Are There Leopards In Mexico? Yes, jaguars, often mistaken for leopards, are present in Mexico. This vibrant country, highlighted on gaymexico.net, offers a wealth of experiences for LGBTQ+ travelers, but it’s also home to incredible wildlife. To get more information, continue reading this article and learn more about these animals, their habitat and conservation efforts.
1. What Big Cats Live In Mexico?
Mexico is home to several species of wild cats, with the jaguar being the largest and most well-known. While leopards are not native to Mexico, jaguars share a similar appearance, often leading to confusion. Other wild cats found in Mexico include:
- Jaguar (Panthera onca): The largest wild cat in the Americas.
- Puma (Puma concolor): Also known as the mountain lion or cougar.
- Ocelot (Leopardus pardalis): A smaller, spotted wild cat.
- Margay (Leopardus wiedii): Another small, tree-dwelling wild cat.
- Jaguarundi (Herpailurus yagouaroundi): A unique-looking wild cat with a long, slender body.
These species contribute to Mexico’s rich biodiversity, creating unique opportunities for wildlife enthusiasts and conservationists.
2. What Is The Difference Between Jaguars And Leopards?
While jaguars and leopards may look similar, they are distinct species with specific differences:
| Feature | Jaguar (Panthera onca) | Leopard (Panthera pardus) |
|---|---|---|
| Habitat | Americas (including Mexico) | Africa and Asia |
| Spot Pattern | Spots with small dots inside | Rosettes (spots without central dots) |
| Build | Stockier, more muscular | More slender and agile |
| Head | Broader head | Smaller head |
| Behavior | Stronger swimmer | Less inclined to swim |
Understanding these differences is essential for identifying and appreciating these magnificent creatures. Jaguars, symbols of power and resilience, have adapted to diverse habitats in Mexico, enriching the nation’s natural heritage.
3. Where Are Jaguars Typically Found In Mexico?
Jaguars are primarily found in the following regions of Mexico:
- Yucatán Peninsula: This area hosts a significant population of jaguars, thriving in the tropical forests and protected areas.
- Chiapas: The dense rainforests of Chiapas provide a suitable habitat for jaguars.
- Oaxaca: Jaguars roam the diverse landscapes of Oaxaca, including coastal regions and mountainous areas.
- Campeche: The Calakmul Biosphere Reserve in Campeche is a crucial jaguar habitat, offering vast stretches of protected land.
- Quintana Roo: Jaguars are present in the Sian Ka’an Biosphere Reserve and other natural reserves along the Caribbean coast.
These regions offer diverse ecosystems, supporting jaguar populations and contributing to the conservation of this iconic species.
4. What Is The Habitat Of Jaguars In Mexico?
Jaguars in Mexico inhabit a variety of environments, including:
- Tropical Rainforests: Dense rainforests provide ample cover and prey for jaguars.
- Deciduous Forests: These forests offer seasonal resources and varied habitats.
- Mangrove Swamps: Jaguars can thrive in coastal mangrove ecosystems.
- Grasslands: Open grasslands provide hunting opportunities and connectivity between habitats.
Jaguars’ adaptability to different habitats underscores their resilience and importance to Mexico’s ecological balance. Protecting these diverse habitats is crucial for jaguar conservation.
5. What Is The Current Population Of Jaguars In Mexico?
Recent surveys indicate a positive trend in the jaguar population in Mexico. According to the first surveys conducted in Mexico, the jaguar population increased by 20% from 2010 to 2018, reaching approximately 4,800 animals. These surveys, highlighted in the journal PLOS One, confirm the effectiveness of Mexico’s national strategy to protect jaguars.
This increase reflects the success of targeted conservation strategies and the commitment of local communities and government agencies to preserve this iconic species.
6. What Conservation Efforts Are In Place To Protect Jaguars In Mexico?
Several conservation initiatives are in place to protect jaguars in Mexico:
- National Alliance for Jaguar Conservation: This alliance unites government agencies, local communities, and the private sector to implement conservation plans.
- Protected Areas and Wildlife Corridors: Prioritizing the protection of wildlife preserves and natural corridors allows jaguars to move freely and maintain genetic diversity.
- Compensation Programs: The government compensates local communities for livestock losses due to jaguar predation, reducing conflicts between humans and jaguars.
- Anti-Deforestation Measures: Payments to local residents to prevent deforestation of critical jaguar habitats.
- Expansion of Protected Areas: Initiatives like the expansion of the Calakmul Biosphere Reserve significantly increase protected tropical forest areas.
These efforts demonstrate Mexico’s dedication to preserving its jaguar population and biodiversity.
7. What Threats Do Jaguars Face In Mexico?
Despite conservation efforts, jaguars in Mexico still face several threats:
- Habitat Loss: Deforestation and land conversion for agriculture and development reduce available habitat.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: Jaguars sometimes prey on livestock, leading to retaliatory killings by ranchers.
- Poaching: Illegal hunting for jaguar parts and fur continues to threaten populations.
- Climate Change: Changing climate patterns can alter habitats and prey availability.
Addressing these threats requires ongoing conservation efforts and collaboration between various stakeholders.
8. How Can I Support Jaguar Conservation In Mexico?
You can support jaguar conservation in Mexico through various means:
- Donate to Conservation Organizations: Support organizations dedicated to jaguar research and conservation.
- Promote Responsible Tourism: Visit ecotourism destinations that prioritize wildlife protection and community involvement.
- Educate Others: Raise awareness about the importance of jaguar conservation among friends, family, and colleagues.
- Support Sustainable Practices: Advocate for sustainable land use and responsible development to minimize habitat loss.
- Volunteer: Participate in conservation projects and community initiatives focused on jaguar protection.
Your involvement can make a significant difference in ensuring the survival of jaguars in Mexico.
9. Are There Any Ecotourism Opportunities To See Jaguars In Mexico?
Yes, several ecotourism opportunities allow you to see jaguars in their natural habitat in Mexico:
- Calakmul Biosphere Reserve: This vast reserve offers guided tours and wildlife viewing opportunities, increasing your chances of spotting jaguars.
- Sian Ka’an Biosphere Reserve: Explore the diverse ecosystems of Sian Ka’an and learn about jaguar conservation efforts.
- Community-Based Tourism: Support local communities involved in ecotourism initiatives that protect jaguar habitats.
Remember to choose responsible and sustainable tourism options that minimize environmental impact and benefit local communities.
10. What Role Do Local Communities Play In Jaguar Conservation In Mexico?
Local communities play a vital role in jaguar conservation in Mexico:
- Guardians of the Habitat: Communities living near protected areas often act as stewards of the land, monitoring and protecting jaguar habitats.
- Ecotourism Partners: Community-based ecotourism initiatives provide sustainable livelihoods while promoting jaguar conservation.
- Conflict Resolution: Local communities participate in programs that mitigate human-wildlife conflict and promote coexistence.
- Traditional Knowledge: Indigenous communities possess valuable knowledge about jaguar behavior and ecology, contributing to conservation strategies.
Engaging and empowering local communities is essential for the long-term success of jaguar conservation efforts.
11. How Does Climate Change Affect Jaguars In Mexico?
Climate change poses a significant threat to jaguars in Mexico:
- Habitat Alteration: Changing temperature and rainfall patterns can alter jaguar habitats, affecting prey availability and distribution.
- Increased Human-Wildlife Conflict: As resources become scarcer, jaguars may be forced to hunt livestock more frequently, increasing conflict with humans.
- Disease Outbreaks: Climate change can exacerbate disease outbreaks, impacting jaguar populations.
- Loss of Genetic Diversity: Habitat fragmentation and reduced connectivity can limit genetic exchange, making jaguars more vulnerable to environmental changes.
Addressing climate change and implementing adaptation strategies are crucial for mitigating its impact on jaguar populations.
12. What Is The Cultural Significance Of Jaguars In Mexico?
Jaguars hold deep cultural significance in Mexico, particularly among indigenous communities:
- Symbol of Power and Strength: In ancient Mesoamerican cultures, jaguars were revered as symbols of power, strength, and leadership.
- Religious Symbolism: Jaguars were often associated with deities and spiritual realms, featuring prominently in religious ceremonies and art.
- Artistic Representations: Jaguars are depicted in various forms of art, including sculptures, murals, and textiles, reflecting their cultural importance.
- Contemporary Symbolism: Today, jaguars continue to be a symbol of national pride and cultural heritage in Mexico.
Understanding the cultural significance of jaguars enhances appreciation for their role in Mexico’s history and identity.
13. What Is The Legal Status Of Jaguars In Mexico?
Jaguars are legally protected in Mexico:
- Endangered Species Status: Jaguars are listed as an endangered species under Mexican law, providing them with legal protection against hunting and habitat destruction.
- Protected Areas: Many jaguar habitats are located within protected areas, providing additional safeguards against human activities.
- International Agreements: Mexico is a signatory to international agreements, such as the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES), which regulates trade in jaguar parts.
These legal protections are essential for ensuring the long-term survival of jaguars in Mexico.
14. What Research Is Being Conducted On Jaguars In Mexico?
Ongoing research efforts are crucial for understanding and protecting jaguars in Mexico:
- Population Monitoring: Researchers use camera traps and other techniques to monitor jaguar populations and track their movements.
- Habitat Assessment: Studies assess the quality and extent of jaguar habitats, identifying critical areas for conservation.
- Genetic Analysis: Genetic studies help determine the genetic diversity and relatedness of jaguar populations, informing conservation management.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict Mitigation: Research focuses on developing strategies to reduce conflict between humans and jaguars, such as livestock management techniques.
These research initiatives provide valuable insights that guide conservation planning and management decisions.
15. How Do Jaguars Adapt To Urban Environments In Mexico?
While jaguars primarily inhabit natural areas, they sometimes adapt to urban environments in Mexico:
- Fragmented Habitats: Urban development can fragment jaguar habitats, forcing them to navigate human-dominated landscapes.
- Nocturnal Behavior: Jaguars tend to be more active at night in urban areas, avoiding human contact.
- Prey Availability: Jaguars may prey on domestic animals and other wildlife found in urban environments.
- Corridors: Maintaining green corridors and natural spaces within urban areas can facilitate jaguar movement and reduce isolation.
Understanding how jaguars adapt to urban environments is essential for minimizing human-wildlife conflict and promoting coexistence.
16. What Are The Challenges Of Counting Jaguars In The Wild?
Counting jaguars in the wild presents several challenges:
- Elusive Nature: Jaguars are secretive and solitary animals, making them difficult to detect.
- Vast Habitats: Jaguars roam over large areas, requiring extensive survey efforts.
- Dense Vegetation: Dense forests and other vegetation can hinder visibility and access.
- Remote Locations: Many jaguar habitats are located in remote and inaccessible areas.
- Cost and Resources: Conducting comprehensive jaguar surveys requires significant funding and resources.
Despite these challenges, researchers have developed innovative techniques, such as camera trapping and genetic analysis, to improve jaguar population estimates.
17. What Are The Main Prey Species For Jaguars In Mexico?
Jaguars in Mexico prey on a variety of animals, including:
- Peccaries: These wild pigs are a common prey item in many jaguar habitats.
- Deer: Various deer species provide a significant food source for jaguars.
- Armadillos: These armored mammals are readily available in some areas.
- Reptiles: Caimans, snakes, and other reptiles are occasionally preyed upon.
- Monkeys: In tropical forests, monkeys can be an important part of the jaguar’s diet.
The availability and abundance of prey species influence jaguar distribution and population dynamics.
18. How Do Jaguars Communicate With Each Other?
Jaguars communicate through various means:
- Scent Marking: Jaguars use urine and feces to mark their territories and communicate with other individuals.
- Vocalizations: Jaguars emit a variety of calls, including roars, growls, and meows, to communicate different messages.
- Body Language: Jaguars use body postures and facial expressions to convey information.
- Scratches: Jaguars scratch trees and other objects to leave visual and olfactory signals.
These communication methods help jaguars establish territories, attract mates, and maintain social relationships.
19. What Is The Lifespan Of A Jaguar In The Wild?
The lifespan of a jaguar in the wild typically ranges from:
- 12 to 15 years: This is the average lifespan for jaguars in their natural habitat.
- Up to 20 years: In captivity, jaguars can live longer due to consistent food supply and veterinary care.
Factors such as habitat quality, prey availability, and human threats can influence jaguar lifespan.
20. How Do Jaguars Raise Their Young In Mexico?
Jaguars exhibit specific parenting behaviors:
- Solitary Mothers: Female jaguars raise their cubs alone, without assistance from males.
- Denning: Mothers create dens in secluded locations, such as caves or dense vegetation.
- Litter Size: Jaguar litters typically consist of one to four cubs.
- Nursing: Cubs nurse for several months, relying on their mother’s milk for nourishment.
- Hunting Lessons: Mothers teach their cubs how to hunt and survive in the wild, gradually introducing them to solid food.
These parenting behaviors are crucial for the survival and success of jaguar offspring.
21. How Does The Fragmentation Of Habitats Affect Jaguar Populations?
Habitat fragmentation significantly impacts jaguar populations:
- Reduced Gene Flow: Fragmentation isolates jaguar populations, limiting genetic exchange and increasing the risk of inbreeding.
- Increased Mortality: Jaguars are more vulnerable to vehicle collisions and other human-related threats when crossing fragmented landscapes.
- Limited Prey Availability: Habitat fragmentation can reduce the availability of prey species, affecting jaguar survival.
- Increased Conflict: Jaguars may venture into agricultural areas and settlements in search of food, leading to conflict with humans.
Maintaining habitat connectivity through corridors and protected areas is essential for mitigating the effects of fragmentation.
22. What Role Do Zoos Play In Jaguar Conservation?
Zoos can contribute to jaguar conservation in several ways:
- Breeding Programs: Zoos participate in captive breeding programs to maintain genetic diversity and increase jaguar populations.
- Public Education: Zoos educate visitors about jaguar biology, behavior, and conservation issues.
- Research Support: Zoos support research efforts aimed at understanding and protecting jaguars in the wild.
- Fundraising: Zoos raise funds for conservation projects in jaguar habitats.
By supporting zoos that prioritize conservation, you can contribute to jaguar protection efforts.
23. What Are The Best Times Of Year To See Jaguars In Mexico?
The best times of year to see jaguars in Mexico vary by location:
- Dry Season: During the dry season (December to May), jaguars may be easier to spot as they congregate near water sources.
- Early Mornings and Late Afternoons: Jaguars are most active during these times, increasing your chances of a sighting.
- Guided Tours: Local guides can provide valuable insights and expertise, increasing your chances of seeing jaguars.
Always respect wildlife and maintain a safe distance to minimize disturbance.
24. How Can Technology Help In Jaguar Conservation?
Technology plays an increasingly important role in jaguar conservation:
- GPS Tracking: GPS collars allow researchers to track jaguar movements and habitat use.
- Camera Traps: Camera traps capture images and videos of jaguars, providing valuable data on population size and behavior.
- Remote Sensing: Satellite imagery and aerial surveys help monitor habitat changes and identify critical areas for conservation.
- Genetic Analysis: DNA sequencing can reveal genetic diversity and relatedness, informing conservation management decisions.
These technologies provide valuable tools for studying and protecting jaguars in the wild.
25. What Are The Economic Benefits Of Jaguar Conservation?
Jaguar conservation can provide economic benefits:
- Ecotourism: Jaguar-related ecotourism can generate revenue for local communities and support conservation efforts.
- Ecosystem Services: Jaguars play a crucial role in maintaining healthy ecosystems, which provide valuable services such as water purification and carbon sequestration.
- Sustainable Livelihoods: Conservation initiatives can create sustainable livelihoods for local communities, such as ecotourism and sustainable agriculture.
By recognizing the economic value of jaguar conservation, we can promote its integration into sustainable development planning.
26. How Does Jaguar Conservation Benefit Other Species?
Jaguar conservation benefits numerous other species:
- Umbrella Species: Jaguars are considered an umbrella species, meaning that protecting them also protects the many other species that share their habitat.
- Ecosystem Health: Jaguars help maintain healthy ecosystems by regulating prey populations and promoting biodiversity.
- Habitat Protection: Jaguar conservation efforts often lead to the protection of large areas of habitat, benefiting a wide range of species.
By focusing on jaguar conservation, we can achieve broader biodiversity conservation goals.
27. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Jaguars?
Several misconceptions exist about jaguars:
- Jaguars are the same as leopards: While they look similar, jaguars and leopards are distinct species with different habitats and characteristics.
- Jaguars are aggressive towards humans: Jaguars are generally shy and avoid human contact unless threatened.
- Jaguars are only found in rainforests: Jaguars inhabit a variety of habitats, including grasslands, wetlands, and dry forests.
- Jaguar populations are declining everywhere: While jaguars face threats in many areas, some populations are stable or increasing due to conservation efforts.
By dispelling these misconceptions, we can promote a better understanding and appreciation of jaguars.
28. How Can Schools And Educators Promote Jaguar Conservation?
Schools and educators can play a vital role in promoting jaguar conservation:
- Curriculum Integration: Incorporate jaguar biology, ecology, and conservation into school curricula.
- Educational Programs: Organize field trips, workshops, and presentations on jaguar conservation.
- Community Engagement: Encourage students to participate in community-based conservation projects.
- Awareness Campaigns: Launch awareness campaigns to educate students, parents, and the community about the importance of jaguar conservation.
By educating future generations about jaguars, we can foster a sense of responsibility and stewardship.
29. How Can Governments Support Jaguar Conservation More Effectively?
Governments can enhance their support for jaguar conservation through:
- Policy Development: Enact and enforce strong laws and policies to protect jaguars and their habitats.
- Protected Area Management: Strengthen the management of protected areas and ensure adequate resources for conservation efforts.
- Community Engagement: Involve local communities in conservation planning and decision-making processes.
- International Collaboration: Collaborate with other countries and organizations to address transboundary conservation issues.
- Research Funding: Invest in research to better understand jaguar ecology and inform conservation management.
These actions can significantly improve the effectiveness of jaguar conservation efforts.
30. What Is The Future Outlook For Jaguars In Mexico?
The future outlook for jaguars in Mexico is cautiously optimistic:
- Positive Trends: Recent surveys indicate that jaguar populations are stable or increasing in some areas due to conservation efforts.
- Ongoing Threats: Jaguars continue to face threats from habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and poaching.
- Continued Conservation Efforts: Sustained conservation efforts are essential for ensuring the long-term survival of jaguars in Mexico.
- Community Involvement: The involvement of local communities is critical for the success of conservation initiatives.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Addressing the impacts of climate change is crucial for protecting jaguar habitats and prey populations.
By continuing to invest in conservation and addressing the challenges facing jaguars, we can help ensure a brighter future for these iconic animals in Mexico.
These detailed insights into the world of jaguars in Mexico provide a comprehensive understanding of their habitat, conservation, and cultural significance. As you plan your visit to Mexico, consider exploring the natural beauty and biodiversity of this incredible country, and remember to visit gaymexico.net for LGBTQ+ travel information and resources.
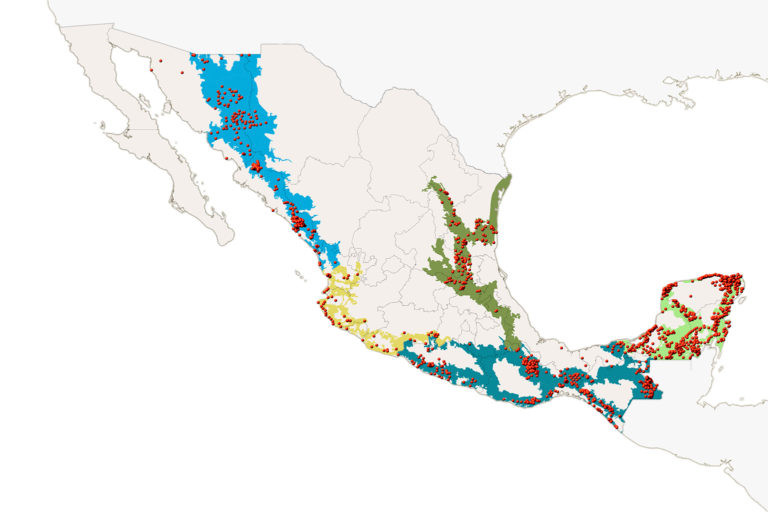 Jaguar census map: Current geographic range of jaguar Panthera onca in Mexico
Jaguar census map: Current geographic range of jaguar Panthera onca in Mexico
31. What Are Some Facts About Leopards?
Although there aren’t leopards in Mexico, here are some interesting facts about them:
- Habitat: Leopards live in Africa and Asia.
- Adaptability: They are known for adapting to many environments.
- Spots: Their spots are called rosettes and are unique to each leopard.
- Climbing: Leopards are strong climbers and often rest in trees.
- Diet: They eat a variety of animals, from small rodents to large antelopes.
32. What Organizations Support Wildlife In Mexico?
There are several organizations you can contact to get more information:
- Pronatura México: Focuses on conserving ecosystems and biodiversity in Mexico.
- Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) Mexico: Works on protecting wildlife and their habitats through scientific research and conservation actions.
- Fondo Mexicano para la Conservación de la Naturaleza (FMCN): Supports projects related to the conservation of biodiversity and sustainable development in Mexico.
- Comisión Nacional de Áreas Naturales Protegidas (CONANP): The Mexican government agency responsible for managing and protecting natural protected areas in Mexico.
33. What Are Some Protected Areas In Mexico?
Mexico boasts numerous protected areas crucial for biodiversity conservation:
- Sian Ka’an Biosphere Reserve: Located in Quintana Roo, this reserve protects diverse ecosystems, including mangroves, coral reefs, and tropical forests.
- Calakmul Biosphere Reserve: Situated in Campeche, it safeguards one of the largest tropical forests in Mexico and numerous archaeological sites.
- Monarch Butterfly Biosphere Reserve: In the states of Michoacán and Mexico, this reserve protects the overwintering habitat of the monarch butterfly.
- El Pinacate and Gran Desierto de Altar Biosphere Reserve: Located in Sonora, this area features unique desert landscapes, volcanic craters, and diverse wildlife.
- Banco Chinchorro Biosphere Reserve: In Quintana Roo, this reserve protects the largest coral atoll in Mexico, supporting a wide array of marine life.
These protected areas are essential for preserving Mexico’s natural heritage.
34. Where Can LGBTQ+ Travelers Find More Information About Traveling In Mexico?
LGBTQ+ travelers can find valuable information and resources on gaymexico.net:
- Travel Guides: Detailed guides to LGBTQ+-friendly destinations in Mexico, including Puerto Vallarta, Mexico City, and Cancun.
- Event Listings: Information on LGBTQ+ events, festivals, and parties throughout Mexico.
- Accommodation Listings: Recommendations for gay-friendly hotels, resorts, and guesthouses.
- Community Forums: Opportunities to connect with other LGBTQ+ travelers and locals, share experiences, and ask questions.
- Safety Tips: Advice on staying safe and navigating LGBTQ+-related issues while traveling in Mexico.
Gaymexico.net is a comprehensive resource for LGBTQ+ travelers seeking information and support for their travels in Mexico.
35. Why Is It Important To Conserve Wildlife In Mexico?
Conserving wildlife in Mexico is crucial for several reasons:
- Biodiversity: Mexico is one of the world’s most biodiverse countries, harboring a vast array of plant and animal species, many of which are found nowhere else.
- Ecosystem Services: Wildlife plays a vital role in maintaining healthy ecosystems, which provide essential services such as clean air and water, pollination, and climate regulation.
- Economic Benefits: Wildlife-related tourism and recreation contribute significantly to Mexico’s economy, providing livelihoods for local communities.
- Cultural Heritage: Many wildlife species are culturally significant to indigenous communities and are an integral part of Mexico’s national identity.
- Ethical Considerations: We have an ethical responsibility to protect wildlife and ensure their survival for future generations.
Conserving wildlife is essential for maintaining Mexico’s natural heritage and ensuring a sustainable future.
36. How Can I Educate Myself More About Mexico’s Biodiversity?
There are several ways to educate yourself about Mexico’s biodiversity:
- Visit National Parks and Reserves: Explore Mexico’s national parks and reserves to experience its diverse ecosystems and wildlife firsthand.
- Read Books and Articles: Learn about Mexico’s biodiversity through books, scientific articles, and online resources.
- Attend Lectures and Workshops: Participate in lectures, workshops, and webinars on Mexican ecology and conservation.
- Follow Conservation Organizations: Stay informed about conservation efforts in Mexico by following relevant organizations on social media and subscribing to their newsletters.
- Support Research: Contribute to research projects aimed at studying and protecting Mexico’s biodiversity.
By educating yourself about Mexico’s biodiversity, you can become a more informed and engaged advocate for its conservation.
37. What Are Some Examples Of Success Stories In Wildlife Conservation In Mexico?
Mexico has achieved notable success stories in wildlife conservation:
- Monarch Butterfly Conservation: Efforts to protect the overwintering habitat of the monarch butterfly have helped stabilize populations and promote sustainable tourism.
- Sea Turtle Conservation: Programs to protect nesting beaches and reduce bycatch have led to increased sea turtle populations.
- Jaguar Conservation: The National Alliance for Jaguar Conservation has contributed to a 20% increase in jaguar populations from 2010 to 2018.
- California Condor Reintroduction: Reintroduction programs have successfully established breeding populations of California condors in Baja California.
- Vaquita Conservation: While still critically endangered, efforts to protect the vaquita porpoise in the Gulf of California continue, including habitat protection and fishing gear modifications.
These success stories demonstrate the effectiveness of targeted conservation efforts and the importance of continued commitment to wildlife protection.
38. What Are Some Myths About Jaguars?
There are many myths surrounding the majestic jaguar, particularly about its behavior and characteristics. Here are some common misconceptions:
- Myth: Jaguars are bloodthirsty killers.
- Fact: Jaguars typically avoid humans, preying mainly on wildlife.
- Myth: Jaguars are exclusive to rainforests.
- Fact: They inhabit various habitats, including wetlands, scrublands, and grasslands.
- Myth: Jaguars always roar loudly.
- Fact: Jaguars primarily use roars for territorial communication.
- Myth: Jaguars are untrainable.
- Fact: With proper care and handling, jaguars are cooperative.
- Myth: Jaguars are a threat to livestock.
- Fact: While they may occasionally prey on livestock, it’s not their primary behavior.
39. What Are Some Jaguar-Related Slang?
Several slang terms are associated with jaguars, particularly within Mexico:
- El Rey de la Selva: (The King of the Jungle) This term highlights the jaguar’s dominance.
- Tigre Americano: (American Tiger) Used to highlight their striking appearance.
- Manchado: (Spotted One) This term is a reference to their unique coat.
- Nahual: (Shape-shifter) This term refers to their spiritual connection.
- Fantasma de la Selva: (Ghost of the Jungle) Their elusiveness earns them this name.
40. What Can We Expect In The Future With Jaguars?
In the future, jaguar conservation efforts will continue to evolve:
- Enhanced Research: Expect continued research into jaguar behavior, ecology, and population genetics.
- Habitat Preservation: Enhanced efforts will prioritize habitat protection and connectivity.
- Community Engagement: Local communities will be integral in conservation efforts.
- Technological Advances: Tools like GPS tracking and camera traps will play a bigger role in monitoring.
- Policy Support: Legislation and policies will continue supporting jaguar preservation.
To explore this topic further or to get travel advice, visit gaymexico.net.
Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States.
Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177.
Website: gaymexico.net.
As you plan your next adventure, let gaymexico.net be your guide, providing insights and resources for an unforgettable LGBTQ+ experience in Mexico.