexico’s reputation for tropical fruit excellence.
Other Notable Regions
Other Mexican states, including Chiapas and Campeche, also contribute to pineapple production, diversifying the country’s agricultural output. These regions benefit from local farming expertise and regional agricultural support.
3. Ideal Growing Conditions for Pineapples
What conditions are necessary for growing pineapples successfully in Mexico? The right climate, soil, and water management are crucial for optimal pineapple growth and yield.
Climate
Pineapples thrive in tropical and subtropical climates, requiring temperatures between 20°C and 30°C (68°F and 86°F). Mexico’s diverse climate zones provide suitable conditions for pineapple cultivation in various regions.
Soil
Well-drained, sandy loam soils are ideal for pineapple cultivation. These soils prevent waterlogging. They provide the necessary nutrients for healthy plant growth. Mexican soils in key pineapple-growing regions often meet these requirements.
Water
Pineapples require adequate rainfall or irrigation to thrive. Consistent moisture levels are essential, especially during the early stages of plant growth. Mexican farmers employ various irrigation techniques to ensure optimal water supply for their pineapple crops.
4. Cultivating Pineapples: A Step-by-Step Guide
How are pineapples cultivated in Mexico? From selecting the right variety to harvesting the fruit, each step requires careful attention and expertise.
Selecting the Right Variety
Choosing the appropriate pineapple variety is the first step in successful cultivation. Different varieties are suited to different climates and soil types. Farmers consider factors such as fruit size, taste, and disease resistance when selecting varieties.
Preparing the Soil
Proper soil preparation is essential for healthy pineapple growth. Farmers till the soil, add organic matter, and ensure good drainage to create an optimal growing environment. Soil testing helps determine the necessary amendments for nutrient balance.
Planting Techniques
Pineapples are typically planted using crowns, slips, or suckers. These are planted in rows or beds, with adequate spacing to allow for proper growth and air circulation. Mexican farmers use traditional and modern planting techniques to maximize yields.
Caring for Your Pineapple Plants
Caring for pineapple plants involves regular watering, fertilization, and weed control. Farmers monitor their crops for pests and diseases. They implement appropriate control measures to protect their plants.
Harvesting Your Pineapple
Pineapples are typically harvested when they reach full maturity, indicated by their color, size, and aroma. Farmers carefully harvest the fruits by hand, ensuring minimal damage. Post-harvest handling includes cleaning, sorting, and packaging for market distribution.
5. Different Varieties of Pineapples Grown in Mexico
What types of pineapples are commonly grown in Mexico? Each variety offers unique characteristics and flavors, catering to different consumer preferences.
Smooth Cayenne
Smooth Cayenne is one of the most widely grown pineapple varieties in Mexico and worldwide. It is prized for its large size, cylindrical shape, and excellent flavor. This variety is popular for both fresh consumption and processing.
Esmeralda
The Esmeralda pineapple is a hybrid variety known for its sweetness, low acidity, and long shelf life. It is increasingly popular in Mexican pineapple farms. It commands premium prices in export markets.
MD-2
MD-2, also known as “Golden Sweet,” is another popular variety recognized for its vibrant yellow flesh, high sugar content, and extended shelf life. It is widely grown in Mexico for export.
Champaka
The Champaka pineapple variety is prized for its aromatic flavor, juicy texture, and unique taste profile. It is grown on a smaller scale in Mexico. It is often sold in local markets.
6. The Economic Impact of Pineapple Farming in Mexico
How does pineapple farming contribute to Mexico’s economy? Pineapple cultivation provides numerous economic benefits, including job creation, export revenue, and support for local communities.
Local Employment
Pineapple farming generates employment opportunities in rural communities, providing livelihoods for farmers, laborers, and support staff. The industry supports thousands of families across Mexico.
Export Markets
Mexico is a significant exporter of pineapples, supplying markets in North America, Europe, and Asia. Pineapple exports contribute substantially to the country’s foreign exchange earnings.
Sustainable Farming Practices
Increasingly, Mexican pineapple farmers are adopting sustainable farming practices. They enhance productivity, protect the environment, and ensure the long-term viability of their operations. These practices include soil conservation, water management, and integrated pest management.
7. Challenges Faced by Pineapple Farmers
What challenges do pineapple farmers in Mexico face? Despite the favorable growing conditions, pineapple farmers encounter various challenges that can impact their yields and profitability.
Pests and Diseases
Pineapple crops are susceptible to various pests and diseases, including mealybugs, mites, and heart rot. These can cause significant damage and reduce yields. Farmers implement integrated pest management strategies to minimize these impacts.
Climate Change
Climate change poses a growing threat to pineapple farming in Mexico, with increased temperatures, altered rainfall patterns, and more frequent extreme weather events. These changes can affect pineapple growth, fruit quality, and overall productivity.
Market Fluctuations
Pineapple prices can fluctuate significantly due to changes in supply and demand, competition from other producing countries, and global economic conditions. Farmers must navigate these market dynamics to remain competitive and profitable.
8. Pineapples in Mexican Culture and Cuisine
How are pineapples used in Mexican culture and cuisine? Pineapples hold a special place in Mexican culture, featuring prominently in traditional dishes, festivals, and celebrations.
Traditional Dishes
Pineapples are used in a variety of Mexican dishes, adding a sweet and tangy flavor to both savory and sweet creations. Popular dishes include tacos al pastor (pork tacos with pineapple), agua de piña (pineapple water), and pineapple salsa.
Festivals and Celebrations
Pineapples are often featured in Mexican festivals and celebrations, symbolizing hospitality, abundance, and good fortune. They are used as decorations, offerings, and ingredients in festive meals.
Health Benefits
Pineapples are rich in vitamins, minerals, and enzymes, offering numerous health benefits. They are a good source of vitamin C, bromelain (an anti-inflammatory enzyme), and antioxidants. Pineapples are believed to aid digestion, boost the immune system, and promote overall health.
9. Sustainable and Organic Pineapple Farming in Mexico
What are the benefits and challenges of sustainable and organic pineapple farming in Mexico? With growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products, sustainable and organic farming practices are gaining traction in Mexico.
Benefits of Organic Farming
Organic pineapple farming avoids synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers. It promotes biodiversity, enhances soil health, and reduces environmental impacts. Organic pineapples often command premium prices.
Challenges of Organic Farming
Organic farming requires more labor, careful management, and adherence to strict certification standards. Pest and disease control can be more challenging without synthetic chemicals.
Government Support and Initiatives
The Mexican government supports sustainable and organic agriculture through various programs, including technical assistance, subsidies, and certification support. These initiatives aim to promote environmentally friendly farming practices and enhance the competitiveness of Mexican agricultural products.
10. Agritourism and Pineapple Tours
Can I visit pineapple farms in Mexico? Agritourism offers unique opportunities to experience pineapple farming firsthand, learn about cultivation practices, and enjoy the natural beauty of the Mexican countryside.
Experiencing Pineapple Farms
Several pineapple farms in Mexico offer tours and activities for visitors, including guided farm tours, pineapple harvesting experiences, and tastings of fresh pineapple products. These tours provide insights into the pineapple industry.
Responsible Tourism
When participating in agritourism activities, it is important to support responsible tourism practices that benefit local communities and protect the environment. This includes respecting local customs, minimizing environmental impacts, and purchasing locally produced goods.
11. The Future of Pineapple Growing in Mexico
What does the future hold for pineapple growing in Mexico? With ongoing research, technological advancements, and a commitment to sustainability, the future of pineapple farming in Mexico looks promising.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements, such as precision farming, drone monitoring, and improved irrigation systems, are enhancing pineapple production efficiency and sustainability. These technologies enable farmers to optimize resource use, reduce waste, and improve yields.
Market Trends
Consumer demand for high-quality, sustainably grown pineapples is increasing, driving innovation and investment in the Mexican pineapple industry. Farmers are adapting to these trends by adopting new varieties, improving post-harvest handling practices, and seeking organic certification.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Pineapple Cultivation in Mexico
Here are some frequently asked questions about pineapple cultivation in Mexico, offering valuable insights for those interested in learning more about this important agricultural sector.
Is pineapple farming a sustainable practice in Mexico?
Yes, increasingly so. Many farmers are adopting sustainable practices like organic farming, water conservation, and integrated pest management to ensure long-term viability and environmental protection.
What are the peak seasons for pineapple harvests in Mexico?
The peak seasons typically fall between March and June, and then again from September to December. However, pineapples can be harvested year-round due to Mexico’s favorable climate.
How can I start my own small-scale pineapple farm in Mexico?
Start by researching ideal locations, soil types, and pineapple varieties suitable for the region. Secure land, prepare the soil, and obtain planting materials. Consider consulting with local agricultural experts for guidance.
Are there any government subsidies for pineapple farmers in Mexico?
Yes, the Mexican government offers various subsidies and support programs for farmers, including those growing pineapples. These programs can include financial assistance, technical support, and training.
What are the common pests and diseases affecting pineapple crops in Mexico?
Common pests include mealybugs and mites, while diseases like heart rot can also affect crops. Implementing integrated pest management strategies and maintaining plant health are crucial for prevention.
How do Mexican pineapple farmers use technology to improve yields?
Farmers use technologies like precision irrigation, drone monitoring for crop health, and advanced soil analysis to optimize growing conditions and improve yields.
Can I visit a pineapple farm in Mexico as a tourist?
Yes, agritourism is growing in Mexico, and many pineapple farms offer tours and experiences for visitors. Check with local tourism boards or online resources to find farms that offer tours.
What are the best pineapple varieties to grow in Mexico for export?
Popular export varieties include Smooth Cayenne, MD-2 (Golden Sweet), and Esmeralda, known for their flavor, size, and shelf life.
How does climate change affect pineapple cultivation in Mexico?
Climate change can lead to increased temperatures, altered rainfall patterns, and more frequent extreme weather events, which can negatively impact pineapple growth and yields. Farmers are adapting by using water-efficient irrigation and selecting climate-resilient varieties.
What role does organic farming play in the Mexican pineapple industry?
Organic farming is gaining importance as consumers demand sustainably grown products. Organic pineapple farms avoid synthetic chemicals, promoting biodiversity and soil health, and often receive premium prices for their produce.
13. Conclusion: Savoring Mexico’s Pineapple Bounty
Are pineapples grown in Mexico? Absolutely, and they represent a significant part of Mexico’s agricultural heritage, culinary traditions, and economic landscape. As you explore Mexico, whether as a member of the LGBTQ+ community or a curious traveler, be sure to savor the sweet taste of Mexican pineapples and appreciate the dedication of the farmers who cultivate them. For more insights into Mexico’s vibrant culture, LGBTQ+ scene, and travel tips, visit gaymexico.net. Discover the best destinations, events, and accommodations that celebrate diversity and inclusion.
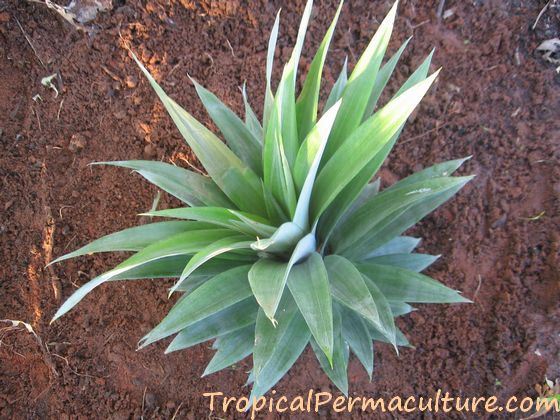 Pineapple top growing.
Pineapple top growing.
A pineapple top growing, illustrating the first step in cultivating this tropical fruit.
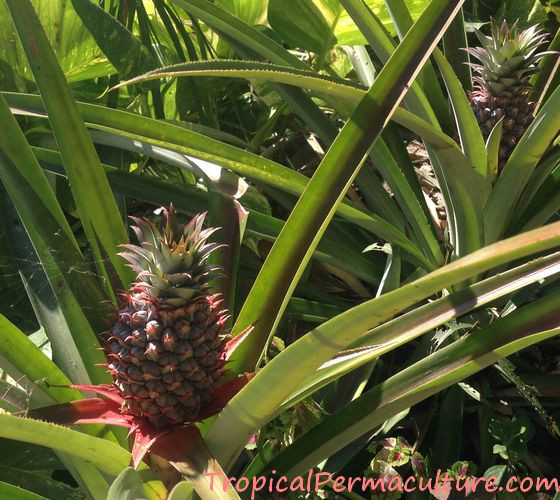 Pineapples growing in the garden.
Pineapples growing in the garden.
Pineapples flourishing in a Mexican garden, reflecting the ideal growing conditions of the region, courtesy of Lisa Preschel from Mexico.
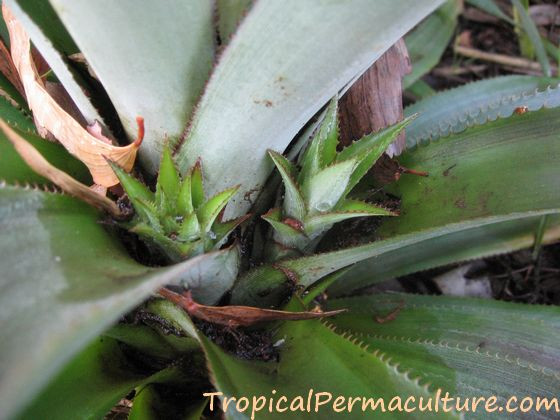 Young pineapple suckers growing
Young pineapple suckers growing
Young pineapple suckers developing, highlighting the propagation methods used in Mexican pineapple farming.
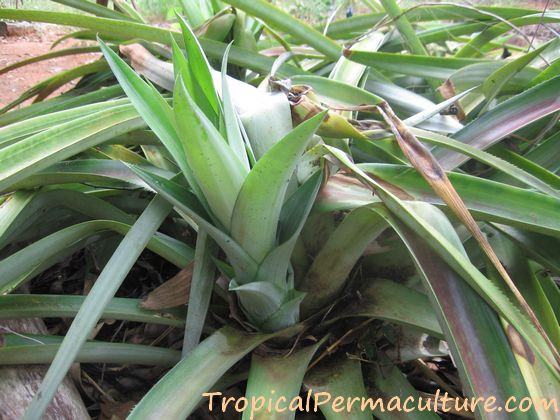 Large pineapple sucker
Large pineapple sucker
A large pineapple sucker ready for planting, showcasing the growth stages in pineapple cultivation.
 Pineapple suckers ready for planting.
Pineapple suckers ready for planting.
Pineapple suckers prepared for planting, illustrating the process of expanding a pineapple crop.
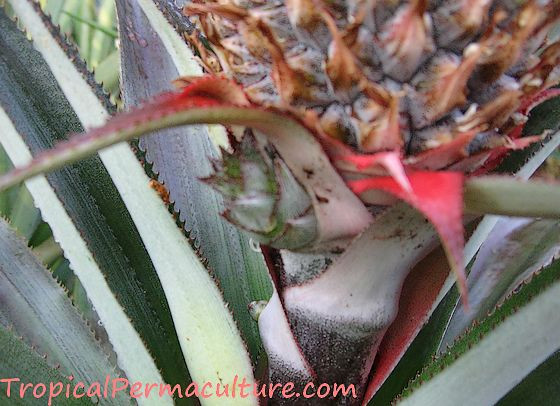 A slip at the base of a pineapple fruit.
A slip at the base of a pineapple fruit.
A slip at the base of a pineapple fruit, demonstrating another propagation method used by Mexican farmers.
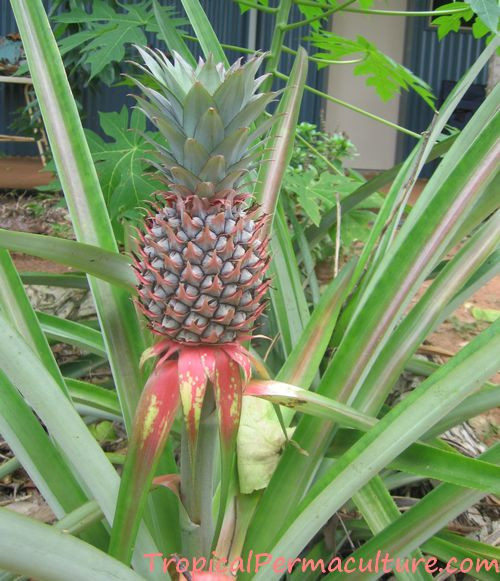 Pineapple growing on long stalk
Pineapple growing on long stalk
Pineapple growing on a long stalk, illustrating the importance of selecting plants with low-growing fruit to prevent sunburn.
 Pineapple flower growing
Pineapple flower growing
A pineapple flower blooming, symbolizing the natural beauty and agricultural richness of Mexico.
Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States
Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177
Website: gaymexico.net