The Mexican border with the US stretches approximately 1,954 miles, offering both challenges and opportunities for LGBTQ+ travelers and communities; gaymexico.net is your guide to navigating this dynamic landscape with confidence. With our resources, discover welcoming destinations, events, and invaluable information for LGBTQ+ individuals exploring the beauty and culture of Mexico. Find trusted travel advice, community insights, and the latest updates on LGBTQ+ life in Mexico, creating a bridge of understanding and connection.
1. Understanding the US-Mexico Border Length
The US-Mexico border spans approximately 1,954 miles (3,145 kilometers). This extensive boundary stretches from the Gulf of Mexico in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west.
1.1. What are the states that Share the Border?
Four U.S. states share the border with Mexico:
- California
- Arizona
- New Mexico
- Texas
Each of these states has a unique culture and landscape, contributing to the diversity of the border region. For LGBTQ+ travelers, these states offer various entry points and opportunities for exploration before venturing into Mexico.
1.2. How is the Border Region Significant?
The border region is significant due to its economic, cultural, and social interactions. It’s a zone of exchange, with a rich history and diverse communities.
- Economic Impact: Trade and commerce flourish across the border, creating jobs and opportunities on both sides.
- Cultural Exchange: The intermingling of cultures leads to unique traditions, cuisine, and artistic expressions.
- Social Dynamics: The border region is home to diverse populations, including many LGBTQ+ individuals and communities with their own stories and experiences.
1.3. What are the Key Border Cities?
Several key cities lie along the US-Mexico border, including:
- San Diego, California / Tijuana, Baja California: A major metropolitan area with significant cultural and economic ties.
- El Paso, Texas / Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua: A historic crossing point with a rich heritage.
- Laredo, Texas / Nuevo Laredo, Tamaulipas: An important trade hub for international commerce.
- Brownsville, Texas / Matamoros, Tamaulipas: Located on the Gulf Coast, with a strong connection to maritime trade.
These cities are hubs for travel, trade, and cultural exchange, offering unique experiences for visitors. They also have vibrant LGBTQ+ communities and friendly establishments that welcome diversity.
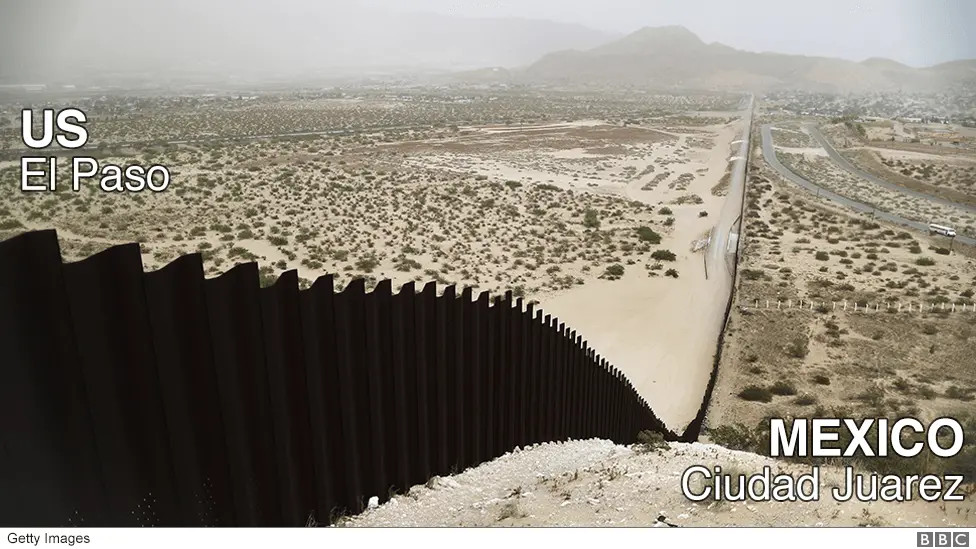 San Diego-Tijuana Border Crossing
San Diego-Tijuana Border Crossing
The San Diego-Tijuana border crossing exemplifies the intersection of cultures and travel.
2. Historical Context of the US-Mexico Border
The US-Mexico border’s history is complex and deeply rooted in territorial disputes and treaties. Understanding this history provides context for current issues and relations.
2.1. What is the History of the Border’s Demarcation?
The border’s demarcation primarily stems from the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848, which concluded the Mexican-American War.
- Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848): Mexico ceded a significant portion of its territory to the United States, including what is now California, Nevada, Utah, and parts of Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, and Wyoming.
- Gadsden Purchase (1854): The US acquired additional land from Mexico, further defining the border’s current alignment.
These historical events shaped the border we know today, influencing the cultural and demographic landscape of the region.
2.2. How have Border Policies Evolved?
Border policies have evolved significantly over time, reflecting changes in political priorities and societal attitudes.
- Early Policies: Initially, border control was relatively lax, with free movement across the boundary.
- 20th Century: Increased regulation and enforcement began in the 20th century, driven by concerns about immigration and security.
- Modern Era: Contemporary policies focus on border security, trade regulation, and immigration control, often sparking debate and controversy.
2.3. What Impact do Historical Treaties Have on Current Border Dynamics?
Historical treaties continue to influence border dynamics, shaping legal frameworks and diplomatic relations.
- Land and Water Rights: Treaties determine the allocation of land and water resources, impacting agriculture and development in the region.
- Cultural Preservation: Agreements address the preservation of cultural heritage and the rights of indigenous communities along the border.
- Migration Patterns: Historical migration patterns have shaped the demographic makeup of border communities, influencing social and cultural interactions.
3. Current Border Security Measures
Border security measures are constantly evolving, reflecting ongoing efforts to manage and control the flow of people and goods.
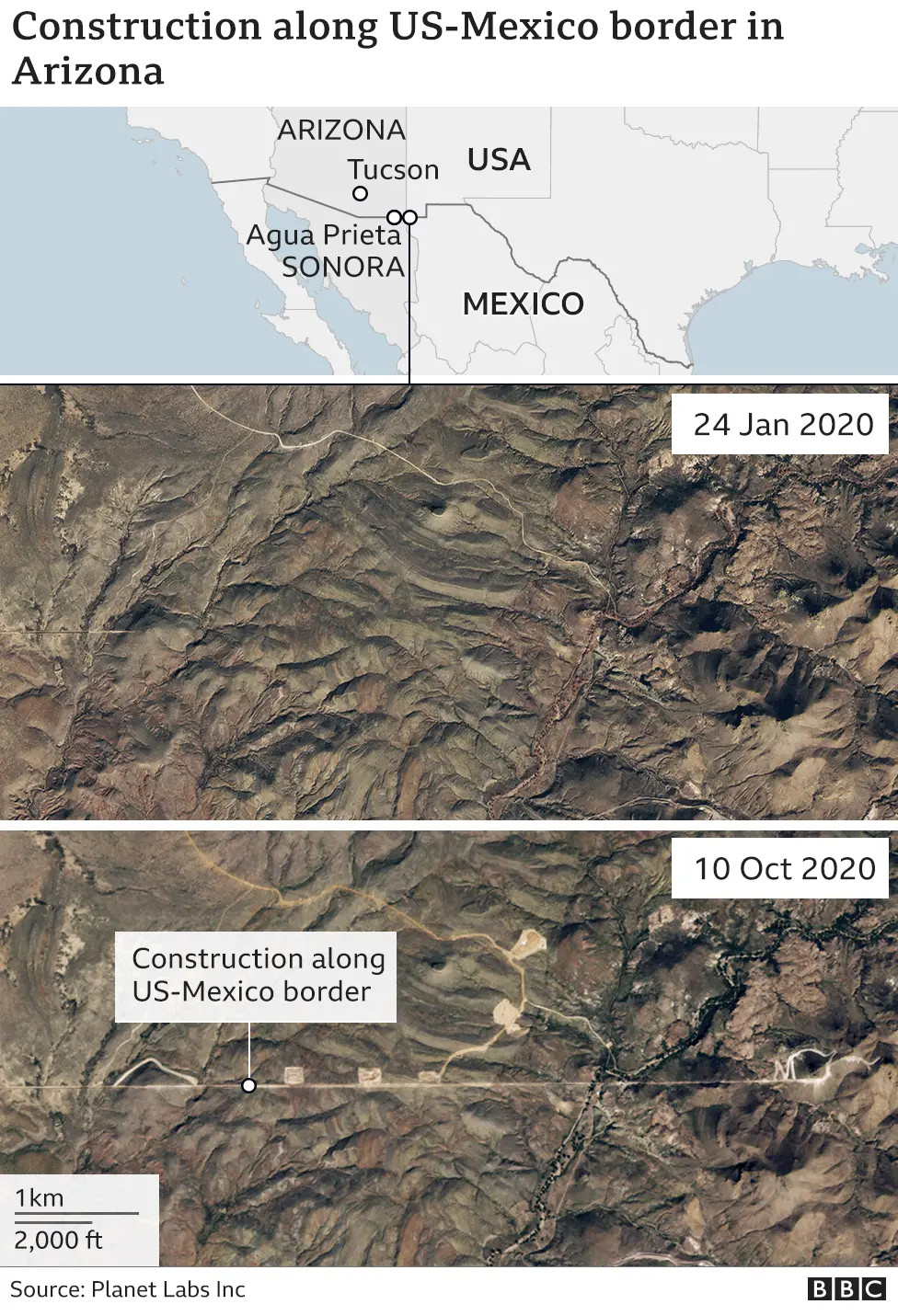
3.1. What Physical Barriers Exist Along the Border?
Physical barriers along the border include fences, walls, and other infrastructure designed to deter illegal crossings.
- Fencing: Various types of fencing are used, ranging from simple wire fences to more substantial steel barriers.
- Walls: Sections of the border feature concrete or steel walls, often equipped with surveillance technology.
- Technology: Surveillance cameras, sensors, and drones are deployed to monitor border activity and detect potential breaches.
The US-Mexico border fence exemplifies modern security measures.
3.2. How is Technology Used in Border Control?
Technology plays a crucial role in modern border control efforts, enhancing surveillance and enforcement capabilities.
- Surveillance Systems: Advanced camera systems and sensors provide real-time monitoring of border activity, detecting unauthorized crossings and other security threats.
- Drones: Unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with cameras and sensors patrol the border, providing aerial surveillance and reconnaissance.
- Data Analytics: Data analytics tools analyze border crossing patterns and trends, helping law enforcement agencies identify potential risks and allocate resources effectively.
3.3. What Role do Border Patrol Agents Play?
Border Patrol agents are responsible for enforcing immigration laws and securing the border against illegal activity.
- Enforcement: Agents patrol the border, apprehend individuals attempting to cross illegally, and seize contraband.
- Intelligence Gathering: Agents gather intelligence on smuggling operations and other criminal activities, working to disrupt and dismantle illicit networks.
- Community Engagement: Agents engage with local communities to build relationships and foster cooperation in border security efforts.
4. Immigration and Cross-Border Travel
Immigration and cross-border travel are complex issues with significant economic, social, and political implications.
4.1. What are the Current Immigration Policies?
Current immigration policies govern who can enter and remain in the United States, with varying rules for different categories of immigrants.
- Visa Programs: The US offers various visa programs for tourists, students, workers, and investors, each with specific requirements and restrictions.
- Asylum and Refugee Status: Individuals fleeing persecution in their home countries can seek asylum or refugee status in the US, subject to strict eligibility criteria.
- Enforcement: Immigration enforcement efforts target individuals who violate immigration laws, including those who enter the country illegally or overstay their visas.
4.2. How do People Legally Cross the Border?
People can legally cross the border through designated ports of entry, using valid travel documents and complying with immigration laws.
- Border Crossing Cards: Mexican citizens can obtain border crossing cards for short-term visits to the US, subject to certain restrictions.
- Visas: Foreign nationals can apply for visas to enter the US for tourism, business, study, or work purposes, following established procedures and requirements.
- Trusted Traveler Programs: Programs like SENTRI and Global Entry expedite border crossings for pre-approved travelers who meet certain security criteria.
4.3. What are the Challenges of Illegal Immigration?
Illegal immigration poses numerous challenges for both immigrants and border communities, including:
- Safety Risks: Individuals attempting to cross the border illegally face significant risks, including exposure to harsh environmental conditions, encounters with criminal organizations, and potential abuse by smugglers.
- Legal Consequences: Illegal immigrants face potential arrest, detention, and deportation, as well as limited access to legal protections and social services.
- Community Impacts: Illegal immigration can strain resources in border communities, leading to overcrowding, increased crime rates, and social tensions.
5. Economic Impact of the Border
The US-Mexico border has a profound economic impact on both countries, driving trade, investment, and job creation.
5.1. How does Trade Occur Between the US and Mexico?
Trade between the US and Mexico occurs through various channels, including:
- NAFTA/USMCA: The North American Free Trade Agreement (now replaced by the US-Mexico-Canada Agreement) eliminated tariffs and other trade barriers, fostering increased commerce between the three countries.
- Cross-Border Trucking: Thousands of trucks cross the border each day, transporting goods between the US and Mexico.
- Rail Transport: Rail lines connect the US and Mexico, facilitating the movement of freight and cargo.
5.2. What are the Major Industries Affected by the Border Economy?
Several major industries are significantly affected by the border economy, including:
- Manufacturing: Many US companies operate manufacturing facilities in Mexico, taking advantage of lower labor costs and proximity to the US market.
- Agriculture: Cross-border trade in agricultural products is substantial, with both countries importing and exporting fruits, vegetables, and other commodities.
- Tourism: Tourism is a major industry in border regions, with visitors traveling between the US and Mexico for leisure, recreation, and cultural experiences.
 Border Trade
Border Trade
Border trade helps improve financial growth for families, businesses and corporations.
5.3. How does the Border Impact Job Creation?
The border impacts job creation in both the US and Mexico, supporting employment in various sectors.
- Manufacturing Jobs: US companies operating in Mexico create jobs for Mexican workers, while also supporting jobs in the US through supply chain activities.
- Trade and Logistics: Cross-border trade generates employment in transportation, warehousing, and logistics industries on both sides of the border.
- Tourism and Hospitality: Tourism-related businesses, such as hotels, restaurants, and tour operators, provide jobs for local residents in border regions.
6. Cultural Exchange and Border Communities
Cultural exchange thrives in border communities, creating unique blends of traditions, languages, and identities.
6.1. What are the Cultural Influences in Border Regions?
Cultural influences in border regions reflect the fusion of Mexican and American traditions, resulting in:
- Cuisine: Border cuisine combines elements of Mexican and American cooking, creating unique dishes and flavors.
- Music: Border music blends traditional Mexican genres with American styles, producing distinctive sounds and rhythms.
- Art: Border art reflects the experiences and perspectives of border communities, often addressing themes of identity, migration, and cultural exchange.
6.2. How do Border Communities Interact?
Border communities interact through various channels, including:
- Family Ties: Many families have members living on both sides of the border, maintaining close relationships and frequent contact.
- Cross-Border Shopping: Residents of border communities often cross the border to shop for goods and services, supporting local businesses in both countries.
- Cultural Events: Cultural events, such as festivals, concerts, and art exhibitions, bring people together from both sides of the border to celebrate their shared heritage.
6.3. What Challenges do Border Communities Face?
Border communities face unique challenges, including:
- Economic Disparities: Economic disparities between the US and Mexico can create social tensions and inequalities in border regions.
- Environmental Issues: Environmental issues, such as air and water pollution, affect border communities, requiring collaborative solutions.
- Security Concerns: Security concerns related to drug trafficking and illegal immigration impact border communities, necessitating coordinated law enforcement efforts.
7. Environmental Issues Along the Border
Environmental issues along the border pose significant challenges for ecosystems and human health, requiring binational cooperation.
7.1. What Environmental Challenges Exist?
Several environmental challenges exist along the border, including:
- Water Scarcity: Water scarcity is a pressing issue in arid border regions, exacerbated by population growth, agricultural demands, and climate change.
- Air Pollution: Air pollution from industrial activities, vehicle emissions, and cross-border pollution sources affects air quality in border communities.
- Habitat Loss: Habitat loss due to urbanization, agriculture, and infrastructure development threatens biodiversity and ecosystem integrity in border regions.
7.2. How do These Issues Impact Local Communities?
These environmental issues impact local communities in various ways:
- Public Health: Air and water pollution can lead to respiratory illnesses, waterborne diseases, and other health problems, disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations.
- Economic Impacts: Environmental degradation can harm agriculture, tourism, and other industries, reducing economic opportunities for local residents.
- Quality of Life: Environmental degradation can diminish the quality of life in border communities, affecting recreational opportunities, aesthetic values, and overall well-being.
7.3. What Conservation Efforts are Underway?
Various conservation efforts are underway to address environmental issues along the border, including:
- Binational Agreements: Binational agreements between the US and Mexico promote cooperation on environmental issues, such as water management, air quality, and wildlife conservation.
- Restoration Projects: Restoration projects aim to rehabilitate degraded ecosystems, such as wetlands, rivers, and forests, enhancing their ecological functions and benefits.
- Community Engagement: Community engagement initiatives involve local residents in conservation efforts, fostering stewardship and promoting sustainable practices.
8. LGBTQ+ Travel and Community in Mexico
For LGBTQ+ travelers, Mexico offers a vibrant and welcoming environment with diverse destinations and communities.
8.1. What are LGBTQ+ Friendly Destinations in Mexico?
Several destinations in Mexico are known for being particularly LGBTQ+ friendly, including:
- Puerto Vallarta: A popular resort town with a thriving LGBTQ+ scene, offering gay-friendly hotels, bars, and beaches.
- Mexico City: A cosmopolitan capital with a diverse LGBTQ+ community, offering a wide range of cultural attractions and nightlife options.
- Cancun: A popular tourist destination with a growing LGBTQ+ scene, offering gay-friendly resorts, beaches, and entertainment venues.
8.2. What Resources are Available for LGBTQ+ Travelers?
Various resources are available for LGBTQ+ travelers planning trips to Mexico, including:
- GayMexico.net: A comprehensive online resource providing information on LGBTQ+ travel, events, and community resources in Mexico.
- LGBTQ+ Travel Guides: Travel guides specifically tailored to LGBTQ+ travelers offer recommendations on gay-friendly hotels, bars, restaurants, and attractions.
- Online Forums and Communities: Online forums and communities provide opportunities for LGBTQ+ travelers to connect with locals, share travel tips, and seek advice.
8.3. What Legal Protections Exist for LGBTQ+ Individuals in Mexico?
Legal protections for LGBTQ+ individuals in Mexico vary by region, but significant progress has been made in recent years.
- Marriage Equality: Same-sex marriage is legal throughout Mexico, providing LGBTQ+ couples with the same rights and protections as heterosexual couples.
- Anti-Discrimination Laws: Many states and cities have enacted anti-discrimination laws protecting LGBTQ+ individuals from discrimination in employment, housing, and public accommodations.
- Gender Identity Recognition: Some jurisdictions have implemented policies allowing transgender individuals to change their legal gender, although challenges remain in some areas.
9. Border Politics and Policy Debates
Border politics and policy debates are ongoing, reflecting differing perspectives on issues such as immigration, security, and trade.
9.1. What are the Key Political Issues?
Key political issues related to the border include:
- Immigration Reform: Immigration reform is a perennial topic of debate, with differing views on issues such as border security, pathways to citizenship, and enforcement policies.
- Border Security: Border security measures are subject to ongoing scrutiny, with debates over the effectiveness of physical barriers, technology, and law enforcement strategies.
- Trade Relations: Trade relations between the US and Mexico are closely monitored, with concerns about the impact of trade policies on jobs, wages, and economic competitiveness.
9.2. How do Different Political Parties View the Border?
Different political parties hold contrasting views on border issues, reflecting their broader ideological positions.
- Democrats: Democrats generally favor comprehensive immigration reform, including pathways to citizenship for undocumented immigrants, and emphasize the importance of humane border policies.
- Republicans: Republicans typically prioritize border security, advocating for stricter enforcement measures and increased investment in physical barriers and technology.
- Third Parties: Third parties often offer alternative perspectives on border issues, challenging the dominant narratives and proposing innovative solutions.
9.3. What Role do Interest Groups Play in Shaping Border Policy?
Interest groups play a significant role in shaping border policy, advocating for their members’ interests and influencing public opinion.
- Business Groups: Business groups advocate for policies that promote trade and investment, seeking to reduce barriers to cross-border commerce.
- Immigrant Rights Organizations: Immigrant rights organizations advocate for the rights and protections of immigrants, seeking to reform immigration laws and challenge discriminatory practices.
- Security Organizations: Security organizations advocate for policies that enhance border security, supporting increased investment in law enforcement and technology.
10. The Future of the US-Mexico Border
The future of the US-Mexico border is uncertain, shaped by evolving political, economic, and social forces.
10.1. What are the Potential Future Scenarios?
Potential future scenarios for the border include:
- Increased Security: Increased security measures could lead to tighter border control, reduced illegal immigration, and enhanced law enforcement capabilities.
- Economic Integration: Deeper economic integration could foster increased trade, investment, and job creation, strengthening economic ties between the US and Mexico.
- Regional Cooperation: Enhanced regional cooperation could address shared challenges, such as environmental issues, security threats, and migration flows, promoting sustainable development and stability.
10.2. How Might Climate Change Impact the Border Region?
Climate change could have significant impacts on the border region, including:
- Water Scarcity: Increased temperatures and reduced rainfall could exacerbate water scarcity, leading to conflicts over water resources and straining agricultural production.
- Extreme Weather Events: More frequent and intense extreme weather events, such as droughts, floods, and hurricanes, could disrupt economic activities and displace communities.
- Migration Flows: Climate change could drive increased migration from vulnerable regions, potentially increasing pressure on border communities and resources.
10.3. What Role Will Technology Play in the Border’s Evolution?
Technology is likely to play an increasingly important role in the border’s evolution, with advancements in:
- Surveillance Technology: Advanced surveillance systems, such as drones, sensors, and facial recognition technology, could enhance border monitoring and enforcement capabilities.
- Automation: Automation technologies, such as robotic border patrol units and automated cargo inspection systems, could streamline border operations and reduce labor costs.
- Data Analytics: Data analytics tools could analyze border crossing patterns and trends, helping law enforcement agencies identify potential risks and allocate resources effectively.
Navigating the complexities of the US-Mexico border requires up-to-date information and a commitment to inclusivity, and gaymexico.net provides the resources you need.
A peaceful sunset over the US-Mexico border symbolizes hope and community.
FAQ: Understanding the US-Mexico Border
1. How long is the Mexican border with the US?
The Mexican border with the US is approximately 1,954 miles (3,145 kilometers) long. This vast expanse stretches across four U.S. states, marking a significant boundary between two nations.
2. Which US states share a border with Mexico?
Four US states share a border with Mexico: California, Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas. Each state brings its own unique culture and landscape to the border region.
3. What is the significance of the US-Mexico border region?
The border region is significant for its economic, cultural, and social interactions. It serves as a hub for trade, cultural exchange, and diverse communities, fostering a unique blend of traditions and influences.
4. How did the US-Mexico border come to be?
The border’s demarcation primarily stems from the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo in 1848, which concluded the Mexican-American War. This treaty ceded a significant portion of Mexican territory to the United States, shaping the border we know today.
5. What physical barriers exist along the US-Mexico border?
Physical barriers include fences, walls, and surveillance technology. These structures aim to deter illegal crossings and enhance border security, although their effectiveness is often debated.
6. How do people legally cross the US-Mexico border?
People can legally cross the border through designated ports of entry using valid travel documents such as visas and border crossing cards. Programs like SENTRI and Global Entry also expedite crossings for pre-approved travelers.
7. What are the economic impacts of the US-Mexico border?
The border significantly impacts trade, manufacturing, agriculture, and tourism. It supports job creation in transportation, warehousing, and hospitality industries on both sides, fostering economic interdependence.
8. What cultural influences are prominent in border regions?
Border regions blend Mexican and American traditions, influencing cuisine, music, and art. This fusion creates unique cultural expressions that reflect the shared heritage and experiences of border communities.
9. What are some LGBTQ+ friendly destinations near the US-Mexico border?
While not directly on the border, cities like Puerto Vallarta and Mexico City are known for being LGBTQ+ friendly, offering welcoming environments with gay-friendly hotels, bars, and cultural attractions.
10. How can I stay informed about LGBTQ+ travel and community in Mexico?
Stay informed by visiting gaymexico.net, a comprehensive online resource providing information on LGBTQ+ travel, events, and community resources in Mexico. It’s your go-to guide for navigating Mexico with confidence and discovering welcoming destinations.
For LGBTQ+ travelers, understanding the US-Mexico border and its surrounding communities is essential for a safe and enriching experience. Whether you’re interested in exploring the region’s culture, history, or natural beauty, knowledge is key to making informed decisions and embracing the diversity of Mexico.
Are you ready to explore the vibrant LGBTQ+ scene in Mexico? Visit gaymexico.net for detailed travel guides, event listings, and community insights. Plan your adventure today and discover a welcoming and inclusive destination! Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States. Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177. Website: gaymexico.net.