The education system in Mexico plays a vital role in shaping the future of its citizens, and at gaymexico.net, we understand how important it is to be informed about education, especially for the LGBTQ+ community. From primary school to higher education, Mexico’s educational structure offers a diverse range of opportunities and challenges. For LGBTQ+ individuals and allies planning a visit or considering relocating, understanding the educational landscape is essential to ensure inclusive environments and informed decisions.
1. What are the Key Stages of Education in Mexico?
Mexico’s education system is divided into three main levels: basic education (educación básica), upper-secondary education (educación media superior), and higher education (educación superior). These levels include preschool, primary school, lower-secondary school, upper-secondary school, and tertiary education.
Basic Education (Educación Básica)
This level is compulsory and free, covering pre-school, primary, and secondary education.
- Preschool (Educación Preescolar): Three years, ages 3-6.
- Primary School (Educación Primaria): Six years, grades 1-6, ages 6-12.
- Lower-Secondary School (Educación Secundaria): Three years, grades 7-9, ages 12-15.
Upper-Secondary Education (Educación Media Superior)
This level includes high school and vocational training, preparing students for higher education or the workforce.
- General Bachillerato: Academic high school, typically grades 10-12.
- Technological Bachillerato: Technical high school, combining academic and vocational training.
- Professional Technical (Profesional Técnico): Vocational and technical education for direct entry into the workforce.
Higher Education (Educación Superior)
This level includes post-secondary and graduate studies at universities and technological institutes.
- Técnico Superior: Associate degree or diploma.
- Licenciatura: Bachelor’s degree.
- Postgrado: Graduate studies, including master’s and doctoral degrees.
2. How Does the Mexican Government Administer and Oversee Education?
The Secretaría de Educación Pública (SEP), or the Ministry of Education, governs the national education system in Mexico. The SEP sets educational policies, develops curricula, and oversees the operation of public schools. The SEP also works with state governments to ensure that national standards are met, and the federal government provides financial support to state education systems.
Key Responsibilities of the SEP
- Setting national education standards
- Developing and implementing curricula
- Overseeing the operation of public schools
- Providing financial support to state education systems
- Monitoring educational quality and outcomes
3. What are the Enrollment Rates and Educational Attainment Levels in Mexico?
Enrollment rates in Mexico have increased significantly over the past few decades, particularly in basic and upper-secondary education. According to UNESCO data, tertiary enrollment more than doubled between 2000 and 2017. However, disparities persist between urban and rural areas, as well as between different states. For example, literacy rates in Chiapas and Oaxaca are significantly lower than in Mexico City.
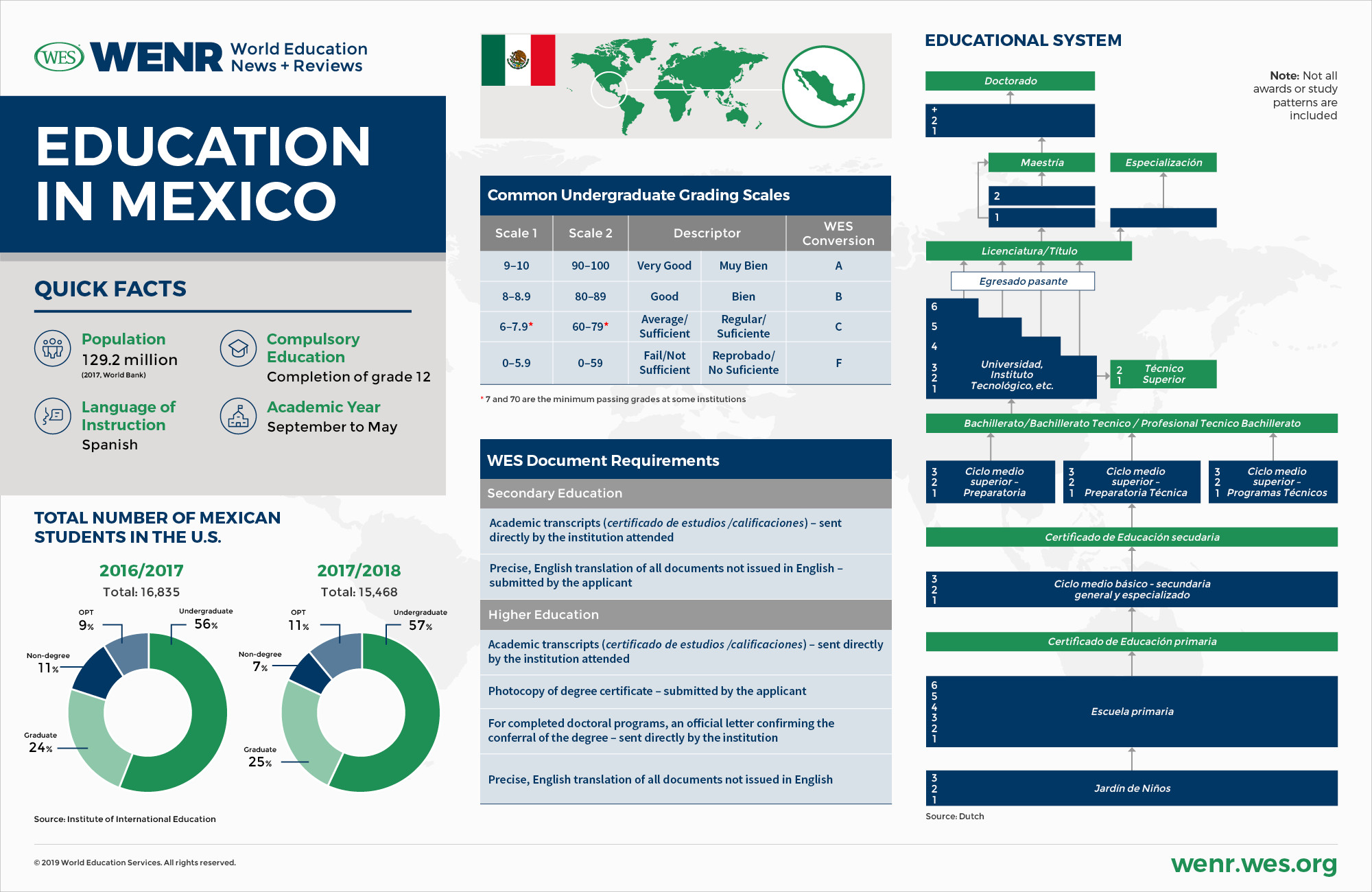 Education in Mexico infographic: quick facts about education in Mexico
Education in Mexico infographic: quick facts about education in Mexico
Enrollment Statistics
- Preschool: High enrollment rates, driven by mandatory attendance laws.
- Primary School: Nearly universal enrollment.
- Lower-Secondary School: Increasing enrollment rates due to mandatory education laws.
- Upper-Secondary School: Significant increases, but graduation rates remain a challenge.
- Higher Education: Growing enrollment, but still lags behind other Latin American countries.
4. What are the Main Challenges Facing the Mexican Education System?
Several challenges remain despite progress in education in Mexico. These include:
- Inequality: Significant disparities in educational opportunities and outcomes between different regions and socioeconomic groups.
- Quality: Concerns about the quality of education, particularly in public schools. Mexico ranks low in OECD PISA studies.
- Funding: Inadequate funding for education, particularly in marginalized rural regions.
- Teacher Training: Need for improved teacher training and professional development.
- Corruption: Issues with corruption in teacher hiring and promotion practices.
5. What is the Role of Private Education in Mexico?
Private education plays a significant role in Mexico, with a wide range of private schools and universities operating alongside public institutions. Private schools often offer smaller class sizes, specialized programs, and higher-quality facilities. However, private education can be expensive and inaccessible to low-income families.
Key Aspects of Private Education
- Variety: Diverse range of private schools, from religious institutions to international schools.
- Quality: Some private schools offer high-quality education, but quality varies.
- Accessibility: Limited accessibility for low-income families due to tuition fees.
- Regulation: Oversight criteria for private HEIs vary and are sometimes inadequate.
6. How Does Mexico Address the Needs of Indigenous and Rural Communities in Education?
Mexico has made efforts to address the needs of indigenous and rural communities through bilingual education programs, community schools, and financial assistance for students. However, significant challenges remain in ensuring equitable access to quality education for these marginalized groups.
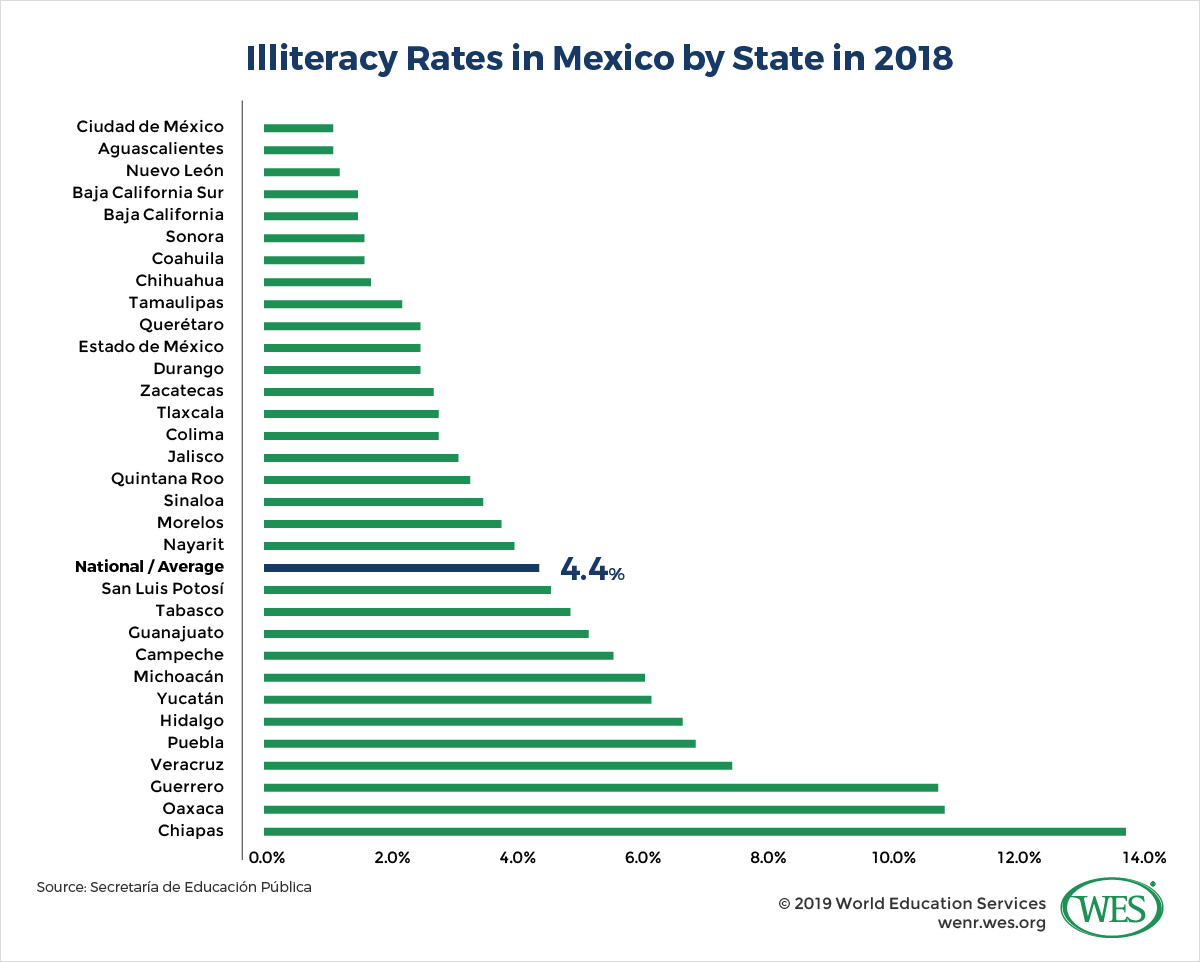 Education in Mexico image 2: Illiteracy rates in Mexico by state in 2018 with the national average at 4.4 percent
Education in Mexico image 2: Illiteracy rates in Mexico by state in 2018 with the national average at 4.4 percent
Strategies for Indigenous and Rural Education
- Bilingual Education: Programs that provide instruction in both Spanish and indigenous languages.
- Community Schools: Schools located in rural districts with small populations.
- Financial Assistance: Scholarships and grants to help students from low-income families attend school.
- Intercultural Universities: Institutions that focus on indigenous cultures and languages.
7. What is the Grading System and Credit System Used in Mexican Schools?
Mexican schools use a numerical grading system, typically on a scale of 0 to 10, with 6 or 7 as the passing grade. There is no nationwide credit system, although some universities use the SATCA credit system. Grading scales vary between HEIs, so it is essential to understand the specific grading system used by each institution.
Common Grading Scales
| Grade Range | Description | WES Conversion |
|---|---|---|
| 9-10 | Excellent | A |
| 8-8.9 | Good | B |
| 7-7.9 | Satisfactory | C |
| 6-6.9 | Passing | D |
| Below 6 | Failing | F |
8. What Types of Higher Education Institutions Exist in Mexico?
Mexico’s higher education system includes public and private institutions, ranging from federal and state universities to technological institutes and private universities. Autonomous HEIs, like the National Autonomous University of Mexico, enjoy a high degree of academic and administrative freedom.
Types of HEIs
- Federal Universities: Overseen and funded by the SEP and other federal agencies.
- State Universities: Operate under the auspices of state governments.
- Autonomous HEIs: Publicly funded but with academic and administrative freedom.
- Private HEIs: Include well-established elite institutions and smaller for-profit schools.
9. What are the Admission Requirements for Mexican Universities?
Admission requirements for Mexican universities vary depending on the institution and program. Completion of upper-secondary education is typically the minimum requirement, but entrance examinations and high school GPAs are also considered. Some universities have open enrollment policies, while others are highly selective.
Common Admission Criteria
- Completion of upper-secondary education
- Entrance examinations (e.g., EXANI-II)
- High school GPA
- Minimum grade average (e.g., 7 or 8 out of 10)
- Related high school track
10. What Measures are Being Taken to Improve the Quality of Education in Mexico?
Mexico has implemented several measures to improve the quality of education, including:
- National Curriculum Framework: Aims to harmonize upper-secondary education.
- Accreditation: Voluntary accreditation of programs by agencies under COPAES.
- Quality Assurance: Efforts to improve quality control in private HEIs.
- Teacher Training: Reforms to strengthen teacher training and professional development.
11. How Does the Education System in Mexico Support LGBTQ+ Students?
While Mexico has made progress in LGBTQ+ rights, the education system may not always provide comprehensive support for LGBTQ+ students. It is vital for LGBTQ+ individuals and allies to be aware of the resources and support systems available in different schools and universities.
Potential Resources and Support
- Inclusive Policies: Look for schools and universities with inclusive policies that protect LGBTQ+ students from discrimination.
- LGBTQ+ Organizations: Connect with local LGBTQ+ organizations for support and resources.
- Safe Spaces: Seek out safe spaces and support groups within educational institutions.
- Awareness Programs: Advocate for LGBTQ+ awareness and inclusion programs in schools.
For those in the LGBTQ+ community considering Mexico for education or travel, resources such as gaymexico.net can provide valuable insights and support. Understanding the educational system and the local LGBTQ+ community can help ensure a more inclusive and welcoming experience.
12. What is Proyecta 100,000 and How Did It Impact Mexican Enrollments in the U.S.?
Proyecta 100,000 was an initiative launched by Mexico in 2014 to increase the number of Mexican students studying in the U.S. to 100,000 by 2018, while also increasing the number of U.S. students in Mexico to 50,000. This project involved scholarships and university partnerships to fuel academic exchange between the two countries. According to data from the Institute of International Education (IIE), Mexican enrollments in the U.S. increased by 15.4 percent between 2012/13 and 2014/15 alone, following a 50 percent increase over the previous 14 years.
Key Impacts of Proyecta 100,000
- Increased Enrollments: Significant growth in Mexican students studying in the U.S.
- Scholarship Programs: Provided financial support for Mexican students.
- University Partnerships: Enhanced academic collaborations between U.S. and Mexican institutions.
13. What Factors Have Led to a Recent Downturn in Student Flows from Mexico to the U.S.?
Despite the initial success of initiatives like Proyecta 100,000, Mexican student enrollments in the U.S. have recently declined. Several factors have contributed to this downturn:
- Anti-Mexican Sentiment: Political rhetoric and policies perceived as anti-Mexican have deterred students.
- Economic Factors: Fluctuations in currency exchange rates and economic conditions can affect affordability.
- Visa Issues: Difficulties in obtaining U.S. student visas.
- Shifting Preferences: Diversification of study destinations among Mexican students.
14. How Does the Curriculum in Mexico Incorporate Cultural and Social Values?
The curriculum in Mexico incorporates cultural and social values by including subjects such as history, civics, and arts, which aim to promote national identity and cultural awareness. Additionally, bilingual education programs for indigenous communities help preserve indigenous languages and cultures. According to the Mexican government, the curriculum is designed to foster respect for diversity and promote social cohesion.
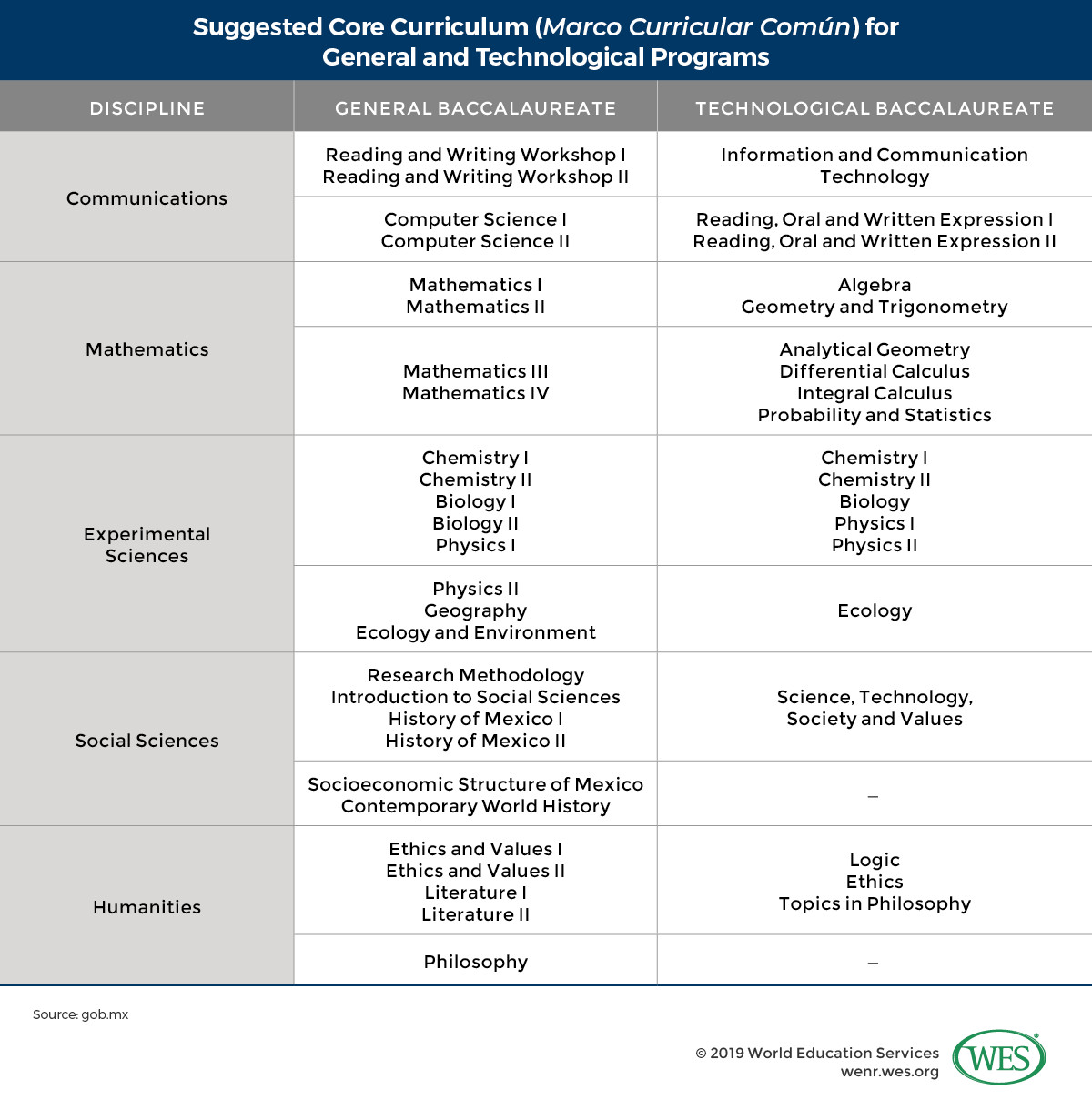 Education in Mexico image 6: the suggested core curriculum for general and technological programs
Education in Mexico image 6: the suggested core curriculum for general and technological programs
Curriculum Components
- History and Civics: Subjects that promote national identity and civic responsibility.
- Arts Education: Encourages cultural expression and appreciation.
- Bilingual Programs: Support indigenous languages and cultures.
- Values Education: Focus on respect, tolerance, and social responsibility.
15. What Support Services are Available for Students with Disabilities in Mexican Schools?
Support services for students with disabilities in Mexican schools vary, but efforts have been made to increase inclusivity. Special education programs, resource centers, and teacher training initiatives aim to provide necessary accommodations and support. According to a report by the Mexican Ministry of Education, inclusive education is a priority, but implementation varies across different regions and schools.
Support Services
- Special Education Programs: Tailored educational programs for students with disabilities.
- Resource Centers: Provide support and resources for students and teachers.
- Teacher Training: Initiatives to train teachers in inclusive education practices.
- Accessibility Measures: Efforts to improve physical accessibility in schools.
16. How Are Technological Skills Integrated Into the Mexican Education System?
Technological skills are increasingly integrated into the Mexican education system through computer labs, digital resources, and online learning platforms. The government has launched initiatives to provide schools with technology infrastructure and train teachers to use digital tools effectively. According to a study by the National Institute for Educational Evaluation (INEE), access to technology varies across schools, with urban areas generally having better resources than rural areas.
Integration of Technology
- Computer Labs: Providing access to computers and internet in schools.
- Digital Resources: Use of online educational materials and software.
- Online Learning Platforms: Offering distance education and virtual classrooms.
- Teacher Training: Training teachers to integrate technology into their teaching methods.
17. What is the Role of Extracurricular Activities in Mexican Schools?
Extracurricular activities play an important role in Mexican schools, providing students with opportunities to develop skills, explore interests, and engage in social and cultural activities. These activities include sports, arts, clubs, and community service. Participation in extracurricular activities can enhance students’ overall educational experience and promote personal growth.
Types of Extracurricular Activities
- Sports: Athletics, soccer, basketball, and other sports.
- Arts: Music, dance, theater, and visual arts.
- Clubs: Academic, cultural, and social clubs.
- Community Service: Volunteer work and community engagement.
18. How Does the Mexican Education System Prepare Students for the Global Job Market?
The Mexican education system prepares students for the global job market by focusing on developing skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, and technological literacy. Additionally, some programs offer international exchange opportunities and language training to enhance students’ global competitiveness. According to a report by the OECD, Mexico needs to further strengthen its education system to better align with the demands of the global job market.
Preparation for the Job Market
- Skills Development: Focus on critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication.
- Technological Literacy: Integration of technology in education.
- International Exchanges: Providing opportunities for international study and work.
- Language Training: Emphasis on learning English and other foreign languages.
19. What Are the Recent Reforms and Policy Changes in the Mexican Education System?
Recent reforms and policy changes in the Mexican education system aim to improve quality, equity, and relevance. These include reforms to teacher evaluation, curriculum updates, and increased investment in educational infrastructure. The current administration has also emphasized the importance of vocational and technical education to meet the needs of the labor market.
Recent Reforms
- Teacher Evaluation: New systems for evaluating and training teachers.
- Curriculum Updates: Modernizing the curriculum to align with global standards.
- Infrastructure Investment: Increased funding for school construction and renovation.
- Vocational Education: Emphasis on technical and vocational training.
20. How Can LGBTQ+ Individuals and Allies Support Inclusive Education in Mexico?
LGBTQ+ individuals and allies can support inclusive education in Mexico by advocating for inclusive policies, promoting LGBTQ+ awareness, and supporting organizations that work to create safe and welcoming environments in schools. Additionally, they can serve as role models and mentors for LGBTQ+ students. According to Human Rights Watch, creating inclusive education environments is essential for promoting the well-being and success of LGBTQ+ students.
Supporting Inclusive Education
- Advocate for Policies: Promote inclusive policies that protect LGBTQ+ students.
- Raise Awareness: Conduct LGBTQ+ awareness campaigns and workshops.
- Support Organizations: Contribute to LGBTQ+ organizations working in education.
- Serve as Mentors: Provide guidance and support to LGBTQ+ students.
For more detailed information and resources, visit gaymexico.net, where you can find comprehensive guides, community support, and up-to-date information on LGBTQ+ life in Mexico.
21. What Types of Financial Aid and Scholarships are Available for Students in Mexico?
Financial aid and scholarships are available to support students at various levels of education in Mexico. These resources come from both government and private organizations, helping to ensure that more students can access educational opportunities. For LGBTQ+ students, specific scholarships or aid programs may be available through advocacy groups and community organizations.
Financial Aid and Scholarship Types
- Government Scholarships: Programs offered by the federal and state governments.
- University Scholarships: Scholarships provided by individual universities.
- Private Scholarships: Scholarships from private foundations and organizations.
- Student Loans: Government-backed and private student loan programs.
22. How Does the Mexican Education System Integrate Technology to Enhance Learning?
The Mexican education system is integrating technology to enhance learning through several initiatives, including providing computer labs, digital resources, and online learning platforms. However, the availability and quality of these resources vary across different regions and schools.
Technology Integration Methods
- Computer Labs: Schools equip computer labs for digital learning.
- Digital Resources: Use of online textbooks, educational software, and multimedia content.
- Online Platforms: Adoption of platforms for distance learning and virtual classrooms.
- Teacher Training: Training teachers to use technology effectively in their instruction.
23. What Are the Key Initiatives for Promoting Lifelong Learning and Adult Education in Mexico?
Mexico has several initiatives aimed at promoting lifelong learning and adult education, including programs for literacy, vocational training, and continuing education. These programs help adults gain new skills and improve their employment prospects.
Lifelong Learning Initiatives
- Literacy Programs: Programs to improve adult literacy rates.
- Vocational Training: Training programs for adults to learn new skills.
- Continuing Education: Courses and programs for professional development and personal enrichment.
- Community Learning Centers: Centers providing educational opportunities in local communities.
24. How Does the Mexican Government Collaborate with International Organizations to Improve Education?
The Mexican government collaborates with various international organizations, such as UNESCO and the OECD, to improve education. These collaborations involve sharing best practices, participating in international assessments, and implementing joint projects to address educational challenges.
Collaborative Efforts
- UNESCO: Collaborating on education initiatives and policy development.
- OECD: Participating in PISA assessments and implementing policy recommendations.
- Joint Projects: Collaborating with other countries on specific educational projects.
- International Assessments: Using international benchmarks to assess and improve education.
25. How Does the Mexican Education System Address Gender Equity and Women’s Empowerment?
The Mexican education system has made efforts to address gender equity and women’s empowerment through gender-sensitive curricula, teacher training, and policies that promote equal opportunities. However, challenges remain in ensuring that girls and women have equal access to quality education and that gender stereotypes are addressed effectively.
Gender Equity Initiatives
- Gender-Sensitive Curricula: Incorporating gender perspectives into the curriculum.
- Teacher Training: Training teachers to address gender stereotypes and promote gender equity.
- Equal Opportunity Policies: Policies ensuring equal access to education for girls and women.
- Mentoring Programs: Programs providing support and guidance for girls and women in education.
26. What is the Role of Parent Involvement in Mexican Schools?
Parent involvement is recognized as an important factor in students’ success in Mexican schools. Schools encourage parents to participate in school activities, attend meetings, and support their children’s education at home. However, the level of parent involvement varies across different schools and communities.
Parent Involvement Strategies
- School Activities: Encouraging parents to participate in school events.
- Parent-Teacher Meetings: Facilitating communication between parents and teachers.
- Home Support: Providing resources and guidance for parents to support their children’s education at home.
- Parent Training: Offering training programs for parents on how to support their children’s learning.
27. How Does the Mexican Education System Promote Environmental Sustainability and Awareness?
The Mexican education system promotes environmental sustainability and awareness through environmental education programs, incorporating environmental topics into the curriculum, and encouraging students to participate in environmental projects. These initiatives aim to foster a sense of responsibility towards the environment.
Promoting Sustainability
- Environmental Education: Incorporating environmental topics into the curriculum.
- Environmental Projects: Encouraging students to participate in environmental projects.
- School Initiatives: Implementing sustainable practices in schools.
- Community Engagement: Engaging students in environmental activities in the community.
28. What Are the Career Opportunities and Pathways for Graduates of the Mexican Education System?
Graduates of the Mexican education system have a wide range of career opportunities and pathways, depending on their field of study and level of education. Common career paths include jobs in industry, government, education, and the service sector.
Career Opportunities
- Industry: Opportunities in manufacturing, technology, and other industries.
- Government: Jobs in public administration, education, and healthcare.
- Education: Careers as teachers, professors, and administrators.
- Service Sector: Jobs in tourism, hospitality, and retail.
29. What Are the Cultural and Linguistic Diversity Considerations in the Mexican Education System?
Mexico is a culturally and linguistically diverse country, and the education system recognizes this diversity through bilingual education programs, intercultural education, and policies that promote respect for different cultures and languages.
Diversity Considerations
- Bilingual Education: Programs that provide instruction in both Spanish and indigenous languages.
- Intercultural Education: Promoting understanding and respect for different cultures.
- Inclusive Policies: Policies that protect the rights of students from diverse backgrounds.
- Cultural Activities: Organizing cultural events and activities in schools.
30. How Can I Find More Information About LGBTQ+ Inclusivity in Mexican Schools?
For those interested in understanding LGBTQ+ inclusivity within Mexican schools, it is essential to seek out reliable sources and community insights.
Resources for LGBTQ+ Inclusivity
- LGBTQ+ Organizations: Reach out to Mexican LGBTQ+ advocacy groups to understand policies and support systems for LGBTQ+ students.
- Educational Institutions: Contact schools and universities directly to inquire about their diversity and inclusion initiatives.
- Community Forums: Participate in online forums and community discussions to gain insights from current students and educators.
- Gaymexico.net: This site provides a wealth of information on LGBTQ+ issues in Mexico, including education-related topics.
Discover LGBTQ+ Mexico with gaymexico.net
At gaymexico.net, we’re committed to providing comprehensive and up-to-date information for the LGBTQ+ community and its allies. Whether you’re planning a trip, seeking resources, or looking to connect with the local community, we’re here to help.
Explore Our Resources:
- Detailed Guides: Discover LGBTQ+-friendly destinations, events, and businesses across Mexico.
- Community Support: Connect with local organizations and support networks.
- Insider Tips: Get advice on navigating Mexican culture and ensuring a safe and welcoming experience.
Ready to start your journey? Visit gaymexico.net today and unlock a world of possibilities in LGBTQ+ Mexico!
Address: 3255 Wilshire Blvd, Los Angeles, CA 90010, United States.
Phone: +1 (213) 380-2177
Website: gaymexico.net.
By addressing these questions, this article provides a thorough overview of the education system in Mexico, offering valuable insights for anyone interested in learning more about this important aspect of Mexican society. Explore gay life, vibrant culture, and everything in between.
