Is The Gulf Of Mexico Fresh Water? No, the Gulf of Mexico is not fresh water; it is a large body of saltwater. Gaymexico.net is your go-to source for navigating the beautiful destinations Mexico has to offer, and understanding the intricacies of its natural wonders. It’s a vital part of the Atlantic Ocean bordered by the United States, Mexico, and Cuba, and is home to many LGBTQ+ friendly cities.
1. What Defines The Gulf Of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is a large body of saltwater, not fresh water, and is an ocean basin nearly surrounded by land, connecting to the Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea. This makes it navigable and crucial for maritime activities, especially for LGBTQ+ travelers exploring coastal regions.
Understanding the Salinity
The salinity of the Gulf of Mexico is one of its defining features. Unlike freshwater bodies, the Gulf has a significant salt content, which supports diverse marine ecosystems. The influx of freshwater from rivers like the Mississippi can slightly reduce salinity in certain areas, but overall, the Gulf remains a saltwater environment.
Geographic Location and Borders
The Gulf of Mexico is bordered by the United States (specifically Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida) to the north, northwest, and northeast, Mexico to the south and southwest, and Cuba and the Caribbean Sea to the southeast. This location makes it a central hub for trade, tourism, and cultural exchange.
Why Salinity Matters
The salinity of the Gulf of Mexico affects its marine life, climate, and human activities. Many species are adapted to live in saltwater, and changes in salinity can impact their survival. The Gulf’s warm, salty waters also play a role in the formation of hurricanes, which can affect coastal communities.
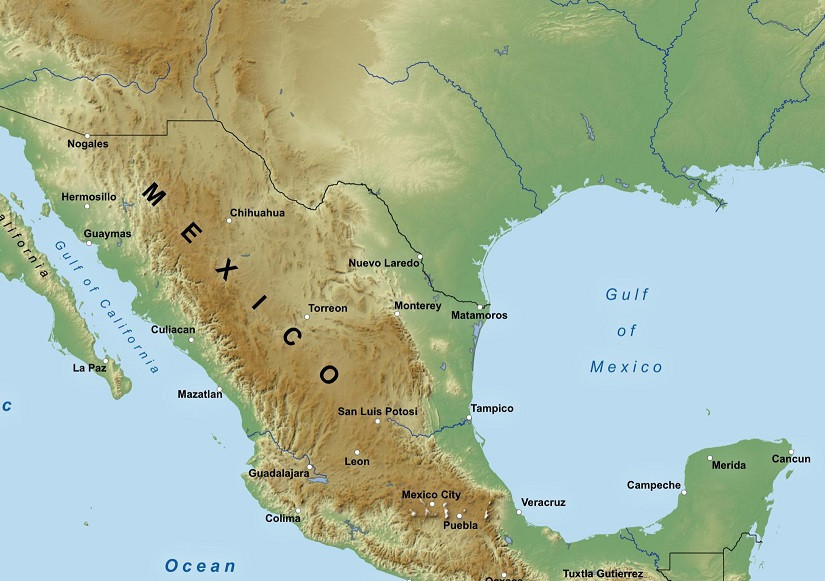 Gulf of Mexico Map
Gulf of Mexico Map
2. What Are The Geographical Characteristics Of The Gulf Of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is an ocean basin with a mostly flat bottom, covering about 615,000 square miles and containing roughly 2,500 quadrillion liters of saltwater. Its geography influences its climate, marine life, and suitability for various activities.
Size and Depth
The Gulf of Mexico is one of the largest bodies of water in the world, spanning a vast area with varying depths. Its deepest point, Sigsbee Deep, reaches approximately 14,383 feet, while most of the Gulf is relatively shallow.
Unique Ocean Basin
As an ocean basin, the Gulf of Mexico is a large area covered with seawater and located below sea level. This unique feature contributes to its distinct characteristics and ecological importance.
Climate Influences
The warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico significantly influence the climate of the surrounding regions. It is a breeding ground for hurricanes, which can impact coastal areas from Texas to Florida. The Gulf Stream, originating from the Gulf, also affects the climate of the eastern United States and western Europe.
Marine Ecosystem
The Gulf of Mexico supports a rich diversity of marine life, including numerous species of fish, sharks, sea turtles, and marine mammals. Its warm waters and diverse habitats make it a crucial area for biodiversity.
3. How Did The Gulf Of Mexico Form?
The Gulf of Mexico likely formed about 300 million years ago due to plate tectonics, causing part of the ocean floor to sink and fill with seawater. This geological history explains its unique shape and characteristics.
Plate Tectonics
The movement of tectonic plates played a significant role in the formation of the Gulf of Mexico. As the Earth’s crust shifted, a portion of the ocean floor gradually subsided, creating a basin that would eventually fill with water.
Filling with Seawater
Over millions of years, the sunken basin filled with seawater, forming the Gulf of Mexico as we know it today. This process involved the gradual accumulation of water from the Atlantic Ocean and surrounding rivers.
Geological Significance
The geological history of the Gulf of Mexico has shaped its physical characteristics, including its depth, shape, and the composition of its seabed. These factors influence the Gulf’s marine ecosystems and its susceptibility to natural disasters like hurricanes and oil spills.
Early Exploration
The Gulf of Mexico has been utilized for centuries as a source of sustenance and resources, predating European contact. Indigenous populations had long relied on the Gulf for their livelihoods. The first documented European exploration was in 1497 by Italian Amerigo Vespucci, followed by other explorers like Francisco Hernández de Córdoba and Pánfilo de Narváez, who often enslaved local people.
4. What Is The History Of Human Interaction With The Gulf Of Mexico?
Humans have interacted with the Gulf of Mexico for centuries, using it for food, navigation, and resources, with increasing pollution from oil drilling and agricultural runoff becoming a significant concern. Balancing resource use with environmental protection is crucial.
Early Uses
For centuries, the Gulf of Mexico has been a vital resource for people living along its coastlines. Indigenous populations relied on it for fishing, transportation, and trade. The Gulf provided essential resources for survival and development.
Population Growth and Pollution
The population along the Gulf Coast surged in the 1950s, leading to increased pollution. Agricultural runoff and industrial waste have had detrimental effects on the Gulf’s ecosystems, impacting marine life and water quality.
Oil Drilling
Oil drilling in the Gulf of Mexico began in 1938, and the region has since become one of the world’s most important offshore petroleum production sites. While it provides a significant portion of the US’s oil supply, it also poses considerable environmental risks.
Major Oil Spills
The Deepwater Horizon explosion in 2010 caused the largest oil spill in history, releasing about 4.9 million barrels of oil into the Gulf. This disaster had devastating effects on marine life, wildlife habitats, and the fishing industry. Recovery efforts are still ongoing, and the incident underscores the need for stricter regulations and safety measures in offshore drilling.
Current Environmental Issues
Today, the Gulf of Mexico faces numerous environmental challenges, including red tide algae blooms, high levels of microplastics, and the presence of thousands of abandoned oil and gas wells. These issues require urgent attention and comprehensive solutions to protect the Gulf’s ecosystems.
5. What Are Some Interesting Facts About The Gulf Of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is the world’s largest gulf, home to over 40 shark species, and fed by 33 American rivers, holding numerous shipwrecks and unique marine life. These facts highlight its ecological importance and historical significance.
Size and Scale
As the largest gulf in the world and the 9th largest body of water, the Gulf of Mexico is a significant geographical feature. Its vastness underscores its importance in global climate patterns and marine ecosystems.
Marine Biodiversity
With over 40 species of sharks, including bull sharks, hammerhead sharks, and lemon sharks, the Gulf of Mexico is a haven for marine biodiversity. It also supports a wide range of other marine species, from shrimp and oysters to sea turtles and dolphins.
River Systems
The Gulf of Mexico is fed by 33 American rivers, with the Mississippi River being the largest contributor. These rivers carry freshwater, sediments, and nutrients into the Gulf, influencing its salinity and ecosystem dynamics.
Coastal Wetlands
Approximately 5 million acres of wetlands border the Gulf of Mexico, providing critical habitats for numerous species and helping to protect coastal areas from erosion and storm surges.
Shipwrecks
The Gulf of Mexico is the site of over 750 known shipwrecks, reflecting its long history of maritime activity and the challenges of navigating its waters. These shipwrecks are often valuable historical and archaeological resources.
The Gulf Stream
Originating in the Gulf of Mexico, the Gulf Stream is a warm Atlantic current that influences the climate of the eastern United States and western Europe. It plays a crucial role in regulating temperatures and weather patterns across the Atlantic.
Ancient Coral
Black coral found in the Gulf of Mexico is estimated to be over 2,000 years old, making it one of the oldest living organisms on Earth. This ancient coral provides valuable insights into the Gulf’s long-term environmental history.
6. Why Is The Gulf Of Mexico Important To The LGBTQ+ Community In Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is bordered by several LGBTQ+ friendly cities and destinations in Mexico, making it an important region for LGBTQ+ tourism and cultural experiences, especially for those seeking safe and welcoming environments.
LGBTQ+ Friendly Destinations
Several cities along the Gulf Coast of Mexico are known for their inclusive and welcoming atmosphere towards the LGBTQ+ community. These destinations offer safe spaces, cultural events, and a sense of community for LGBTQ+ travelers.
Tourism and Economic Impact
LGBTQ+ tourism contributes significantly to the economies of these coastal cities. The presence of LGBTQ+ travelers supports local businesses, creates employment opportunities, and promotes a culture of acceptance and diversity.
Cultural Events and Pride Celebrations
Many cities along the Gulf Coast host LGBTQ+ pride celebrations and cultural events, attracting visitors from around the world. These events provide platforms for self-expression, community building, and advocacy for LGBTQ+ rights.
Safe and Welcoming Environments
The Gulf Coast destinations offer safe and welcoming environments for LGBTQ+ individuals, where they can feel comfortable being themselves and exploring the local culture. This sense of safety and acceptance is essential for fostering a positive tourism experience.
Connecting with Local Communities
LGBTQ+ travelers can connect with local communities through various organizations, social groups, and cultural centers. These connections provide opportunities for cultural exchange, mutual understanding, and lasting friendships.
7. How Does The Salinity Of The Gulf Of Mexico Affect Marine Life?
The salinity of the Gulf of Mexico is crucial for the survival and distribution of its marine life, with different species adapted to varying levels of salt concentration. Changes in salinity can disrupt ecosystems and impact biodiversity.
Saltwater Adaptations
Most marine organisms in the Gulf of Mexico are adapted to live in saltwater. Their physiological processes, such as osmoregulation, are designed to maintain a balance between their internal fluids and the surrounding seawater.
Species Distribution
The salinity gradient in the Gulf of Mexico influences the distribution of different species. Some species thrive in higher salinity areas, while others prefer brackish waters near river mouths. This variation contributes to the overall biodiversity of the Gulf.
Estuarine Ecosystems
Estuaries, where freshwater from rivers mixes with saltwater from the Gulf, are particularly important habitats. These brackish water environments support unique communities of plants and animals adapted to fluctuating salinity levels.
Impacts of Freshwater Inflow
Excessive freshwater inflow from rivers can lower salinity levels in certain areas, potentially harming marine organisms that are not adapted to low-salinity conditions. Conversely, reduced freshwater inflow can increase salinity, impacting estuarine ecosystems.
Climate Change Effects
Climate change can alter salinity patterns in the Gulf of Mexico through changes in precipitation, river runoff, and sea level rise. These changes can have cascading effects on marine ecosystems, affecting species distribution, abundance, and overall health.
8. What Role Does The Gulf Of Mexico Play In Hurricane Formation?
The warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico provide the energy needed for hurricanes to form and intensify, making it a critical region for monitoring and understanding these powerful storms.
Warm Water as Fuel
Hurricanes are fueled by warm ocean waters, and the Gulf of Mexico is known for its high water temperatures, especially during the summer months. This warmth provides the energy that drives the development and intensification of hurricanes.
Evaporation and Moisture
Warm water evaporates more readily, adding moisture to the atmosphere. This moisture condenses to form clouds and thunderstorms, which are essential components of a hurricane. The Gulf of Mexico’s high evaporation rates contribute to the formation of these storm systems.
Low Wind Shear
Low wind shear, which is the change in wind speed and direction with altitude, is another factor that favors hurricane formation. The Gulf of Mexico often experiences periods of low wind shear, allowing thunderstorms to organize and strengthen into tropical cyclones.
Hurricane Tracks
Many hurricanes that form in the Atlantic Ocean or the Caribbean Sea eventually track into the Gulf of Mexico, where they can further intensify before making landfall along the US or Mexican coastlines. The Gulf’s geographic location makes it a hotspot for hurricane activity.
Monitoring and Prediction
Given the Gulf of Mexico’s role in hurricane formation, it is closely monitored by meteorologists and scientists. Advanced forecasting models and observational tools are used to predict the development, track, and intensity of hurricanes, helping to protect coastal communities.
9. How Does Agricultural Runoff Affect The Gulf Of Mexico?
Agricultural runoff introduces excess nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, into the Gulf of Mexico, leading to harmful algal blooms and hypoxia, which can devastate marine life.
Nutrient Pollution
Agricultural runoff contains fertilizers, pesticides, and animal waste, which are rich in nitrogen and phosphorus. When these nutrients enter the Gulf of Mexico, they can trigger excessive growth of algae.
Algal Blooms
The excess nutrients from agricultural runoff fuel the growth of algal blooms, including harmful algal blooms known as “red tides.” These blooms can produce toxins that harm marine life and pose risks to human health.
Hypoxia and Dead Zones
As algal blooms die and decompose, they consume oxygen in the water, leading to hypoxia, or low oxygen levels. In severe cases, this can create “dead zones” where marine life cannot survive.
Impacts on Marine Ecosystems
Agricultural runoff can disrupt the balance of marine ecosystems, affecting fish populations, shellfish beds, and other marine organisms. It can also lead to habitat degradation and loss of biodiversity.
Mitigation Strategies
Addressing agricultural runoff requires implementing best management practices on farms, such as reducing fertilizer use, improving nutrient management, and implementing erosion control measures. These strategies can help to minimize the amount of nutrients entering the Gulf of Mexico.
10. What Are The Potential Impacts Of Climate Change On The Gulf Of Mexico?
Climate change poses significant threats to the Gulf of Mexico, including rising sea levels, increased water temperatures, ocean acidification, and more intense hurricanes, which can severely impact coastal communities and marine ecosystems.
Rising Sea Levels
As global temperatures rise, glaciers and ice sheets melt, causing sea levels to rise. This can lead to coastal erosion, flooding of low-lying areas, and loss of valuable habitats in the Gulf of Mexico.
Increased Water Temperatures
Climate change is causing water temperatures in the Gulf of Mexico to increase. This can affect marine life, alter species distributions, and contribute to the formation of more intense hurricanes.
Ocean Acidification
As the ocean absorbs excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, it becomes more acidic. This can harm marine organisms that rely on calcium carbonate to build their shells and skeletons, such as corals and shellfish.
More Intense Hurricanes
Climate change is expected to lead to more intense hurricanes, with higher wind speeds, heavier rainfall, and greater storm surge. This can increase the risk of coastal flooding, property damage, and loss of life in the Gulf of Mexico.
Impacts on Coastal Communities
Climate change poses significant challenges for coastal communities in the Gulf of Mexico. Rising sea levels, more intense hurricanes, and other climate-related impacts can threaten infrastructure, economies, and livelihoods.
Conservation and Adaptation
Addressing the impacts of climate change on the Gulf of Mexico requires a combination of mitigation efforts, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and adaptation strategies, such as building seawalls and restoring coastal wetlands. These efforts can help to protect coastal communities and marine ecosystems from the effects of climate change.
Gaymexico.net is your premier resource for discovering Mexico’s vibrant LGBTQ+ scene. From bustling cityscapes to serene coastal getaways, we provide the insights you need to plan your perfect trip.
Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States
Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177
Website: gaymexico.net
Ready to explore the beauty and diversity of Mexico? Visit gaymexico.net today to discover LGBTQ+ friendly destinations, events, and communities. Your adventure awaits!
FAQ: Gulf of Mexico Salinity
1. Is the Gulf of Mexico fresh water or saltwater?
The Gulf of Mexico is saltwater, not fresh water, due to its connection to the Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea.
2. How does the salinity of the Gulf of Mexico compare to the ocean?
The Gulf of Mexico is generally shallower, saltier, and warmer than the open Atlantic Ocean.
3. What factors influence the salinity of the Gulf of Mexico?
Factors include freshwater inflow from rivers, evaporation rates, and exchange with the Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea.
4. How does freshwater inflow from rivers affect the Gulf of Mexico’s salinity?
Freshwater inflow from rivers like the Mississippi can lower salinity levels in certain areas, especially near river mouths.
5. What happens when there’s excessive agricultural runoff into the Gulf of Mexico?
Excessive agricultural runoff introduces excess nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, into the Gulf of Mexico, leading to harmful algal blooms and hypoxia, which can devastate marine life.
6. How does climate change affect the salinity of the Gulf of Mexico?
Climate change can alter salinity patterns through changes in precipitation, river runoff, and sea level rise, with cascading effects on marine ecosystems.
7. Why is the Gulf of Mexico important for LGBTQ+ tourism in Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is bordered by several LGBTQ+ friendly cities and destinations in Mexico, making it an important region for LGBTQ+ tourism and cultural experiences, especially for those seeking safe and welcoming environments.
8. What role does the Gulf of Mexico play in the formation of hurricanes?
The warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico provide the energy needed for hurricanes to form and intensify, making it a critical region for monitoring and understanding these powerful storms.
9. How do rising sea levels, due to climate change, affect the Gulf of Mexico?
Rising sea levels from climate change can lead to coastal erosion, flooding of low-lying areas, and loss of valuable habitats in the Gulf of Mexico.
10. What mitigation strategies can help protect the Gulf of Mexico from climate change impacts?
Addressing climate change impacts on the Gulf of Mexico requires mitigation efforts, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and adaptation strategies, such as building seawalls and restoring coastal wetlands.