The 2024 Mexican Presidential Election, which saw Claudia Sheinbaum of the MORENA party win, holds significant implications for LGBTQ+ individuals and allies in Mexico and beyond; gaymexico.net provides comprehensive coverage. This election will shape policies, influence social attitudes, and potentially alter the landscape for LGBTQ+ rights and acceptance in Mexico, impacting everything from travel safety to community resources. To discover LGBTQ-friendly destinations and events, visit gaymexico.net for updated travel advisories, community connections, and details on legal advancements.
1. What Were the Key Outcomes of the 2024 Mexican Presidential Election?
Claudia Sheinbaum of the Movimiento de Regeneración Nacional (MORENA) party won the 2024 presidential election with nearly 60% of the vote, marking a historic moment as the first woman president of Mexico. Alongside the presidential election, voters also participated in legislative, state, and municipal elections. The election cycle was marred by violence, with over 330 incidents against political figures recorded by ACLED between March 1 and June 2, including at least 95 fatal incidents.
How Did Violence Affect the Electoral Process?
The high levels of violence during the 2024 campaign period were unprecedented, surpassing the violence seen in the 2018 and 2021 elections. Many candidates, fearing for their safety, requested state protection, while others withdrew from the race due to threats, highlighting a critical challenge to democratic processes in Mexico. Despite these issues, substantive proposals to address the violence were notably absent from the leading presidential candidates’ platforms.
2. Where Did Violent Attacks Primarily Occur During the Election?
The majority of violent attacks during the 2024 Mexican elections were concentrated at the local level, with over 80% of incidents targeting candidates running for local positions such as mayoralties and municipal councils. While national attention often focuses on presidential races, these local contests frequently become flashpoints for violence due to intense competition and the involvement of organized crime groups.
Why Were Local Elections More Prone to Violence?
Local elections tend to be more vulnerable to violence because they directly impact the control of resources, local governance, and law enforcement within communities. This proximity to power attracts the interest of organized crime groups and rival political factions, leading to heightened tensions and violent incidents.
Case Study: Veracruz and Municipal Elections
Veracruz provides a clear example of how local elections can escalate violence. In the 2021 municipal elections, Veracruz experienced the highest level of violence against political figures, with 57 events recorded in the six months leading up to the vote. However, with no municipal elections in 2024, violence significantly decreased, illustrating the direct correlation between local electoral contests and political violence.
3. How Were Local Authorities Targeted During the Election Period?
Current and former officials who were not running for new positions were targeted in more than 40% of violent events, indicating a deliberate effort to exert pressure on local authorities. This trend underscores attempts to influence political processes beyond election cycles and highlights the risks faced by public servants in Mexico.
Who Were the Most Frequent Targets Among Non-Elected Officials?
Officials dealing with judicial and security matters, as well as public administration treasurers, were the most frequently targeted non-elected officials. This targeting often stems from organized crime groups seeking to control local resources and critical administrative areas.
The Impact on Officials’ Families
Family members of politicians were also victims in approximately 14% of attacks, either as direct targets or related casualties. Violence against family members is often intended to pressure political figures, as illustrated by the attempted assassination of the Tacámbaro mayor’s brother by suspected CJNG members.
4. When Did Electoral Violence Occur During the Election Cycle?
Violence targeting political figures began increasing well before the official campaign period, with an initial spike in October 2023, following the start of the “citizen support” period. This violence escalated further in February, coinciding with the end of the pre-campaign period, and peaked during the official campaign months of March, April, and May.
Why Does Violence Escalate Before and After the Campaign?
Violence occurring early in the election cycle is often aimed at marking territory and deterring candidates perceived as threats. Post-election violence is also common, with attacks continuing through the “Toma de Protesta” ceremonies and into new administrations, indicating ongoing instability.
Data on Post-Election Violence
ACLED data from previous election cycles shows a consistent pattern of post-election violence, with 210 and 179 events recorded in the six months following the 2018 and 2021 elections, respectively. This highlights the enduring risks faced by political figures in Mexico.
5. How Does Organized Crime Influence Electoral Violence?
Competition between organized crime groups is a significant driver of election-related violence in Mexico. States with high levels of organized crime violence, such as Guanajuato, Michoacán, and Guerrero, also experience high levels of violence against political figures. This indicates that criminal organizations use violence to influence elections and maintain control.
Exceptions to the Rule: Jalisco and Sinaloa
However, there are exceptions to this trend. In Jalisco and Sinaloa, strongholds of the CJNG and Sinaloa Cartel, respectively, lower levels of violence against political figures suggest that these groups exert such dominance that they do not need to resort to violence to secure their influence.
The Role of Hegemony in Reducing Violence
When a single organized crime group holds a hegemonic position, it may reduce the need for widespread violence against political figures. Instead, these groups focus on maintaining territorial control and addressing localized disputes with smaller rival groups.
6. What Role Do Local Power Struggles Play in Generating Violence?
Beyond direct attacks on political figures, a substantial portion (30%) of incidents during the 2024 elections involved riots and property destruction. These events often reflect public discontent with local representatives or rivalries between political actors.
Where Was This Type of Violence Most Prominent?
These types of incidents were particularly prominent in Chiapas, Puebla, and Hidalgo, states known for their susceptibility to local power struggles and electoral disputes. Pre-existing inter-community conflicts and the concentration of power in the hands of local strongmen (caciques) exacerbate these tensions.
How Are Protests and Demonstrations Linked to Electoral Violence?
Before election campaigns begin, violence often erupts during protests where demonstrators confront representatives for failing to meet their demands. Property destruction and collective violence are also used by political contenders to intimidate adversaries.
7. How Did Gender Impact Violence in the 2024 Mexican Elections?
Women, particularly those running for public office, faced significant violence during the 2024 election cycle. At least 69 incidents targeted women, representing 13% of the violence, and female candidates often received more threats than their male counterparts.
What Challenges Do Women Face in Mexican Politics?
Despite directives from the National Electoral Institute to ensure gender parity in candidacies, women remain underrepresented in local official bodies. In 2023, only 28% of local positions were held by women, making them particularly vulnerable to threats and violence aimed at deterring their participation in politics.
The Impact of Threats on Female Candidates
Many female candidates are forced to withdraw from the race due to threats, as exemplified by the 217 women who resigned from their candidacies in Zacatecas alone. This underscores the need for greater protection and support for women in Mexican politics.
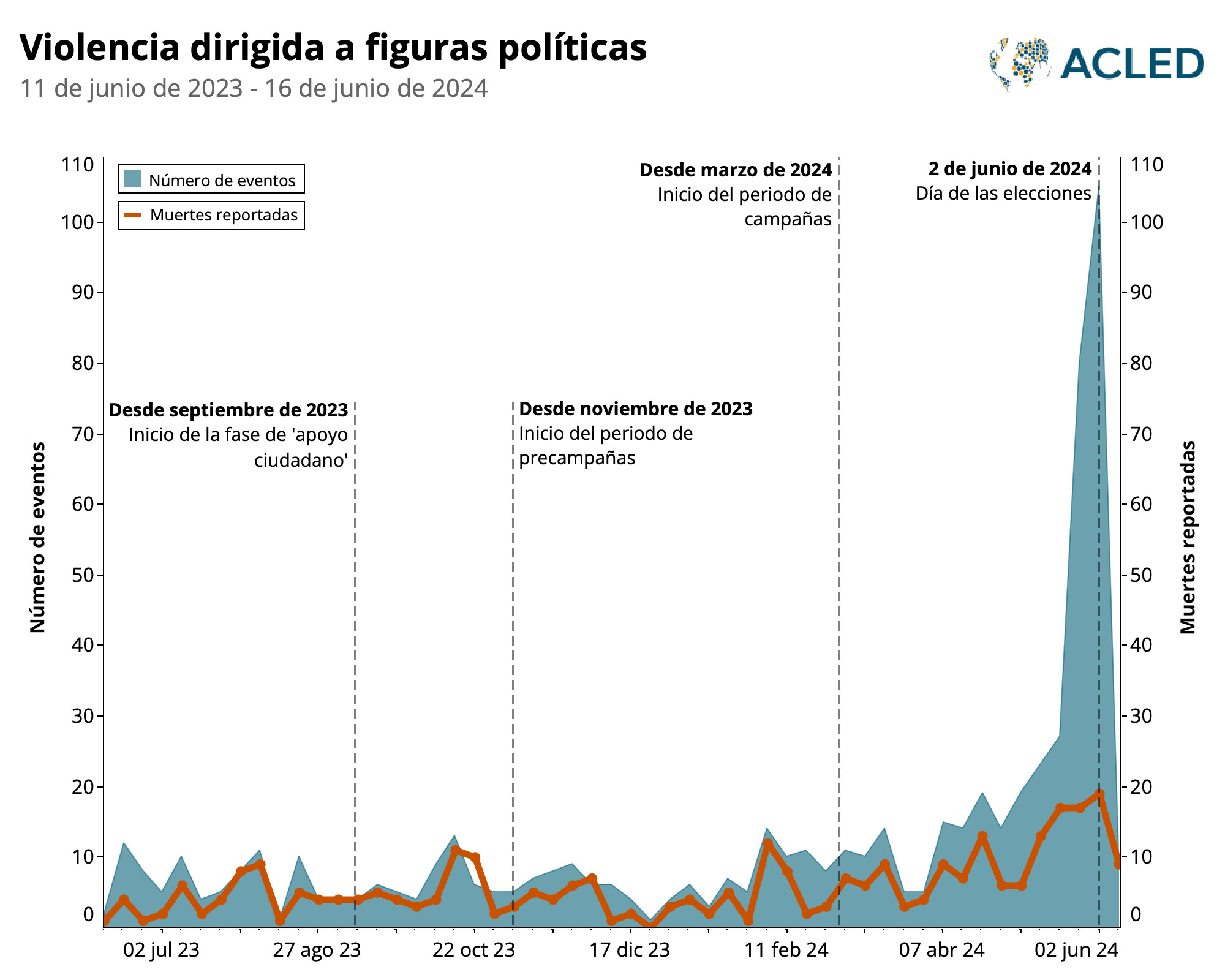 Violence targeting political figures in Mexico, showing an increase in the months leading up to the 2024 elections.
Violence targeting political figures in Mexico, showing an increase in the months leading up to the 2024 elections.
8. What Were the Main Types of Violence Experienced During the Election?
The violence during the 2024 Mexican elections encompassed a range of incidents, from direct attacks on political figures to broader acts of social and political unrest. Understanding these different forms of violence is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate electoral conflict.
Assassination and Homicides
Assassination and homicides are the most severe forms of violence, often targeting candidates, current or former officials, and their families. These acts are intended to eliminate political rivals or intimidate those in power.
Armed Attacks
Armed attacks involve the use of firearms and other weapons to cause injury or death. These attacks can range from targeted shootings to larger-scale assaults on political rallies or campaign events.
Threats and Intimidation
Threats and intimidation are used to create fear and deter political participation. These can include verbal threats, harassment, and the display of force, aimed at influencing candidates, voters, or election officials.
Kidnappings
Kidnappings are carried out to exert pressure on political figures or to extract information or concessions. Kidnappings can have a chilling effect on political activity and undermine trust in the electoral process.
Riots and Protests
Riots and protests often erupt in response to perceived injustices or grievances related to the electoral process. These events can escalate into violence, resulting in property damage, injuries, and even fatalities.
Property Destruction
Property destruction involves the deliberate damaging or destroying of property, such as campaign offices, vehicles, or homes. This form of violence is intended to disrupt political activity and send a message of intimidation.
Voter Suppression
Voter suppression tactics are used to prevent or discourage certain groups from participating in elections. These tactics can include restrictive voter ID laws, gerrymandering, and intimidation at polling places.
9. What Legal and Policy Changes Can Address Electoral Violence?
Addressing electoral violence requires a multi-faceted approach involving legal reforms, enhanced security measures, and efforts to strengthen democratic institutions. Several strategies can be implemented to mitigate the risk of violence and ensure free and fair elections.
Strengthening Legal Frameworks
Strengthening legal frameworks involves enacting and enforcing laws that criminalize electoral violence and provide penalties for perpetrators. This includes laws against intimidation, voter suppression, and attacks on political figures.
Enhancing Security Measures
Enhancing security measures includes providing protection for candidates, election officials, and polling places. This can involve deploying security forces, implementing surveillance technology, and establishing safe zones around electoral events.
Promoting Transparency and Accountability
Promoting transparency and accountability involves ensuring that the electoral process is open and accessible to all citizens. This includes measures such as public disclosure of campaign finance, independent monitoring of elections, and mechanisms for addressing complaints and grievances.
Strengthening Democratic Institutions
Strengthening democratic institutions involves building the capacity of electoral bodies, promoting civic education, and fostering a culture of respect for the rule of law. This can help to reduce political polarization and promote peaceful resolution of disputes.
Addressing Root Causes of Violence
Addressing the root causes of violence involves tackling issues such as poverty, inequality, and organized crime. This requires a comprehensive approach that includes social and economic development programs, as well as efforts to combat corruption and impunity.
10. What Can International Organizations Do to Support Peaceful Elections?
International organizations can play a crucial role in supporting peaceful elections in Mexico and other countries. This support can take various forms, including providing technical assistance, monitoring elections, and advocating for reforms.
Providing Technical Assistance
International organizations can provide technical assistance to electoral bodies, helping them to improve their capacity to conduct free, fair, and transparent elections. This can include assistance with voter registration, election administration, and dispute resolution.
Monitoring Elections
International election observers can monitor elections to ensure that they are conducted in accordance with international standards. Their presence can deter fraud and intimidation, and their reports can provide valuable insights into the electoral process.
Advocating for Reforms
International organizations can advocate for reforms to address electoral violence and strengthen democratic institutions. This can include advocating for legal reforms, promoting transparency and accountability, and supporting civil society organizations working to promote peaceful elections.
Providing Humanitarian Assistance
In cases where electoral violence results in humanitarian crises, international organizations can provide assistance to those affected. This can include providing food, shelter, medical care, and other essential services.
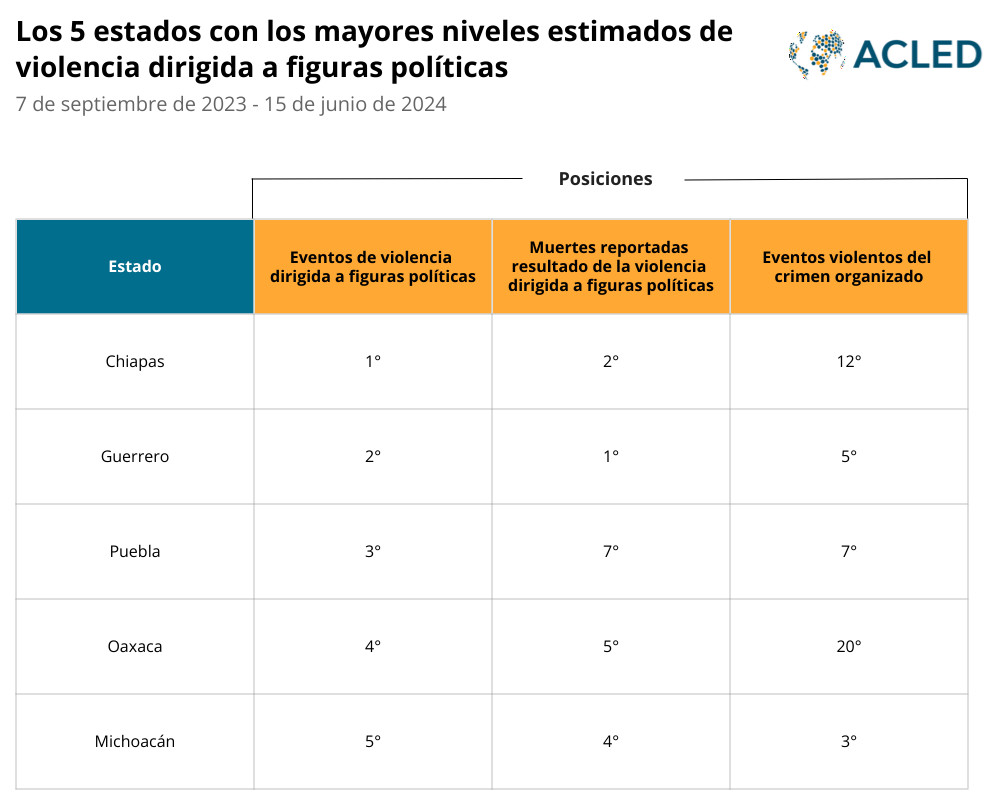 Mexican states ranked by violence against political figures, highlighting regional disparities in electoral security.
Mexican states ranked by violence against political figures, highlighting regional disparities in electoral security.
By understanding these key aspects of the 2024 Mexican presidential election and its implications, readers can gain valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities facing Mexico’s democratic processes. For more detailed information, resources, and community connections, visit gaymexico.net.
The 2024 Mexican presidential election underscores the ongoing challenges of political violence and organized crime’s influence, highlighting the necessity for sustained reforms and community support. gaymexico.net remains committed to providing up-to-date information, safety tips, and resources for the LGBTQ+ community traveling to and residing in Mexico. Stay informed and connected by visiting us at gaymexico.net, or visit our office at 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States, or call +1 (213) 380-2177 for more details.
FAQ Section on the Mexican Presidential Election
-
What was the main outcome of the 2024 Mexican Presidential Election?
Claudia Sheinbaum of the MORENA party won the election, becoming Mexico’s first female president with nearly 60% of the vote. -
How did violence affect the 2024 Mexican elections?
The election cycle was marked by unprecedented violence, with over 330 incidents against political figures, leading some candidates to request protection or withdraw from the race. -
Which areas experienced the most violence during the election?
Most violent attacks targeted local-level candidates, particularly in states like Chiapas, Guerrero, and Michoacán. -
Why were local elections more susceptible to violence?
Local elections often involve intense competition for resources and governance, attracting interference from organized crime groups and rival political factions. -
Who was targeted besides candidates during the election period?
Current and former officials not running for election, along with their families, were also frequently targeted in violent acts. -
When did most of the electoral violence occur?
Violence began increasing before the official campaign, with spikes in October 2023 and February 2024, peaking during the campaign months. -
How does organized crime influence electoral violence in Mexico?
Organized crime groups use violence to control local politics and resources, particularly in states like Guanajuato and Michoacán, though strongholds like Jalisco and Sinaloa may see less direct violence due to existing dominance. -
What role do local power struggles play in generating violence?
Local power struggles often result in riots and property destruction, especially in states with existing inter-community conflicts like Chiapas, Puebla, and Hidalgo. -
How did gender impact violence during the 2024 Mexican elections?
Women, particularly those running for office, faced significant threats and violence, leading to withdrawals and highlighting underrepresentation in local government. -
What can be done to address electoral violence in Mexico?
Addressing electoral violence requires strengthening legal frameworks, enhancing security measures, promoting transparency, and tackling the root causes of violence like poverty and inequality.